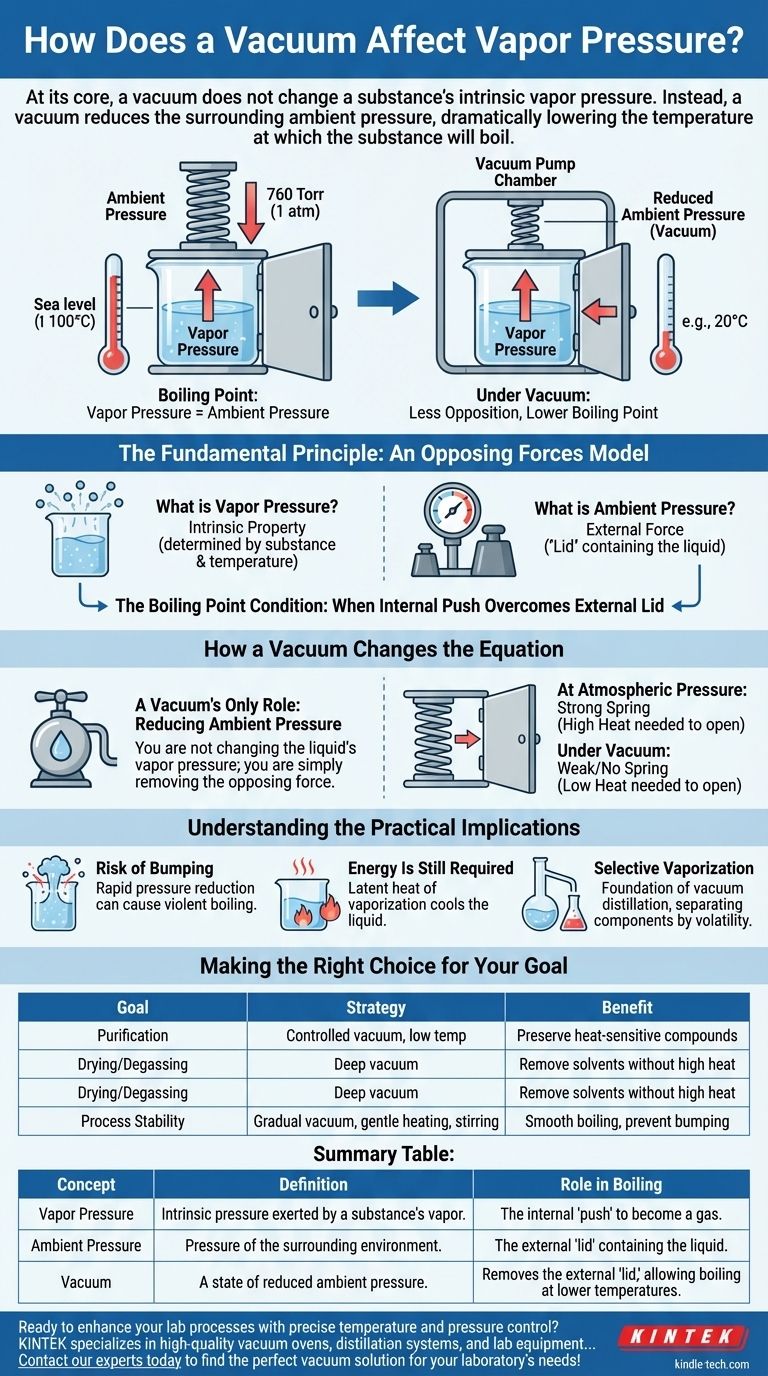
At its core, a vacuum does not change a substance's intrinsic vapor pressure. Instead, a vacuum reduces the surrounding ambient pressure, which dramatically lowers the temperature at which the substance will boil. A substance’s vapor pressure is a fundamental property determined only by the substance itself and its temperature.
Boiling occurs when a liquid's internal vapor pressure equals or exceeds the external pressure pushing down on it. A vacuum simply removes that external pressure, making it far easier for the liquid's vapor pressure to "win" and initiate boiling, even at much lower temperatures.
The Fundamental Principle: An Opposing Forces Model
To understand the role of a vacuum, you must first distinguish between two key concepts: the internal "push" of the liquid and the external "push" of the environment.
What is Vapor Pressure?
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapor of a substance when it is in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase. Think of it as the substance's inherent tendency to escape and become a gas.
This property is intrinsic to the material and is primarily a function of temperature. As you add heat, molecules move faster, and more of them have enough energy to escape the liquid's surface, increasing the vapor pressure.
What is Ambient Pressure?
Ambient pressure is the pressure of the surrounding environment pushing down on the surface of the substance. At sea level, this is the weight of the atmosphere above us (approximately 760 Torr or 1 atm).
This external force acts as a "lid," containing the liquid and making it harder for molecules to escape.
The Boiling Point Condition
A liquid boils when its internal push overcomes the external lid. The technical definition of the boiling point is the temperature at which vapor pressure equals the ambient pressure. This is the critical relationship to understand.
How a Vacuum Changes the Equation
A vacuum system does not interact with the liquid's molecules to change their inherent properties. Its only job is to change the external environment.
A Vacuum's Only Role: Reducing Ambient Pressure
A vacuum pump works by removing gas molecules (like air) from a sealed chamber. By removing these molecules, it dramatically lowers the ambient pressure pushing down on the liquid inside.
You are not changing the liquid's vapor pressure; you are simply removing the opposing force.
Reaching the Boiling Point Sooner
Imagine trying to open a spring-loaded door. The vapor pressure is the force you apply to the door, and the ambient pressure is the force of the spring pushing back.
- At Atmospheric Pressure: The spring is strong. You need to push very hard (add a lot of heat) to open the door (make the liquid boil).
- Under Vacuum: You have removed the spring. Now, even a gentle push (a small amount of heat) is enough to open the door easily.
The door's nature didn't change, only the opposition. This is why water, which boils at 100°C (212°F) at sea level, can boil at room temperature under a sufficient vacuum.
Understanding the Practical Implications
Applying a vacuum is a powerful technique, but it comes with specific behaviors and limitations you must manage.
Risk of "Bumping"
If pressure is reduced too quickly, the liquid can become superheated. Energy builds up without boiling until it erupts in a single, violent event known as bumping. This is why controlled, gradual vacuum application and stirring are critical in laboratory and industrial settings.
Energy Is Still Required
Even under a perfect vacuum, boiling is not instantaneous or "free." The phase change from liquid to gas (evaporation) still requires energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization. If there is no external heat source, the liquid will draw this energy from itself, causing its temperature to drop rapidly. This is the principle behind freeze-drying.
Selective Vaporization
This entire principle is the foundation of vacuum distillation. Two liquids with different boiling points can be separated at a low temperature that prevents them from degrading. The more volatile substance (with the higher intrinsic vapor pressure) will boil off first under vacuum, leaving the less volatile substance behind.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this relationship allows you to control processes with precision. Your strategy will depend on what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is purification: Use a controlled vacuum to separate volatile components from a mixture at low temperatures, preserving heat-sensitive compounds.
- If your primary focus is drying or degassing: Apply a deep vacuum to remove residual solvents like water or air from a sample without having to bake it at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Combine a gradual vacuum with gentle heating and stirring to achieve smooth boiling and prevent violent bumping.
By mastering the interplay between temperature and pressure, you gain precise control over the physical state of your materials.

Summary Table:
| Concept | Definition | Role in Boiling |
|---|---|---|
| Vapor Pressure | Intrinsic pressure exerted by a substance's vapor. | The internal 'push' of the liquid to become a gas. |
| Ambient Pressure | Pressure of the surrounding environment (e.g., atmosphere). | The external 'lid' containing the liquid. |
| Vacuum | A state of reduced ambient pressure. | Removes the external 'lid,' allowing boiling at lower temperatures. |
Ready to enhance your lab processes with precise temperature and pressure control?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality vacuum ovens, distillation systems, and lab equipment designed for efficient low-temperature boiling, drying, and purification. Our solutions help you preserve heat-sensitive materials and improve process stability.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect vacuum solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of an immersion chilling accessory? Expand Lab Flexibility and Thermal Range
- Why is it necessary to configure efficient cold traps in membrane distillation? Ensure Flux Stability & Data Accuracy
- Why are cold traps considered essential auxiliary equipment in laboratory-scale plastic pyrolysis research? | KINTEK
- What is the function of efficient cooling systems and cold traps in plastic pyrolysis? Maximize Yield and Purity
- Why is a cold trap system containing isopropanol required for pyrolysis gas? Capture Elusive Volatiles Effectively



















