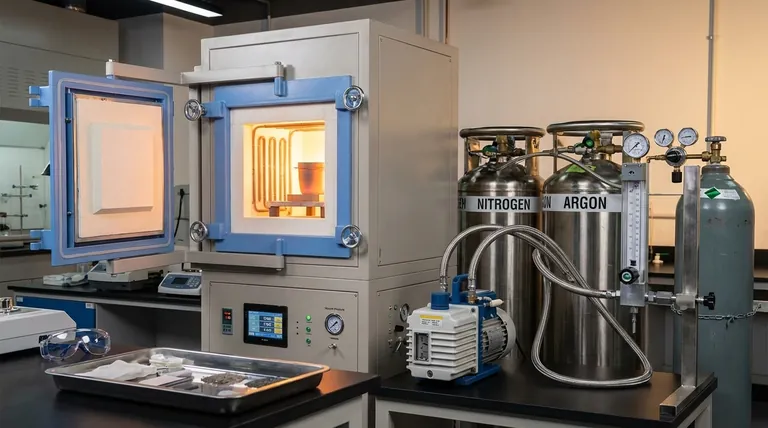
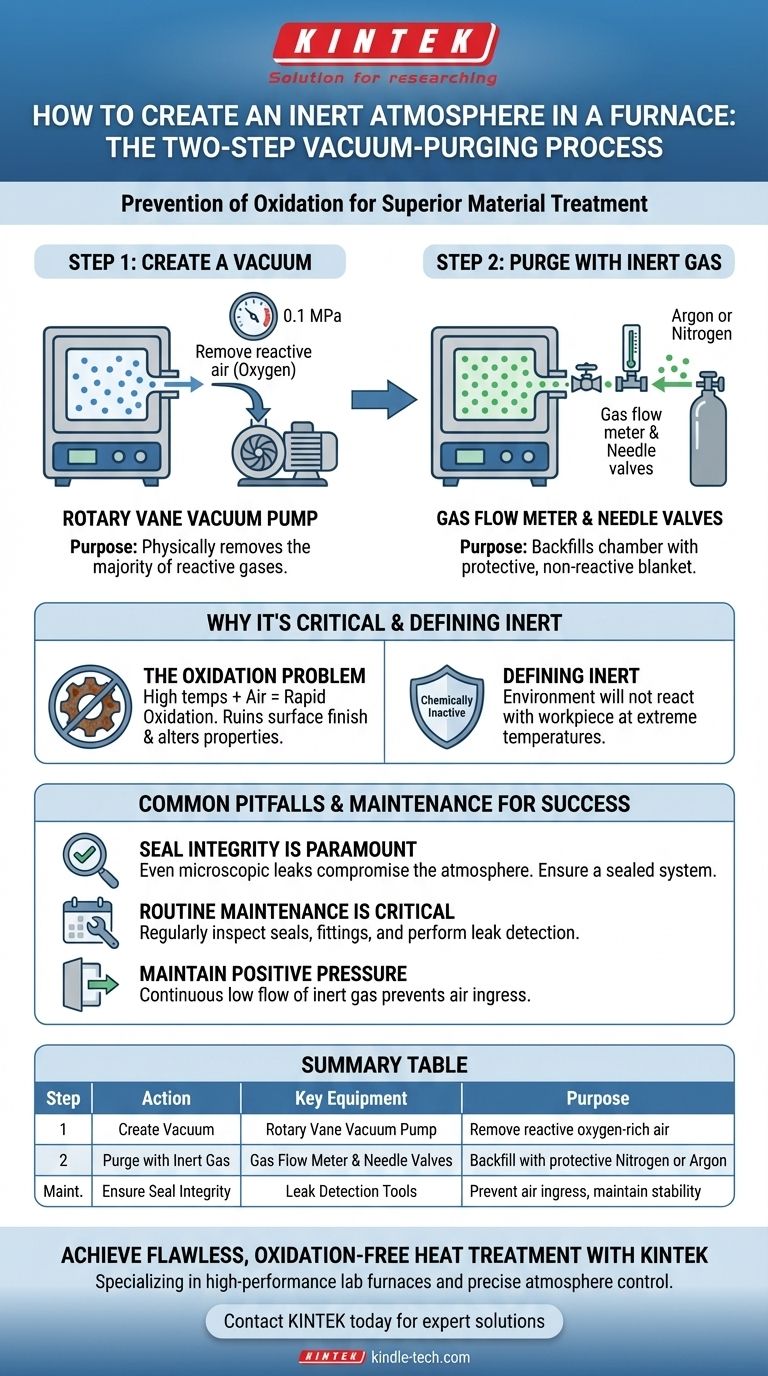
The most effective method for creating an inert atmosphere in a furnace is a two-step process known as vacuum-purging. First, a vacuum pump is used to remove the reactive air from the furnace chamber. Once the vacuum is established, the chamber is backfilled, or "purged," with a chemically inactive gas like nitrogen or argon, which protects the material from oxidation during heat treatment.
The core principle is not simply adding an inert gas, but actively displacing the reactive oxygen-rich atmosphere first. A successful inert environment depends entirely on removing the initial air before introducing the protective gas.

Why an Inert Atmosphere is Critical
To properly execute the process, it's essential to understand the fundamental problem an inert atmosphere solves. At high temperatures, materials become highly susceptible to chemical reactions with the air around them, primarily with oxygen.
The Problem of Oxidation
Most heat-treating applications aim to alter a material's physical properties, not its chemical composition. When heated in the presence of air, materials can rapidly oxidize, forming an unwanted surface layer (like rust on steel). This oxide layer can ruin surface finish, compromise structural integrity, and alter the material's intended characteristics.
Defining "Inert" in This Context
In this context, "inert" simply means chemically inactive. The goal is to create an internal furnace environment that will not react with the workpiece, even at extreme temperatures. This ensures the heat-treatment process is clean, predictable, and delivers the desired outcome without contamination.
The Two-Step Process for Achieving Inertness
Creating this environment is a deliberate procedure requiring specific equipment. The process is universally applicable for furnaces designed for atmosphere control.
Step 1: Create a Vacuum
The first and most critical step is to remove the existing air from the sealed furnace chamber. This is accomplished using a rotary vane vacuum pump to pull the chamber down to a slight vacuum, typically up to 0.1MPa. This action physically removes the vast majority of the oxygen and other reactive gases.
Step 2: Purge with Inert Gas
After the vacuum is achieved, a valve is opened to introduce an inert gas, most commonly argon or nitrogen. This gas, managed by a gas flow meter and needle valves, backfills the chamber, surrounding the material in a protective, non-reactive blanket. A pressure gauge is used to monitor the chamber's internal atmosphere.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Simply following the two steps is not enough to guarantee a stable inert atmosphere. The integrity of the furnace system itself is paramount to success.
The Critical Role of a Sealed System
The entire vacuum and purge process is rendered ineffective if the furnace has leaks. Even a microscopic leak can allow ambient air to seep back into the chamber, re-introducing oxygen and compromising the inert environment over the course of the heat treatment.
The Necessity of Routine Maintenance
Maintaining the furnace is not optional. Regular preventative maintenance, including visually inspecting all seals and fittings, is crucial. For high-purity applications, thorough leak detection methods are necessary to identify and repair any potential sources of atmospheric contamination.
Maintaining Positive Pressure
Once purged, the furnace is often kept at a slight positive pressure with a very low, continuous flow of inert gas. This ensures that if any minor leaks exist, the inert gas will flow outward, preventing any reactive air from flowing inward.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The rigor of your process should match the sensitivity of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for sensitive materials: Perform multiple vacuum and purge cycles to remove virtually all trace oxygen before starting the heating process.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and repeatability: Make routine leak detection and preventative maintenance a non-negotiable part of your operational checklist.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Ensure your equipment, including the vacuum pump, gas flow meter, and valves, is properly calibrated for precise and reliable control.
By first removing the reactive air and then replacing it with a stable inert gas, you gain complete control over your material's thermal processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Step | Action | Key Equipment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create Vacuum | Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump | Remove reactive oxygen-rich air from the chamber |
| 2 | Purge with Inert Gas | Gas Flow Meter & Needle Valves | Backfill chamber with protective nitrogen or argon |
| Maintenance | Ensure Seal Integrity | Leak Detection Tools | Prevent air ingress and maintain a stable inert environment |
Achieve flawless, oxidation-free heat treatment with KINTEK's expert solutions.
Whether you are processing sensitive alloys, advanced ceramics, or other high-value materials, a reliable inert atmosphere is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, vacuum systems, and consumables designed for precise atmosphere control.
Our team can help you select the right equipment and establish maintenance protocols to ensure process consistency, maximum material purity, and operational efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific furnace requirements and let our experts help you protect your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of atmospheres are used during sintering? Choose the Right Gas for Your Material
- Why an inert atmosphere is used in the manufacture of the alloy? Prevent Contamination & Ensure Material Integrity
- What is the function of nitrogen gas in the annealing process? Ensure Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What roles do temperature-controlled furnaces and inert gas play in hot-dip aluminizing? Master Coating Precision
- What is the necessity of an annealing furnace with an argon atmosphere? Protecting ODS Ferritic Steel Quality
- What role does a high-temperature annealing furnace play in regulating the properties of Cerium Oxide nanoparticles?
- What is the role of an Atmosphere Furnace in the preparation of lignin-based graphene oxide? Key Carbonization Insights
- How does the temperature control precision of a solid-state reaction sintering furnace affect lithium-rich materials?



















