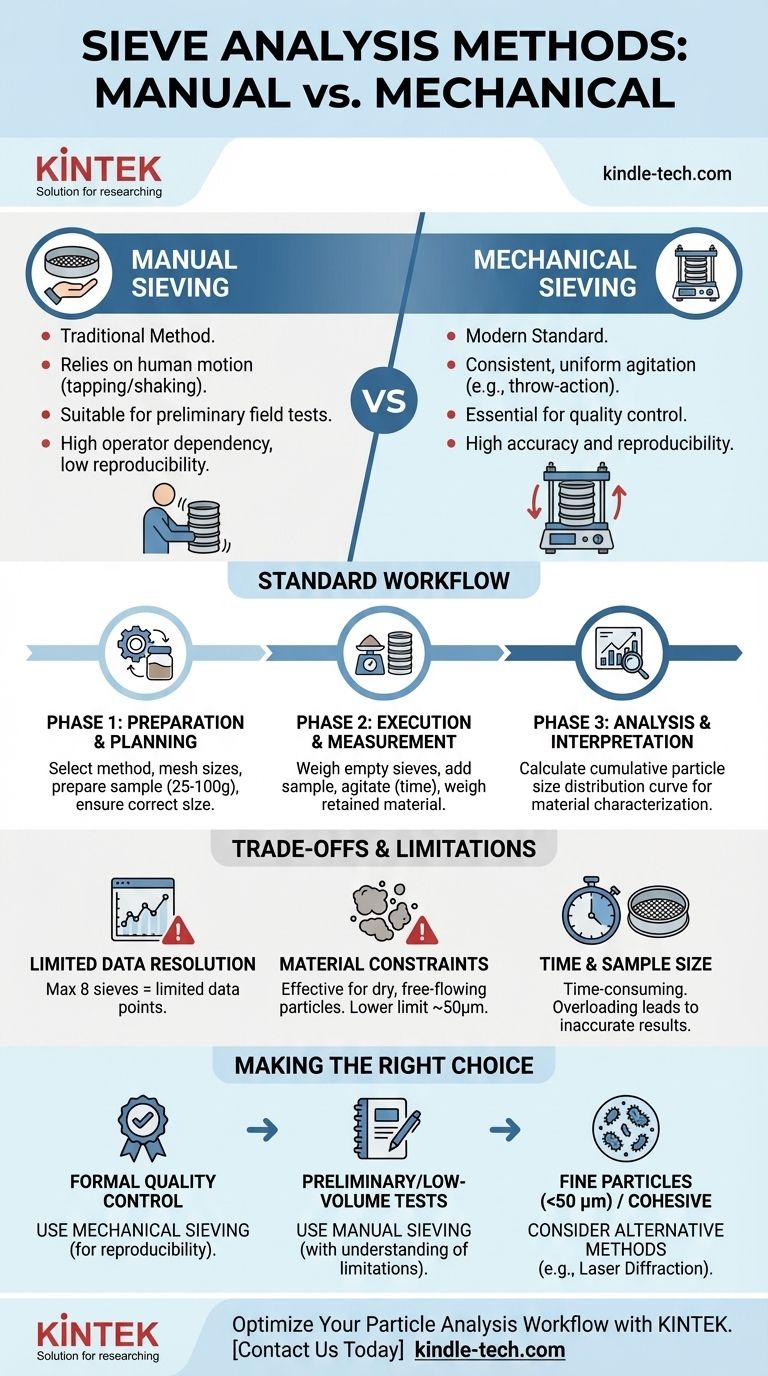
At its core, sieve analysis can be conducted in two fundamental ways: manually or mechanically using a sieve shaker. While the underlying principle of separating particles by size remains the same, the method of agitation is the key differentiator that dictates the precision, reproducibility, and efficiency of your results.
The choice between manual and mechanical sieving is not merely about convenience. It is a critical decision that directly impacts the reliability of your data, balancing the need for reproducible quality control against the practical constraints of cost and sample volume.
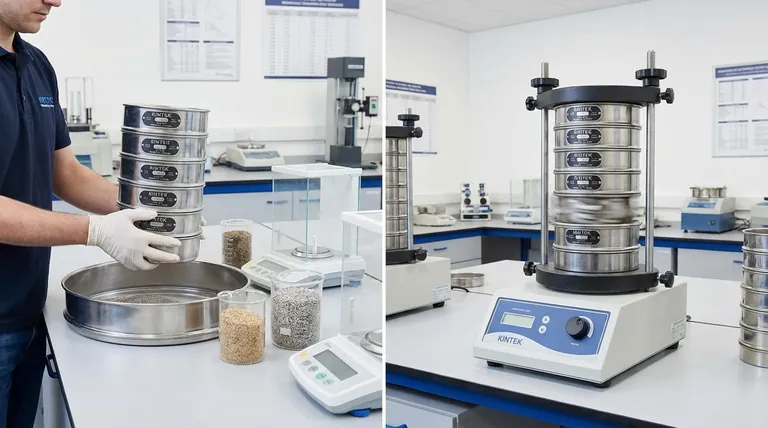

The Two Fundamental Sieving Methods
The primary distinction in how sieve analysis is performed lies in the energy source used to agitate the sample through the stack of test sieves.
Manual Sieving
Manual sieving is the traditional method, relying on human motion. An operator holds the sieve stack and uses a combination of tapping and shaking motions to encourage particles to pass through the mesh apertures.
This approach is often sufficient for preliminary field tests or in settings where a mechanical shaker is unavailable. However, it is highly dependent on the operator's technique, making it difficult to achieve consistent, reproducible results between different tests or technicians.
Mechanical Sieving (Sieve Shakers)
Mechanical sieving is the modern standard for any application requiring accuracy and repeatability, such as formal quality control. A sieve shaker imparts a consistent and uniform motion to the sieve stack.
One common and highly effective technique is the throw-action method. This imparts a vertical throwing motion combined with a slight circular movement, which distributes the sample across the entire sieve surface and efficiently separates the particles. This mechanical precision eliminates the variability of manual shaking, ensuring that results are reliable and comparable over time.
The Standard Sieve Analysis Workflow
Regardless of whether you sieve manually or mechanically, the procedural steps for a valid analysis are consistent. This workflow ensures that from sample preparation to final interpretation, the process is systematic and traceable.
Phase 1: Preparation and Planning
Before any sieving occurs, you must establish the test parameters. This involves selecting a standard method (like an ASTM or ISO standard), choosing the appropriate sieve mesh sizes for your material, and preparing the sample.
Proper sample preparation may involve pre-drying and, crucially, ensuring the correct sample size. Using a sample splitter to obtain a representative portion—typically between 25 and 100 grams—is critical. An overloaded sieve prevents individual particles from reaching the mesh surface, compromising the accuracy of the entire test.
Phase 2: Execution and Measurement
This is the hands-on portion of the analysis. It begins by weighing each individual sieve while it is empty and recording its mass.
The prepared sample is then added to the top sieve in the stack, which is capped with a lid and placed on a collection pan. The stack is then agitated for a predetermined duration. Afterward, each sieve is weighed again to determine the mass of the material retained on it.
Phase 3: Analysis and Interpretation
The final step is to calculate the results. By subtracting the empty sieve weights from the final weights, you determine the mass of particles in each size fraction.
This data is used to calculate a cumulative particle size distribution curve. This curve is the ultimate output, allowing you to characterize the material and determine its suitability for a specific purpose, such as whether an aggregate is appropriate for a concrete mix or asphalt design.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While sieve analysis is a robust and widely used technique, it is essential to understand its inherent limitations to ensure you are applying it correctly.
Limited Data Resolution
A standard sieve stack typically consists of a maximum of eight sieves. This means your final particle size distribution curve will be based on only eight data points, which may not provide the high resolution needed for some advanced materials research.
Material and Particle Constraints
Sieve analysis is generally effective only for dry, free-flowing particles. It is not suitable for materials that are sticky, agglomerate easily, or are in a slurry. Furthermore, there is a practical lower limit to the particle size that can be measured, typically around 50 micrometers (µm).
Time and Sample Size
The process can be time-consuming, from sample preparation and drying to the sieving itself and the final weighing and cleaning. Using samples that are too large in an attempt to save time is a common mistake that leads to inaccurate results by "blinding" the sieve mesh.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements should dictate your approach to sieve analysis.
- If your primary focus is formal quality control or certification: Mechanical sieving is the only acceptable method to ensure the necessary reproducibility and accuracy.
- If your primary focus is preliminary field analysis or occasional, low-volume tests: Manual sieving can be a practical and cost-effective option, provided you understand its limitations in precision.
- If your material consists of very fine particles (<50 µm) or is cohesive: Sieve analysis is likely the wrong tool, and you should consider alternative particle sizing methods like laser diffraction.
Ultimately, understanding the core methods and the procedural framework empowers you to generate meaningful and reliable data for your project.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Sieving | Operator-dependent shaking/tapping | Preliminary field tests, low-volume use |
| Mechanical Sieving | Consistent, automated agitation (e.g., throw-action) | Quality control, high reproducibility |
Struggling to achieve consistent particle size data? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including high-precision sieve shakers designed for reliable quality control. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to ensure your sieve analysis is accurate and reproducible. Contact our team today to optimize your particle analysis workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















