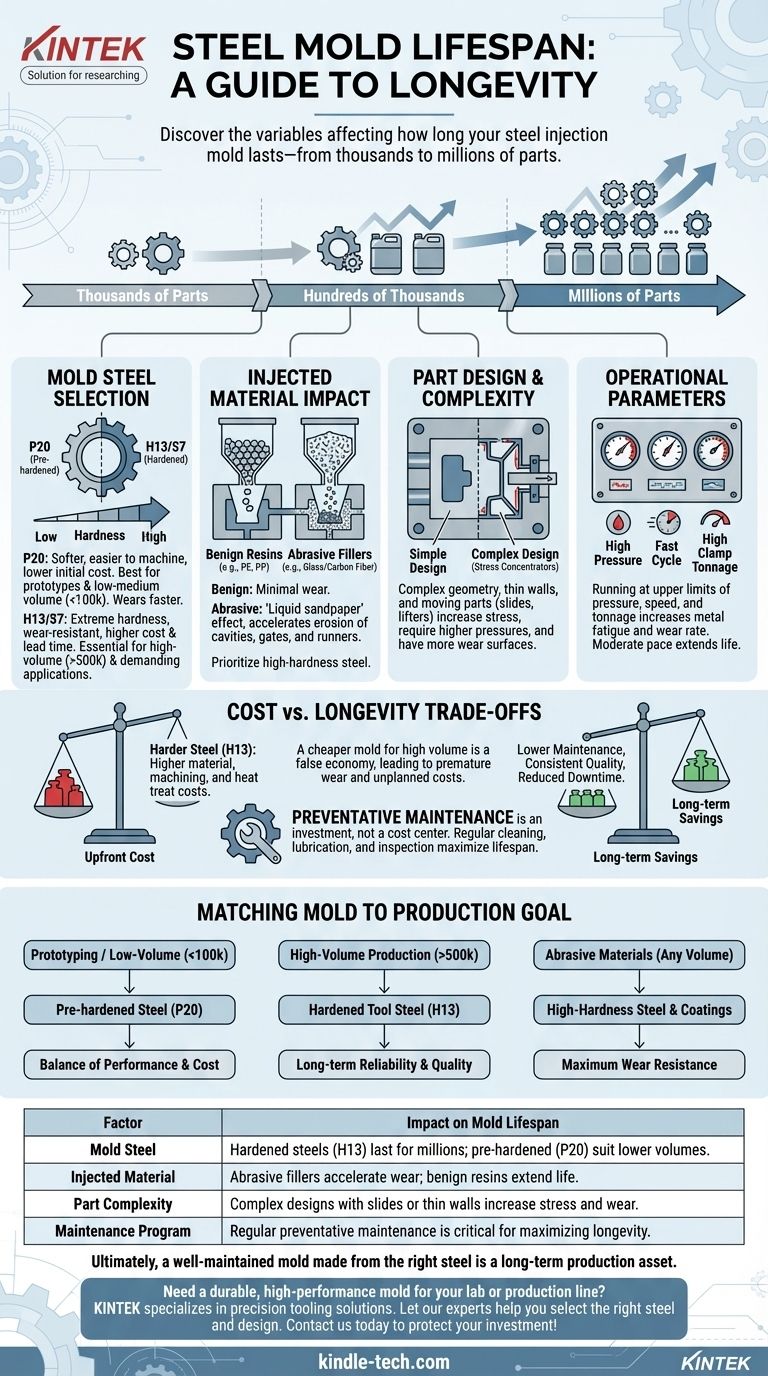
The operational lifespan of a steel injection mold is not a single number, but a wide spectrum determined by its engineering and use. A mold can produce anywhere from a few thousand parts to well over a million before requiring major refurbishment or replacement. The key factors dictating this lifespan are the type of steel used, the complexity of the part, the abrasiveness of the plastic being injected, and the discipline of the maintenance program.
A mold's lifespan is less a fixed property of the steel and more a dynamic outcome of the interplay between material choice, part design, operational stress, and maintenance. Understanding these factors is the key to forecasting and maximizing your return on investment.
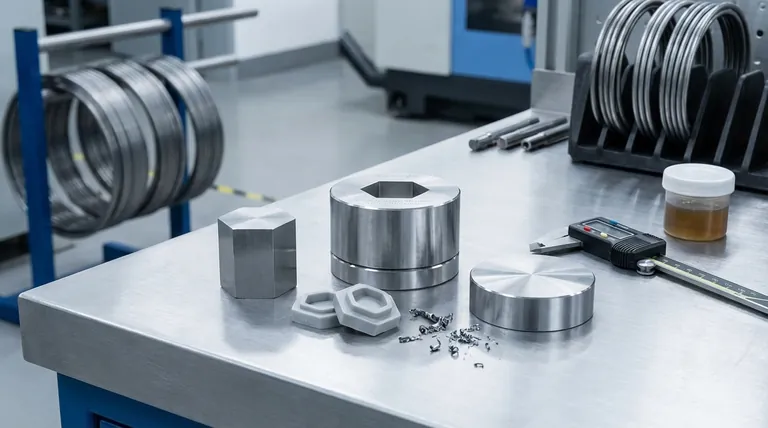

The Core Factors Defining Mold Lifespan
The "how long" question is best answered by examining the variables that either preserve or degrade the mold over its operational life.
Mold Steel Selection
The choice of steel is the foundation of the mold's longevity. Steels are chosen based on the required production volume and the nature of the injected material.
Softer, pre-hardened steels like P20 are common for prototypes and low-to-medium volume production runs. They are easier and faster to machine, reducing the initial cost of the tool, but will wear more quickly.
For high-volume production and demanding applications, hardened tool steels like H13 or S7 are the standard. These are heat-treated after machining to achieve extreme hardness and wear resistance, enabling them to withstand millions of cycles.
The Injected Material
The plastic resin being molded has a significant impact on the mold's surface.
Benign materials like polypropylene or polyethylene cause very little wear. However, resins with abrasive fillers, such as glass or carbon fiber, act like liquid sandpaper with every shot, accelerating the erosion of cavities, gates, and runner systems.
Part Design and Mold Complexity
The geometry of the part itself introduces stress into the mold.
Complex designs with thin walls, sharp internal corners, or deep ribs create stress concentrators and require higher injection pressures, increasing wear.
Molds with moving parts like slides, lifters, or collapsing cores have more wear surfaces. These mechanisms are often the first points of failure if not designed and maintained correctly.
Operational Parameters
How the mold is run in the press directly affects its life.
High injection pressures and speeds, fast cycle times, and high clamping tonnage all contribute to metal fatigue and wear over time. Running a mold consistently at the upper limit of its processing window will shorten its lifespan compared to running at a more moderate pace.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Longevity
Choosing the right mold is a business decision that balances upfront investment against long-term production needs.
The Upfront Cost of Harder Steels
Hardened tool steels like H13 are more expensive than P20. They also require more time and specialized equipment to machine, and the post-machining heat treatment adds another step and cost. This results in a significantly higher initial tool price.
The Hidden Cost of Softer Steels
Opting for a cheaper P20 mold for a high-volume program is a classic false economy. The tool will likely wear out prematurely, leading to part quality issues, unplanned downtime, and potentially the cost of building a second replacement mold mid-program.
Maintenance as an Investment
A rigorous preventative maintenance program is not a cost center; it is a direct investment in the mold's lifespan. Deferring regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection saves a little money in the short term but guarantees expensive repairs and a shorter overall tool life.
Matching the Mold to Your Production Goal
Use your project's core requirements to guide your decision-making.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume production (< 100,000 parts): A pre-hardened steel like P20 offers the best balance of performance and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production (> 500,000 parts): Investing in a hardened tool steel like H13 is essential for ensuring long-term reliability and consistent part quality.
- If your project involves abrasive materials (e.g., glass-filled nylon): Prioritize a high-hardness, wear-resistant tool steel (and potentially specialized surface coatings) regardless of the production volume.
Ultimately, a well-maintained mold made from the right steel is not an expense, but a long-term production asset.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Mold Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Mold Steel | Hardened steels (H13) last for millions of cycles; pre-hardened steels (P20) suit lower volumes. |
| Injected Material | Abrasive fillers (glass fiber) accelerate wear; benign resins (polyethylene) extend life. |
| Part Complexity | Complex designs with slides or thin walls increase stress and wear. |
| Maintenance Program | Regular preventative maintenance is critical for maximizing longevity. |
Need a durable, high-performance mold for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision tooling solutions. Let our experts help you select the right steel and design for your project's volume and material requirements. Contact us today to protect your investment and ensure long-term production success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is a mold assembly? The Critical Final Step to a Functional Injection Mold
- What role do high-purity graphite molds play in TiAl composite sintering? Achieve Full Densification & Precision
- What are the key functions of graphite hot-press molds? Optimize WC/Cu Sintering Success
- What are the primary functions of high-purity graphite molds? Enhance Vacuum Hot Press Sintering Precision
- How to work with ceramic molds? Master the Art of Slip Casting for Consistent Results
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- What is the top half of a mold called? The Cavity (A-Side) Explained for Better Molding
- What is the core function of high-strength graphite molds? Master Vacuum Hot Press Sintering Efficiency



















