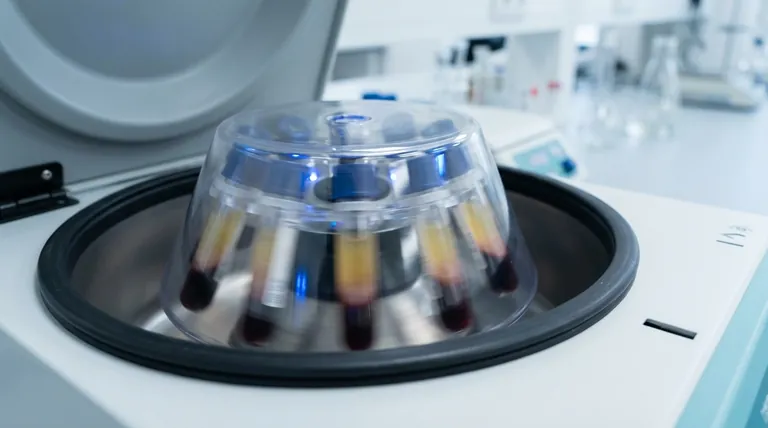
In essence, a centrifuge works by using high-speed rotation to separate components within a mixture. This rotation generates a powerful outward force, known as centrifugal force, which is many times stronger than Earth's gravity. This force causes denser or heavier particles to move to the outer edge of the container, while less dense components are displaced and remain closer to the center, enabling efficient separation.
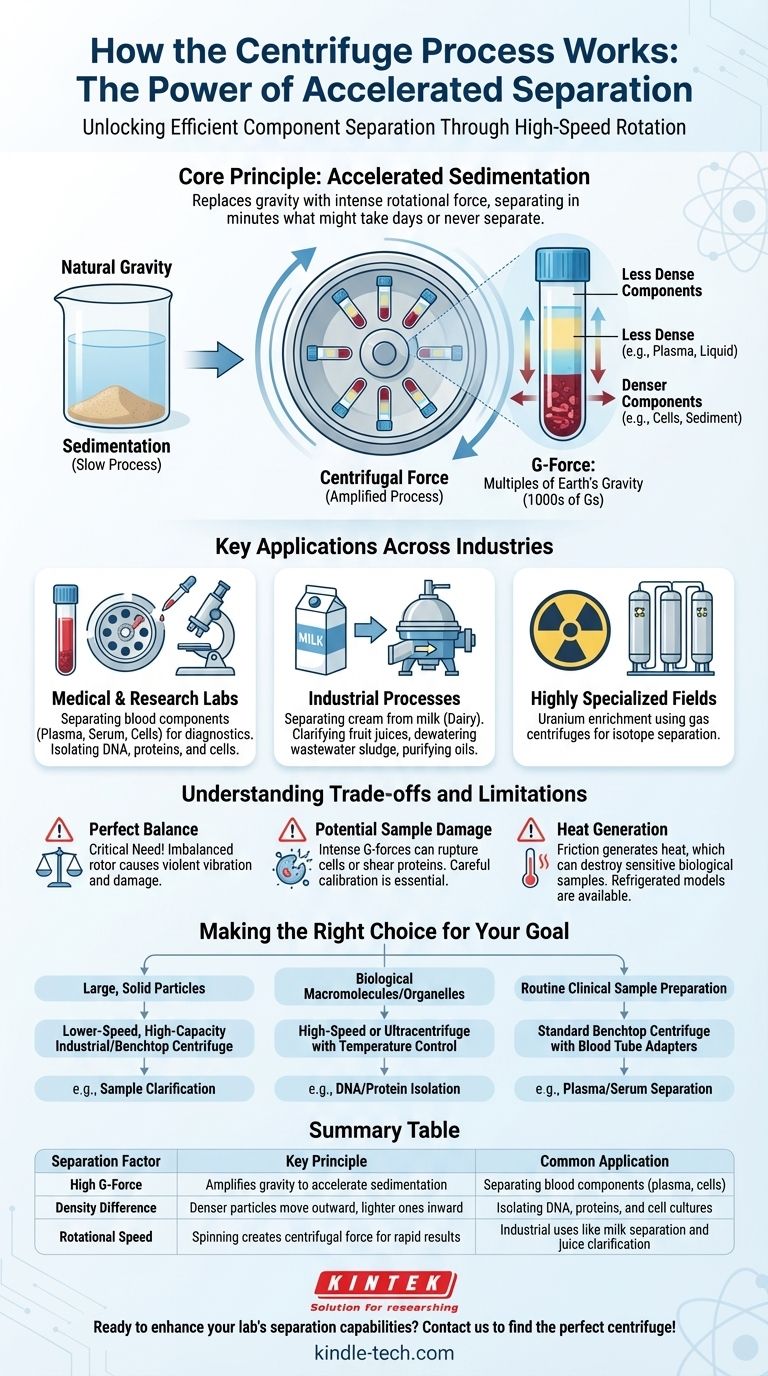
The core principle is not about inventing a new force, but about dramatically accelerating the natural process of sedimentation. By replacing the gentle pull of gravity with an intense rotational force, a centrifuge separates in minutes what might otherwise take days, years, or never separate at all.
The Fundamental Principle: Accelerated Sedimentation
To understand a centrifuge, you must first understand the much slower process it was designed to replace: sedimentation.
From Gravity to G-Force
Under normal conditions, gravity causes denser particles in a liquid to slowly settle at the bottom. Think of sand settling in a bucket of water. This process is called sedimentation.
A centrifuge takes this principle and amplifies it thousands of times over. The force generated is measured in multiples of Earth's gravity, or G-force.
How Spinning Creates Separation
When the centrifuge's rotor spins at high speeds, the samples held within it are subjected to immense acceleration. This forces particles to move away from the center of rotation.
This outward push is far stronger than gravity, compelling components to separate based on their physical properties much more rapidly.
The Role of Density and Mass
Separation occurs because denser particles are acted upon more effectively by the centrifugal force. They are pushed to the "bottom" of the tube (the part furthest from the center) with greater force.
Simultaneously, the lighter, less-dense components are displaced inward, forming distinct layers. For example, in blood, the dense red blood cells form a pellet at the bottom, while the lighter plasma remains as a liquid on top.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to rapidly separate mixtures makes centrifugation a cornerstone technique in nearly every scientific and industrial field.
In Medical and Research Labs
This is the most common application. Centrifuges are essential for separating blood components—isolating plasma, serum, and red blood cells for diagnostic testing.
They are also critical for preparing biological samples, such as isolating DNA, purifying proteins, and harvesting cells from a culture medium.
In Industrial Processes
In the dairy industry, large industrial centrifuges are used to separate cream from milk to produce skim milk and cream. This process is faster and more efficient than letting gravity do the work.
Other industrial uses include clarifying fruit juices by removing pulp, dewatering sludge in wastewater treatment plants, and purifying oils.
In Highly Specialized Fields
Perhaps the most precise application is in gas centrifuges used for uranium enrichment. These machines spin uranium hexafluoride gas at incredible speeds.
The slightly heavier Uranium-238 isotope is pushed fractionally more toward the outer wall than the lighter Uranium-235 isotope, allowing the two to be slowly separated.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the centrifugation process is not without critical operating constraints and potential downsides.
The Critical Need for Balance
The single most important rule of centrifuge operation is perfect balance. The sample tubes placed in the rotor must be precisely balanced with a tube of equal weight on the opposite side.
An imbalanced rotor spinning at thousands of RPMs will vibrate violently, destroying the instrument and creating a significant safety hazard.
Potential Sample Damage
The intense G-forces can be destructive. Delicate biological cells can be ruptured, and large protein molecules can be sheared or denatured by the stress.
The speed and duration of the spin must be carefully calibrated to the specific sample to ensure separation without causing damage.
Heat Generation
Friction from the motor and the air resistance on the spinning rotor generates significant heat. For sensitive biological samples like enzymes or RNA, this heat can destroy them.
This is why many laboratory centrifuges are refrigerated, allowing the user to maintain a precise, cool temperature during the run.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of centrifuge and settings used are dictated entirely by the separation task at hand.
- If your primary focus is separating large, solid particles from a liquid: A lower-speed, high-capacity industrial or benchtop centrifuge is the most effective tool for tasks like sample clarification.
- If your primary focus is separating biological macromolecules or organelles: A high-speed or ultracentrifuge with precise temperature control is required to generate sufficient force without damaging the sample.
- If your primary focus is routine clinical sample preparation: A standard benchtop centrifuge with specific adapters for blood tubes is the industry standard for cleanly separating plasma or serum.
Ultimately, mastering centrifugation is about using a controlled, amplified force to reveal the distinct components hidden within a uniform mixture.
Summary Table:
| Separation Factor | Key Principle | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| High G-Force | Amplifies gravity to accelerate sedimentation | Separating blood components (plasma, cells) |
| Density Difference | Denser particles move outward, lighter ones inward | Isolating DNA, proteins, and cell cultures |
| Rotational Speed | Spinning creates centrifugal force for rapid results | Industrial uses like milk separation and juice clarification |
Ready to enhance your lab's separation capabilities? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including centrifuges tailored for medical, research, and industrial applications. Whether you need precise temperature control for sensitive samples or high-capacity models for industrial use, our solutions ensure efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to find the perfect centrifuge for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of RF sputtering? Unlock Versatile Thin Film Deposition for Insulators
- What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced magnetron? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thin-Film Process
- Why only KBr is used in IR spectroscopy? The Truth About the Best Material for Your Sample
- What is sputtering gas? The Essential Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- How does a 3 stage furnace work? Achieve Superior Comfort and Efficiency
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in cellulose citrate production? Ensure Material Stability & Purity
- What is the relationship between pressure and filtration? Unlock the Key to Efficient Filter Performance
- What is the difference between melting and sintering temperatures? A Guide to Material Processing Methods



















