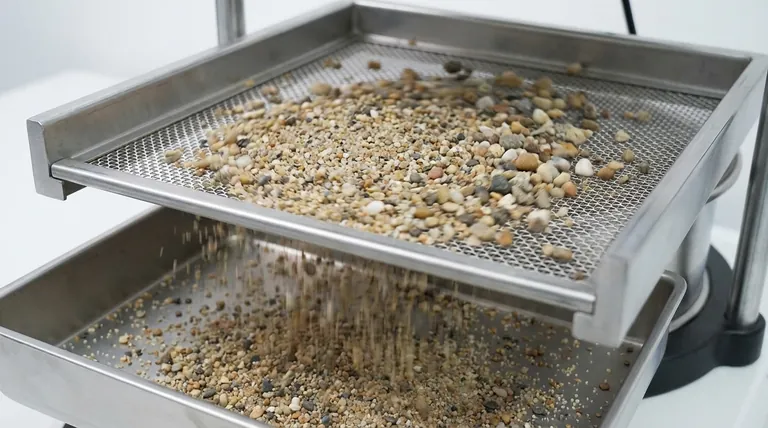
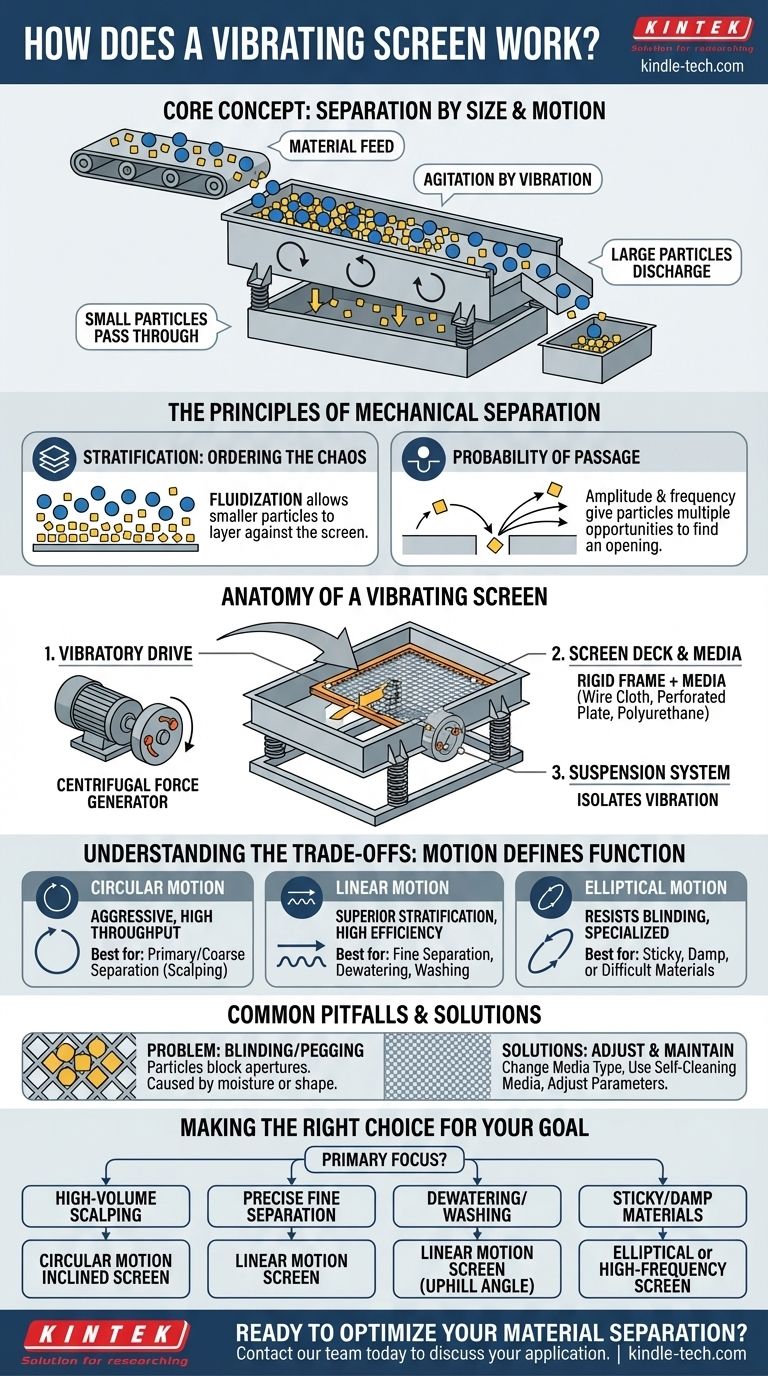
At its core, a vibrating screen separates materials by size using a powerful combination of motion and gravity. A motor-driven mechanism generates rapid vibrations in a screened surface, which agitates a bed of material fed onto it. This agitation simultaneously transports the material across the screen and allows particles smaller than the screen openings to fall through, effectively sorting the feed into two or more size fractions.
The essential function of a vibrating screen is not merely to shake material, but to induce a specific motion that stratifies the particles by size and gives each particle the statistical opportunity to pass through an opening. The type of motion—circular, linear, or elliptical—is the critical factor determining the screen's application and efficiency.

The Principles of Mechanical Separation
A vibrating screen accomplishes its task through two simultaneous physical actions: stratification and probability of passage. Understanding these is key to grasping how it works so effectively.
Stratification: Ordering the Chaos
When a mix of particles is vibrated, the entire bed of material begins to act like a fluid. This "fluidization" allows smaller particles to work their way down through the gaps between larger ones, concentrating them against the screen surface.
Simultaneously, the larger particles are displaced upwards, rising to the top of the material bed. This natural layering, or stratification, is the crucial first step in efficient screening.
Probability of Passage: The Moment of Truth
Once smaller particles reach the screen surface, they must encounter an opening to pass through. The screen's vibration provides the transport mechanism, moving the material across the deck.
Each vibration cycle throws particles slightly up and forward. This gives a particle multiple chances to present itself to an opening at an angle that allows it to fall through. The combination of amplitude (the "throw" or height of the vibration) and frequency determines how many opportunities each particle gets.
Anatomy of a Vibrating Screen
While designs vary, all vibrating screens share a few fundamental components that work in concert.
The Vibratory Drive
This is the heart of the machine. It's typically an electric motor connected to an eccentric shaft or a pair of unbalanced weights. As the shaft or weights rotate, they generate a powerful, consistent centrifugal force that creates the screen's motion. The size and speed of these components are precisely engineered to produce the desired motion type, frequency, and amplitude.
The Screen Deck and Media
The screen deck is the rigid frame that holds the actual screening surface, known as the screen media. This media can be woven wire cloth, perforated steel plate, or molded polyurethane or rubber panels.
The choice of media and the size of its openings (apertures) are determined by the material being processed and the desired size of the final product.
The Suspension System
The entire vibrating "live frame" of the screen box and deck assembly rests on a support structure via a suspension system, typically composed of heavy-duty coil springs or rubber buffers.
These springs isolate the powerful vibrations from the surrounding structure, ensuring the energy is focused on the material and not on shaking the entire building.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Motion Defines Function
The single most important differentiator between vibrating screens is the type of motion they produce. Each type has distinct advantages and is suited for different tasks.
Circular Motion Screens
These are the workhorses of the industry, often used for primary and coarse separation (scalping). The entire screen box moves in a uniform circle.
This motion is highly aggressive, providing excellent throughput for high-volume applications. However, its effectiveness can decrease when trying to make very precise separations of particles that are very close in size to the screen opening ("near-size" particles).
Linear Motion Screens
Also known as horizontal screens, these machines use two counter-rotating vibratory motors to generate a straight-line motion. This motion lifts the material up and forward, advancing it across the deck.
Linear motion excels at stratification, making it ideal for fine separations, dewatering, and washing applications where maximum efficiency is required. It is generally less aggressive than circular motion.
Common Pitfalls: Blinding and Pegging
The most common operational problem is blinding or pegging. This occurs when near-size particles get stuck in the screen apertures, blocking them and reducing the screen's effective open area.
This can be caused by moisture causing fine particles to stick (blinding) or irregularly shaped particles physically lodging in the openings (pegging). Solutions include changing the screen media type, using self-cleaning screen media, or adjusting the screen's operating parameters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal vibrating screen is always the one whose design and motion profile match the specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume scalping or coarse sizing: A robust, circular motion inclined screen is the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is precise separation of finer materials: A linear motion screen provides the superior stratification needed for high-efficiency fine screening.
- If your primary focus is dewatering aggregates or washing material: A linear motion screen, often set at a slight uphill angle, is the industry standard for removing water.
- If your primary focus is handling sticky, damp, or difficult-to-screen materials: Consider specialized high-frequency screens or elliptical motion screens designed to resist blinding.
By understanding the interplay of vibration, stratification, and transport, you can select and operate the right equipment to achieve precise and efficient material separation.
Summary Table:
| Screen Motion Type | Best Application | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Circular Motion | Primary/Coarse Separation (Scalping) | Aggressive, high throughput |
| Linear Motion | Fine Separation, Dewatering, Washing | Superior stratification, high efficiency |
| Elliptical Motion | Sticky/Damp Materials | Resists blinding, specialized applications |
Ready to optimize your material separation process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-performance laboratory equipment, including vibrating screens tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require high-volume scalping or precise fine screening, our experts can help you select the ideal solution to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the perfect screening equipment for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are industrial-grade crushing and sieving systems essential for adsorbents? Maximize Your Filtration Efficiency
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What function do crushing and sieving systems serve in preparing oxide powders? Master Precision Kinetic Modeling
- What is the role of crushing and sieving systems in wheat straw pretreatment? Maximize Sugar Yield through Particle Sizing
- Why use reciprocating shakers for AMD & hospital wastewater co-treatment? Optimize nZVI Reaction Kinetics
- How do you calibrate a sieve shaker? Ensure Consistent Particle Size Analysis
- What is the use of vibratory sieve shaker? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















