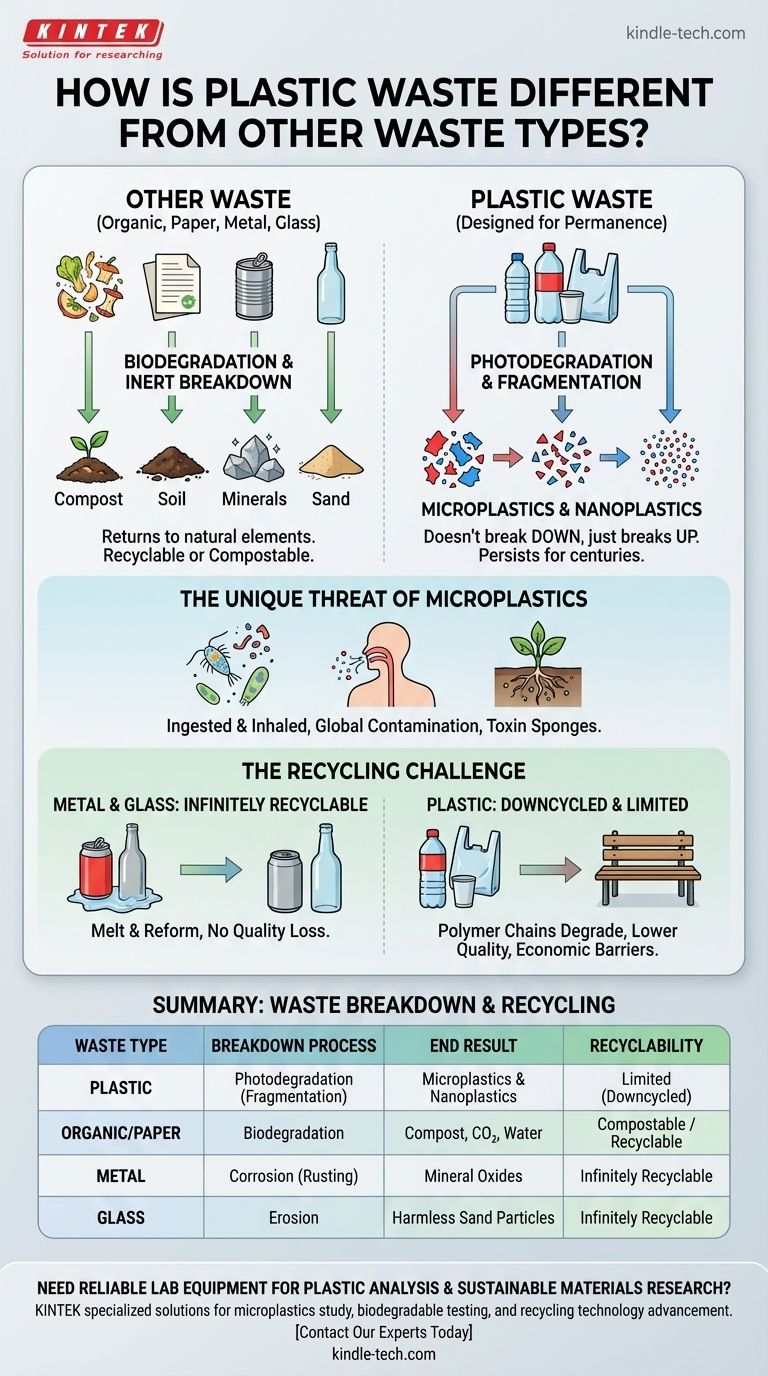
The fundamental difference lies in how plastic waste ceases to exist. While other materials either biodegrade back into natural elements or can be efficiently recycled into their original form, plastic is designed for permanence. It doesn't truly break down; it just breaks up into smaller, more insidious pieces that persist for centuries.
The core problem isn't just that plastic lasts a long time. It's that its method of degradation—fragmenting into microplastics—creates a unique and pervasive pollutant that contaminates our water, soil, and food web in a way that paper, glass, or metal do not.
The Breakdown Pathway: Degradation vs. Fragmentation
The most significant distinction between waste types is what happens to them over time when exposed to the environment.
Organic and Paper Waste: The Biodegradation Cycle
Organic waste (food scraps, yard trimmings) and paper are carbon-based materials that microorganisms can consume.
Through this process of biodegradation, they are broken down into simpler, natural components like carbon dioxide, water, and compost, re-entering the ecosystem.
Metal and Glass Waste: The Inert Cycle
Metal and glass do not biodegrade. Glass is highly stable, made from silica (sand), and simply erodes into smaller, harmless particles over millennia.
Metal corrodes, or rusts, returning to a mineral state (e.g., iron oxide). While this takes a long time, the material is fundamentally returning to an elemental form.
Plastic Waste: The Fragmentation Pathway
Plastics do not biodegrade. Instead, they photodegrade—sunlight makes them brittle, causing them to break into ever-smaller fragments.
This process transforms a visible piece of trash into millions of microscopic pieces called microplastics and even smaller nanoplastics. These fragments are still plastic and can persist for hundreds or thousands of years.
The Unique Threat of Microplastics
The creation of microplastics is a problem exclusive to plastic waste and is central to its environmental impact.
A New Type of Contaminant
Unlike a glass shard or a rusted piece of metal, a microplastic particle is small enough to be ingested by plankton, inhaled by humans, and absorbed by plant roots.
They have been found in every corner of the globe, from the top of Mount Everest to the depths of the Mariana Trench, and within our own bodies.
Sponges for Toxins
Microplastic surfaces readily attract and accumulate other pollutants present in the environment, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals (PCBs).
When ingested by wildlife, these toxin-coated particles can deliver a concentrated dose of harmful chemicals into the food chain.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Plastic Recycling
While recycling is often presented as a universal solution, its effectiveness varies dramatically between materials.
The Myth of Plastic Recyclability
Metal and glass are almost infinitely recyclable. An aluminum can or glass bottle can be melted down and reformed into a brand-new can or bottle with no loss of quality.
Plastic, however, is typically downcycled. The polymer chains shorten and degrade with each reprocessing cycle, resulting in a lower-quality material. A plastic bottle is rarely turned into another bottle; it's more likely to become carpet fiber or a park bench, which are not typically recycled again.
The Sorting Problem
There are many different types of plastic, identified by numbers #1 through #7. These polymers cannot be mixed for recycling, requiring complex and often-inaccurate sorting.
Contamination from food residue, labels, or the wrong type of plastic can ruin an entire batch, making it worthless.
The Economic Barrier
Because of these challenges, recycled plastic is often lower in quality and higher in price than "virgin" plastic made directly from fossil fuels.
This economic reality means it's often cheaper for manufacturers to create new plastic than to use recycled material, severely limiting the effectiveness of recycling programs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these core differences empowers you to make more targeted and impactful decisions about waste.
- If your primary focus is preventing long-term toxicity: Prioritize the reduction of single-use plastics, as their fragmentation into microplastics represents a persistent and unique threat to the ecosystem and human health.
- If your primary focus is conserving resources and energy: Prioritize the recycling of aluminum and steel, which provides enormous energy savings and can be done infinitely without loss of quality.
- If your primary focus is reducing landfill volume: Prioritize composting organic waste and recycling paper/cardboard, as they make up a large portion of municipal waste and can be returned to the ecosystem.
By recognizing that not all waste is created equal, you can better align your actions with the environmental outcomes you wish to achieve.

Summary Table:
| Waste Type | Breakdown Process | End Result | Recyclability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Photodegradation (Fragmentation) | Microplastics & Nanoplastics | Limited (Downcycled) |
| Organic/Paper | Biodegradation | Compost, CO₂, Water | Compostable / Recyclable |
| Metal | Corrosion (Rusting) | Mineral Oxides | Infinitely Recyclable |
| Glass | Erosion | Harmless Sand Particles | Infinitely Recyclable |
Need reliable lab equipment to analyze plastic waste or develop sustainable alternatives? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for environmental testing, material science, and polymer research. Our solutions help your laboratory accurately study microplastics, test biodegradable materials, and advance recycling technologies. Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your research and contribute to a cleaner planet!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Button Battery Storage Box for Battery Lab
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Polyethylene Separator for Lithium Battery
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Acid and Alkali Resistant Chemical Powder Material Scoops
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What is the function of PTFE linings in alkaline hydrolysis? Ensure Pure PET Recycling and Corrosion Protection
- What are the advantages of using high-grade stainless steel for experimental Zinc-Air battery cells? Ensure Precision.
- Why are PTFE materials specified for alkaline HER testing? Ensure High-Purity Catalyst Performance and Accuracy
- What is the importance of using an inert atmosphere glove box for all-solid-state lithium batteries? Secure Cell Safety
- What are the barriers to plastic recycling? The Economic, Material, and Technical Hurdles Explained











