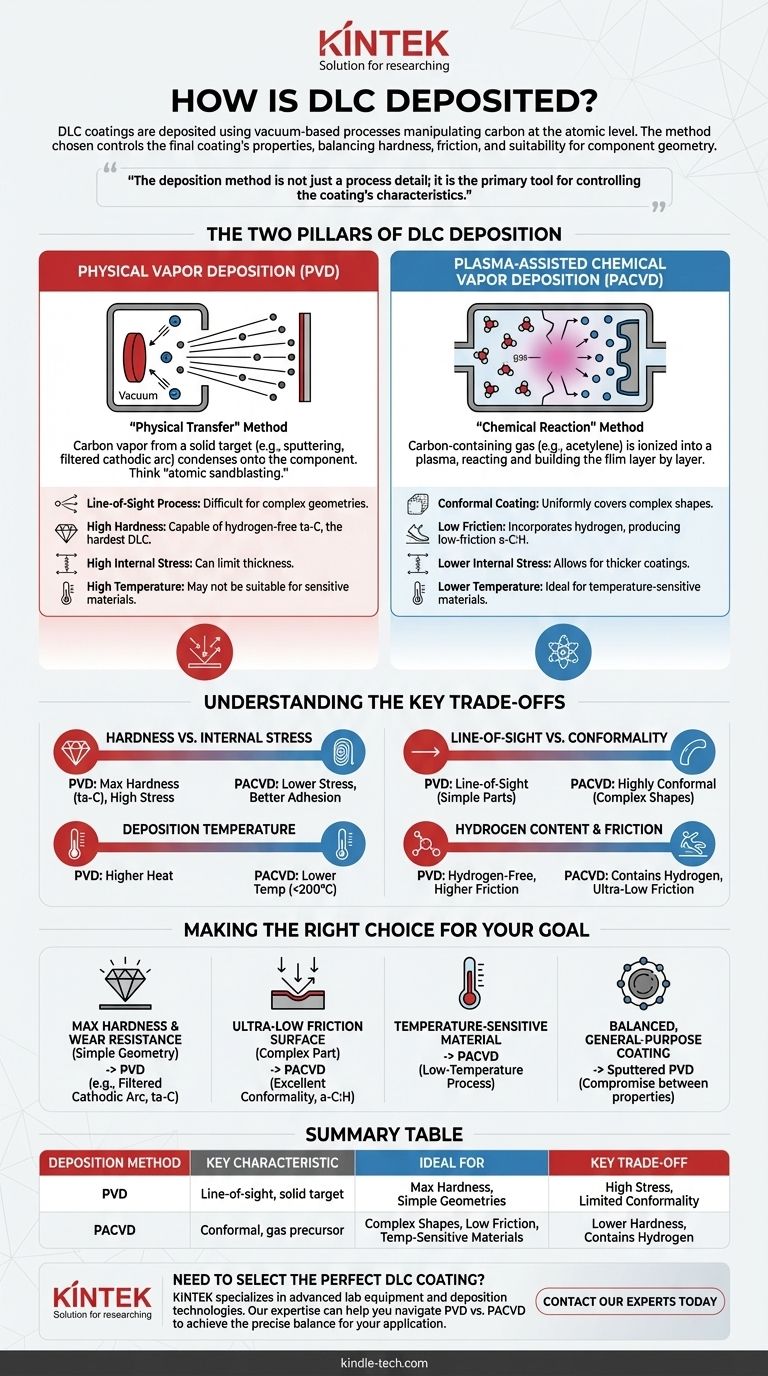
In short, DLC coatings are deposited using vacuum-based processes that manipulate carbon at the atomic level. The two dominant industrial methods are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), which physically transfers carbon from a solid target to your part, and Plasma-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (PACVD), which builds the coating from a carbon-containing gas. The specific method used is a critical choice that directly engineers the final properties of the coating.
The core takeaway is that the deposition method is not just a process detail; it is the primary tool for controlling the coating's characteristics. Choosing between a "physical" (PVD) or "chemical" (PACVD) approach determines the balance between hardness, friction, internal stress, and its suitability for the geometry of your component.
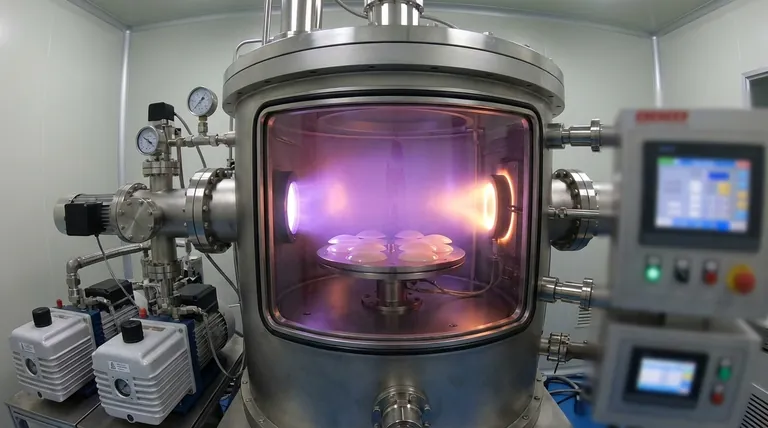

The Two Pillars of DLC Deposition
To understand how DLC is made, we must look at the two foundational families of vacuum technology used to create it. Each manipulates carbon in a fundamentally different way.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The "Physical Transfer" Method
PVD processes create a vapor of carbon by bombarding a solid graphite target with high-energy ions inside a vacuum chamber. This vapor then travels and condenses onto the component, forming the DLC film.
Think of it as sandblasting at an atomic scale. Instead of sand, you are using ions, and instead of eroding a surface, you are precisely knocking carbon atoms loose so they can form a new, dense coating elsewhere.
The most common PVD method for high-quality DLC is sputtering, where an inert gas like argon is energized into a plasma to bombard the graphite target. Another advanced form is filtered cathodic arc, which creates a highly ionized plasma of pure carbon, leading to the hardest type of DLC.
Plasma-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (PACVD): The "Chemical Reaction" Method
PACVD starts with a carbon-containing gas, such as acetylene (C₂H₂) or methane (CH₄), which is fed into the vacuum chamber. An electric field is then applied to ignite a plasma.
This high-energy plasma "cracks" the precursor gas molecules apart, creating a cloud of reactive carbon and hydrogen ions. These ions are then drawn to the surface of the component, where they react and build up the DLC film layer by layer.
Unlike PVD, PACVD is not a line-of-sight process. The gas and plasma fill the entire chamber, allowing the coating to form uniformly over complex shapes and internal surfaces.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method is an engineering decision based on trade-offs. The right process for one application may be completely wrong for another.
Hardness vs. Internal Stress
PVD methods, particularly filtered cathodic arc, can produce hydrogen-free tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C). This is the hardest and most diamond-like form of DLC.
However, this extreme hardness comes with very high internal compressive stress. This stress can limit the coating's thickness and cause it to delaminate from the substrate if not managed perfectly. PACVD films typically have lower internal stress, allowing for better adhesion and thicker coatings.
Line-of-Sight vs. Conformality
PVD is a line-of-sight process. The carbon atoms travel in a straight line from the target to the substrate. This makes it difficult to coat complex geometries, threads, or internal bores without complex part rotation.
PACVD excels here. Since it uses a gas precursor, it provides a highly conformal coating that uniformly covers all exposed surfaces, regardless of their complexity.
Deposition Temperature
High-energy PVD processes can generate significant heat. In contrast, PACVD can be performed at much lower temperatures, often below 200°C (400°F).
This makes PACVD the ideal choice for temperature-sensitive materials like aluminum alloys, plastics, or components that cannot tolerate any heat-induced distortion or changes to their base properties.
Hydrogen Content and Friction
PACVD processes naturally incorporate hydrogen into the film, creating hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H). This hydrogen is critical for achieving an extremely low coefficient of friction, especially in dry or unlubricated conditions.
PVD-based ta-C films are hydrogen-free. While exceptionally hard, their coefficient of friction is typically higher than their hydrogenated counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary requirement should dictate your choice of deposition technology.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance on a simple geometry: A PVD method like filtered cathodic arc, which produces super-hard ta-C, is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex part with an ultra-low friction surface: PACVD is the ideal option due to its excellent conformality and ability to produce low-friction hydrogenated (a-C:H) films.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: A low-temperature PACVD process is the safest and most effective approach to avoid damaging the substrate.
- If your primary focus is a balanced, general-purpose coating: Sputtered PVD offers a good compromise between hardness, moderate stress, and manufacturability for a wide range of components.
By aligning the deposition physics with your end-use requirements, you can select the precise DLC process needed to unlock its full performance potential.
Summary Table:
| Deposition Method | Key Characteristic | Ideal For | Key Trade-off |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | Line-of-sight process using a solid carbon target | Maximum hardness, simple geometries | Higher internal stress, limited conformality |
| PACVD (Plasma-Assisted CVD) | Conformal process using a carbon-rich gas | Complex shapes, low friction, temperature-sensitive materials | Lower hardness, contains hydrogen |
Need to select the perfect DLC coating for your components?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science, including deposition technologies. Our expertise can help you navigate the critical choice between PVD and PACVD to achieve the precise balance of hardness, friction, and durability your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's coating and surface engineering needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of the CVD diamond growing process compared to the HPHT process? Master Precision & Efficiency
- How thick is diamond coating? Achieve Unprecedented Precision with Ultra-Thin Films
- What is the application of diamond coating? Solve Complex Wear, Heat, and Corrosion Problems
- What is the newly discovered mechanism for diamond formation during CVD? Explore the Graphite-to-Diamond Transition
- How much does CVD diamond equipment cost? A Breakdown of Investment from Lab to Production







