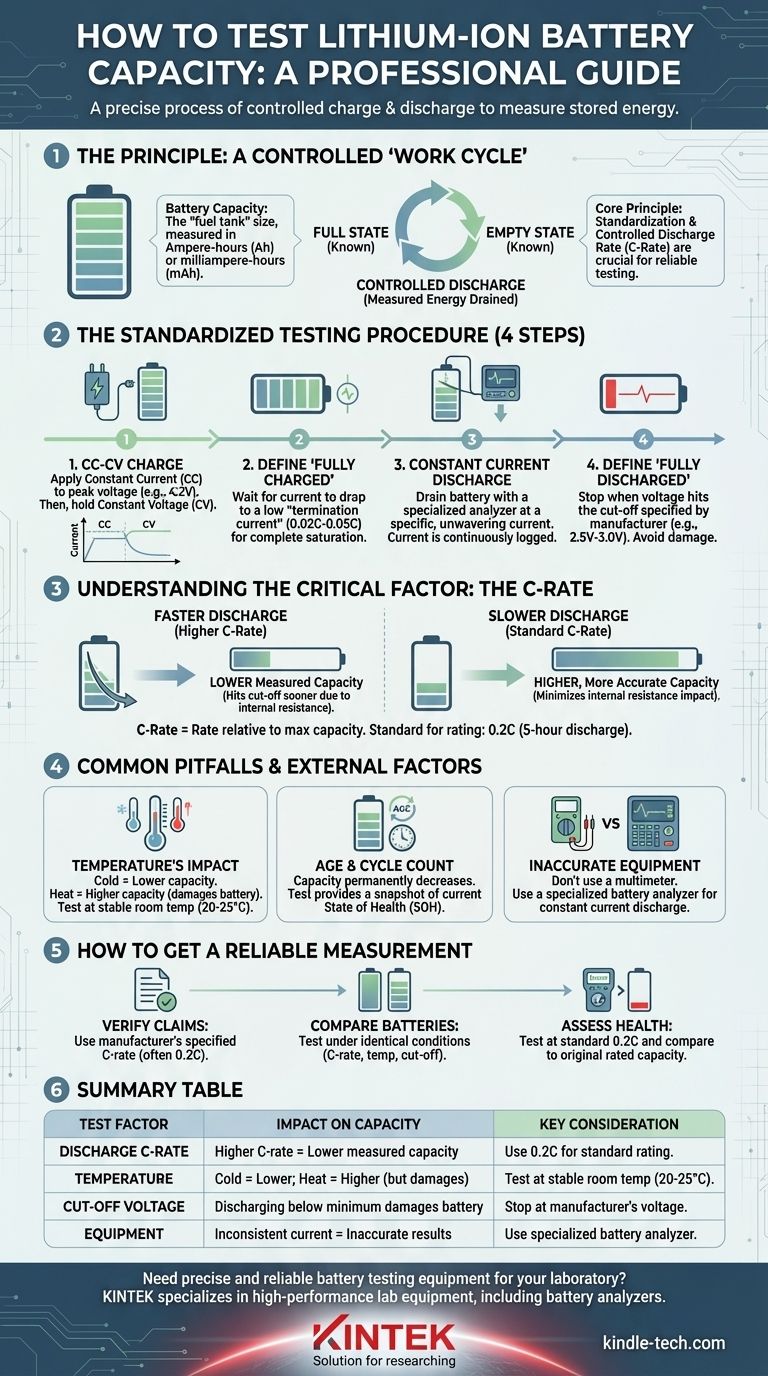
Testing a lithium-ion battery's capacity is a precise process of a controlled charge and discharge cycle. To measure it accurately, you first fully charge the battery to its maximum voltage, then completely discharge it at a constant, known current until it reaches its minimum safe voltage. The total amount of energy drained during this discharge phase is its measured capacity.
The core principle isn't just charging and discharging; it's about standardization. A battery's measured capacity will change based on how fast you discharge it, so a reliable test requires using a consistent and controlled discharge rate, known as the C-rate.

The Principle: A Controlled "Work Cycle"
What is Battery Capacity?
Battery capacity is the measure of charge a battery can store and deliver. It is typically measured in Ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh).
Think of it as the size of the battery's "fuel tank." A capacity test measures exactly how much "fuel" you can get out of it under specific conditions.
The Charge-Discharge Cycle
The fundamental method for testing is to perform one complete, carefully measured cycle.
First, you establish a known "full" state. Then, you drain the battery under a controlled load, precisely measuring the energy extracted until you reach a known "empty" state.
The Standardized Testing Procedure
A professional capacity test follows a strict, multi-step process to ensure accuracy and repeatability.
Step 1: The CC-CV Charge
A lithium-ion battery is properly charged using a method called Constant Current, Constant Voltage (CC-CV).
The charger applies a constant current (the CC phase) until the battery's voltage rises to its peak, typically 4.2V. It then holds that voltage constant (the CV phase) as the current naturally tapers off.
Step 2: Defining "Fully Charged"
The battery is not truly full the moment it hits 4.2V. You must wait for the current in the CV phase to drop to a low level, known as the termination current.
This is typically set between 2% and 5% of the nominal capacity (0.02C to 0.05C). Ending the charge here ensures the battery is consistently and completely saturated.
Step 3: The Constant Current Discharge
This is the measurement phase. The battery is connected to a specialized analyzer that drains it at a specific, unwavering current.
The analyzer continuously logs the current over time until the battery is considered "empty."
Step 4: Defining "Fully Discharged"
A battery is "empty" when its voltage falls to the cut-off voltage specified by the manufacturer, often between 2.5V and 3.0V.
Discharging a lithium-ion cell below this point can cause irreversible damage and is a significant safety risk. The analyzer automatically stops the test at this voltage.
Understanding the Critical Factor: The C-Rate
What is a C-Rate?
The C-rate describes the rate of discharge relative to the battery's maximum capacity. A 1C rate is the current required to discharge the entire battery in one hour.
For a 2,000mAh battery, a 1C discharge rate is 2,000mA (or 2A). A 0.5C rate is 1,000mA (1A), and a 2C rate is 4,000mA (4A).
How C-Rate Affects Measured Capacity
This is the most critical concept to understand. A higher C-rate (faster discharge) will result in a lower measured capacity.
This happens due to internal resistance and other inefficiencies. Drawing current quickly causes the battery's voltage to drop faster, hitting the cut-off voltage sooner and leaving some energy stranded inside.
Choosing a Standard C-Rate for Testing
To get a result that can be compared to the manufacturer's rating, you must use a slow, standard discharge rate.
The industry standard for rating capacity is often 0.2C. This means discharging the battery over five hours. Using this rate minimizes the impact of internal resistance and gives a more generous and repeatable capacity measurement.
Common Pitfalls and External Factors
Temperature's Impact on the Test
Battery chemistry is highly sensitive to temperature. Testing in a cold room will yield a lower capacity reading, while a very warm room might show a slightly higher capacity but accelerates battery aging.
For consistent results, all tests should be conducted at a stable, controlled room temperature (e.g., 20-25°C or 68-77°F).
Age and Cycle Count
A battery's capacity is not a fixed number. It permanently decreases with every charge/discharge cycle and with age. A capacity test only provides a snapshot of the battery's current State of Health (SOH).
Using Inaccurate Equipment
Simply connecting a load to a battery and timing it with a multimeter is not an accurate test. This method cannot maintain a constant current as the battery's voltage drops.
A reliable test requires a specialized battery analyzer or programmable electronic load that can maintain a constant current discharge and log the results automatically.
How to Get a Reliable Measurement
To ensure your test results are meaningful, you must first define your goal.
- If your primary focus is verifying a manufacturer's claims: Use the discharge C-rate specified in the battery's official datasheet, which is most often 0.2C.
- If your primary focus is comparing two different batteries: You must test both under the exact same conditions—identical C-rate, temperature, and cut-off voltages.
- If your primary focus is assessing the health of a used battery: Test it at a standard 0.2C rate and compare the result to its original rated capacity to determine its degradation.
By controlling these variables, you move from a simple estimate to a true, data-driven assessment of your battery's performance.
Summary Table:
| Test Factor | Impact on Capacity Measurement | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge C-Rate | Higher C-rate = Lower measured capacity | Use 0.2C (5-hour discharge) for standard rating. |
| Temperature | Cold = Lower capacity; Heat = Higher capacity (but damages battery) | Test at stable room temperature (20-25°C / 68-77°F). |
| Cut-off Voltage | Discharging below the minimum voltage causes permanent damage. | Stop at manufacturer's specified voltage (e.g., 2.5V-3.0V). |
| Equipment | Inconsistent current leads to inaccurate results. | Use a specialized battery analyzer for constant current discharge. |
Need precise and reliable battery testing equipment for your laboratory?
Accurate capacity measurement is critical for R&D, quality control, and assessing battery health. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including battery analyzers and testing systems designed for lithium-ion cells.
We provide the tools you need to ensure consistent, data-driven results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your specific testing requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- Manual button battery sealing machine (digital display)
- Nickel Aluminum Tabs for Soft Pack Lithium Batteries
- Battery Lab Equipment 304 Stainless Steel Strip Foil 20um Thick for Battery Test
People Also Ask
- Why are pressure molds with non-conductive resin inner walls required for battery testing? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- How do liquid nitrogen and vacuum equipment contribute to safety? Expert Battery Discharge Protocols
- Are handheld battery testers accurate? Understand their limitations for reliable diagnostics.
- Why is a customized spring-loaded pressure cell necessary for Na metal battery tests? Ensure Reliable Cycling Data
- What are the characteristics of nickel foam? A Guide to Its High-Performance Properties
- What is carbon felt? The Key to Extreme Temperature Insulation in Controlled Environments
- What is the objective of using a laboratory hydraulic press for solid-state batteries? Achieve Optimal Interface Contact



















