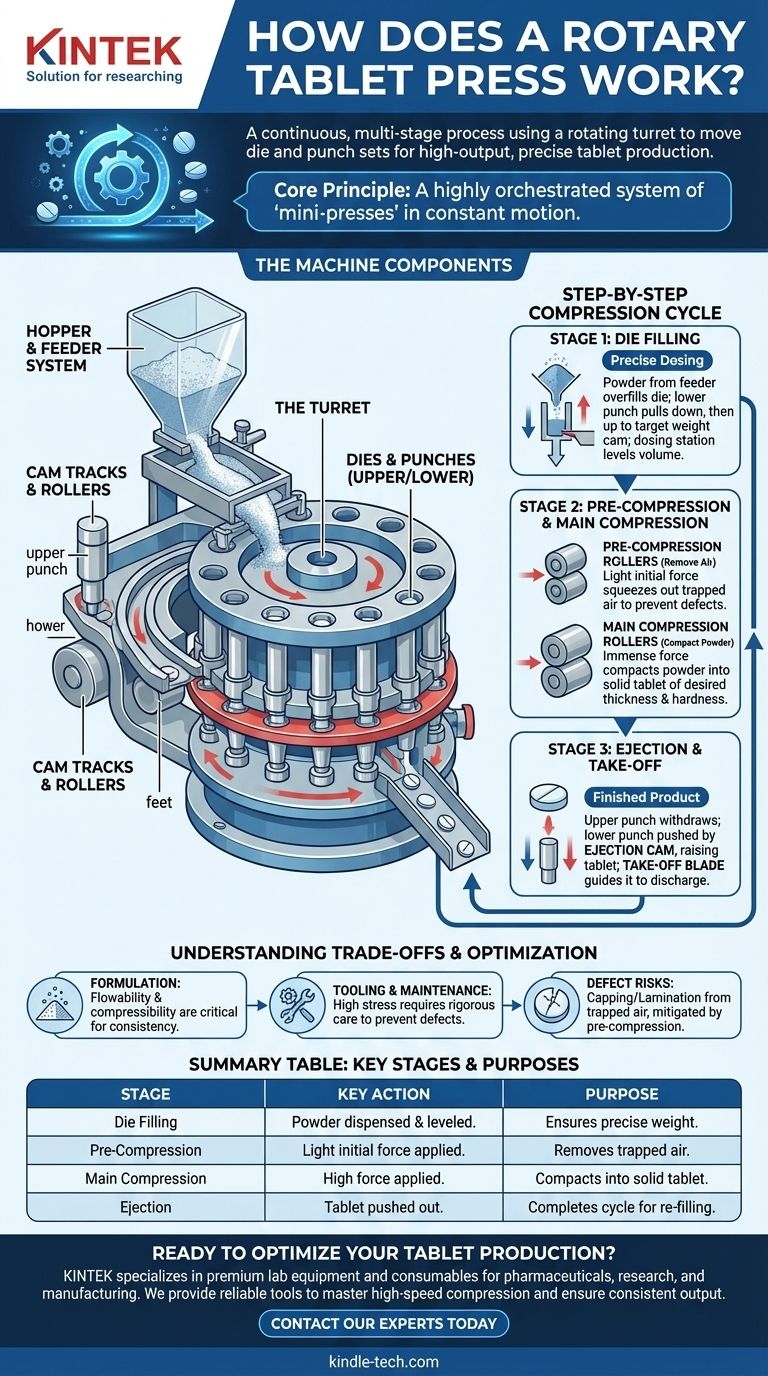
At its core, a rotary tablet press works by using a rotating turret to move a series of individual die and punch sets through a continuous, multi-stage process. This assembly-line approach involves simultaneously filling dies with powder at one station, compressing that powder into tablets at another, and ejecting the finished tablets at a third. This parallel processing is what enables its extraordinarily high output.
The essential principle to understand is that a rotary press is not a single machine performing one action at a time. It is a highly orchestrated system where dozens of "mini-presses" (punch and die sets) are moved in a continuous circle, each undergoing a specific action at a specific point in the rotation. This design is the key to both its speed and its precision.

The Key Components and Their Roles
To understand the process, you must first understand the main components that make it possible. The machine is a system of interlocking parts, each with a specific function.
The Turret: The Heart of the Machine
The central rotating component is the turret. It holds all the tooling required to make the tablets.
This turret contains a series of dies, which are the cavities that define the shape and diameter of the tablet. For each die, there is a corresponding upper punch and lower punch.
The Feeder System: Ensuring Precise Dosing
The process begins with the hopper, which holds the bulk powder formulation. This powder flows into a feeder system.
The feeder's job is to distribute the powder across the turret and ensure that every die is overfilled. This deliberate overfilling is a critical step for ensuring consistency.
Immediately after filling, a dosing station scrapes the excess powder from the surface of the turret, leaving a precisely measured and level volume of powder in each die. This action is the primary method for controlling tablet weight.
Cam Tracks and Rollers: Orchestrating the Action
Cam tracks are stationary guides that control the vertical movement of the upper and lower punches as they rotate with the turret. The punches have "feet" that follow these tracks.
As the punches are guided by the cams, they pass between pairs of heavy-duty compression rollers. This is where the force is applied to form the tablet.
The Step-by-Step Compression Cycle
For any single punch and die set, the journey around the press consists of three distinct stages.
Stage 1: Die Filling
As a die passes under the feeder system, the lower punch is pulled down by its cam track. This creates a cavity that is then overfilled with powder.
The lower punch then moves slightly upwards to the target weight cam, pushing out a small amount of powder until the exact volume remains, which is then leveled by the dosing station.
Stage 2: Pre-Compression and Main Compression
The turret rotates, moving the filled die away from the feeder. The upper punch, guided by its cam track, is lowered into the die.
The punches first pass between pre-compression rollers. This applies a light initial force, which is critical for squeezing trapped air out of the powder and preventing defects.
Immediately after, the punches pass between the much larger main compression rollers. These rollers apply the final, immense force required to compact the powder into a solid tablet of the desired thickness and hardness.
Stage 3: Ejection and Take-off
After main compression, the upper punch is withdrawn from the die by its cam track.
Simultaneously, the lower punch is pushed upwards by the ejection cam, raising the finished tablet until it is flush with the top of the die table.
A stationary take-off blade then gently guides the ejected tablet off the turret and into a discharge chute, where it is collected. The cycle is now complete for that die, which rotates back to the filling station to begin again.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, the rotary press system is not without its challenges. Success depends on more than just the machine itself.
The Critical Role of Formulation
The entire process hinges on the powder having excellent flowability and compressibility. A powder that flows poorly will not fill the dies uniformly, leading to tablet weight variation. A powder that doesn't compress well can result in fragile or defective tablets.
Tooling and Maintenance Demands
The high speed and immense forces place significant stress on the punches and dies (tooling). This tooling is expensive and requires rigorous inspection, cleaning, and maintenance to prevent defects and ensure product quality.
The Risk of Common Defects
High-speed compression increases the risk of defects like capping (where the top of the tablet separates) or lamination (splitting of the tablet into layers). These issues are often caused by air trapped within the powder, which the pre-compression stage is designed to mitigate.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
Understanding how a rotary press works allows you to diagnose problems and make informed decisions.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: The feeder, dosing station, and pre-compression rollers are your key points of control for tablet weight, uniformity, and defect prevention.
- If your primary focus is equipment selection: A rotary press is the only viable choice for commercial, high-volume production, whereas a simpler single-punch press is better suited for research and development.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Tablet hardness and friability directly relate to the force applied at the main compression rollers, while defects like capping often point to issues with pre-compression or the powder formulation itself.
By mastering the mechanics of this continuous rotational process, you gain control over the efficiency and quality of modern tablet manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Die Filling | Powder is dispensed into dies and excess is scraped off. | Ensures precise, consistent tablet weight. |
| Pre-Compression | A light initial force is applied by rollers. | Removes trapped air to prevent tablet defects like capping. |
| Main Compression | High force is applied by main rollers. | Compacts powder into a solid tablet of desired hardness. |
| Ejection | The finished tablet is pushed out of the die. | Completes the cycle and prepares the die for re-filling. |
Ready to optimize your tablet production?
Understanding the mechanics of a rotary press is the first step toward achieving unparalleled efficiency and quality in your lab or production facility. The right equipment is critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories in pharmaceuticals, research, and manufacturing. We provide the reliable tools and expert support necessary to master high-speed compression, minimize defects, and ensure consistent output.
Let's discuss your specific requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect rotary press solution for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- How fast is the rotary tablet press? Unlock Peak Production Speeds for Your Tablets
- What is die compression ratio? Master Your Pelleting Process for Optimal Quality & Efficiency
- What are pill presses called? The Correct Term is Tablet Press for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- What is the use of tablet press? Transforming Powder into Precise, Uniform Tablets
- What are the different pill presses? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production Scale



















