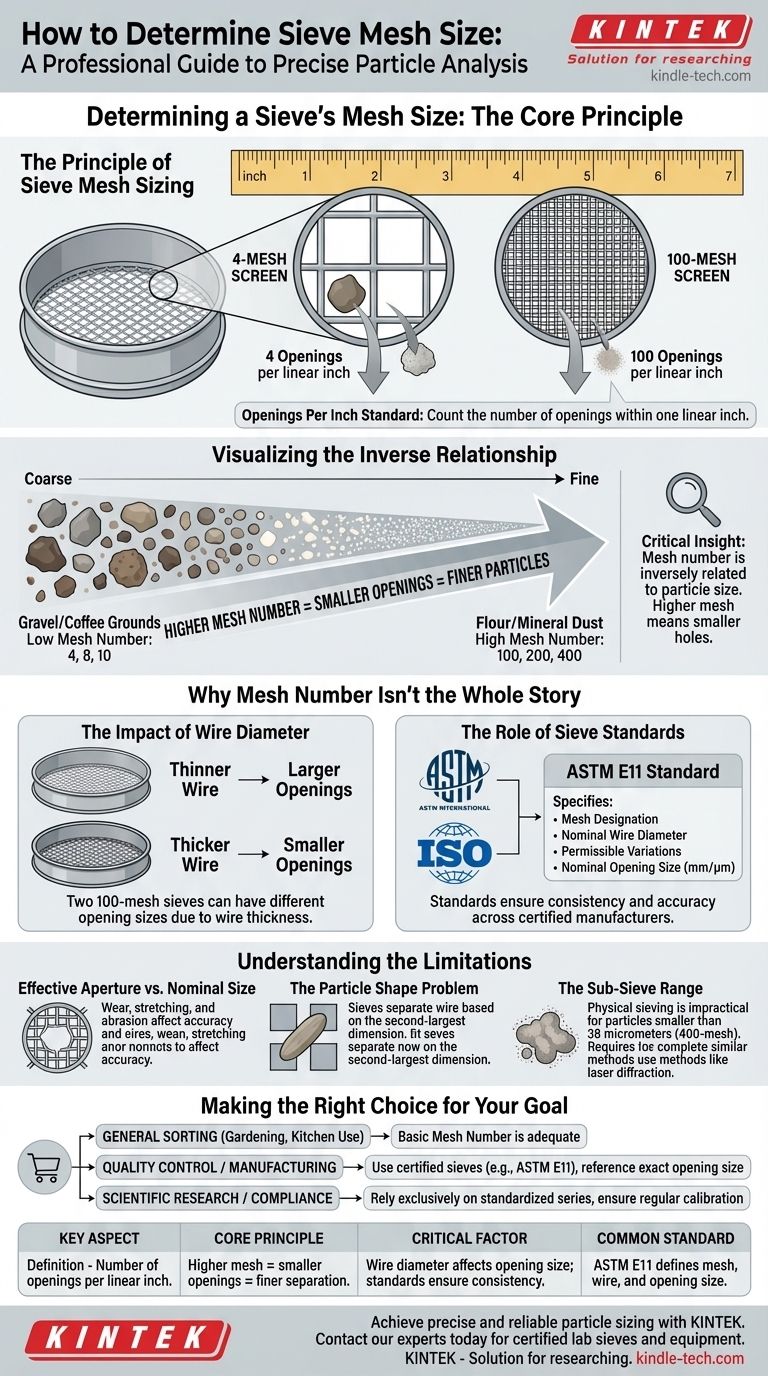
Determining a sieve's mesh size is a straightforward process based on a simple physical count. You count the number of openings found within one linear inch of the screen. This number directly corresponds to the sieve's mesh designation; for example, a 100-mesh screen has 100 openings per linear inch.
While the mesh number is a simple count of openings, the critical insight is its inverse relationship to particle size. A higher mesh number always signifies smaller openings and the ability to separate finer particles.
The Principle of Sieve Mesh Sizing
The "Openings Per Inch" Standard
The U.S. mesh size standard is defined by the number of openings in the screening surface per linear inch. This measurement is counted from the center of one wire to a point one inch distant.
For example, a 4-mesh screen means there are four openings across one inch. A 325-mesh screen has 325 openings in that same span.
Visualizing the Inverse Relationship
Think of the mesh number like the resolution of a digital image (pixels per inch). A higher resolution means more, smaller pixels packed into the same space.
Similarly, a higher mesh number means more, smaller holes are packed into one inch of the sieve. This is the most important concept: as mesh number goes up, the size of the particle that can pass through goes down.
From Coarse to Fine
This system creates an intuitive scale. Low mesh numbers (e.g., 4, 8, 10) are used for coarse materials like gravel or coffee grounds. High mesh numbers (e.g., 100, 200, 400) are used for fine powders like flour or mineral dust.
Why Mesh Number Isn't the Whole Story
The Impact of Wire Diameter
The mesh number only tells you how many openings there are, not the exact size of those openings. The thickness of the wire used to weave the mesh also takes up space.
Two 100-mesh sieves can have different opening sizes if one is woven with a thicker wire than the other. The thicker wire will result in smaller openings.
The Role of Sieve Standards
To ensure consistency in science and industry, organizations like ASTM International and ISO define standard sieve series. The most common in the United States is ASTM E11.
These standards specify not only the mesh designation but also the nominal wire diameter, the permissible variations, and the resulting nominal opening size (in millimeters or micrometers). This guarantees that a No. 100 sieve from one certified manufacturer is functionally identical to a No. 100 sieve from another.
Understanding the Limitations
Effective Aperture vs. Nominal Size
Over time, sieve wires can stretch or sag from use, and abrasive materials can wear them down. This distortion changes the actual size and shape of the openings, affecting separation accuracy. Regular inspection and calibration are essential for precise work.
The Particle Shape Problem
Sieving assumes particles are roughly spherical. However, elongated or flat particles can pass through a mesh "end-on" or "sideways" even if their largest dimension is bigger than the mesh opening.
This means a sieve analysis technically separates particles based on their second-largest dimension.
The Sub-Sieve Range
For extremely fine particles (typically smaller than 38 micrometers, or a 400-mesh sieve), physical sieving becomes impractical. The fine wires are fragile, and particles tend to clump together due to electrostatic forces.
At this point, other methods like laser diffraction or air classification are used to determine particle size distribution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a sieve, your application determines the level of precision you need.
- If your primary focus is general sorting (e.g., gardening, kitchen use): The basic mesh number is a perfectly adequate guide for separating coarse from fine materials.
- If your primary focus is quality control or process manufacturing: You must use sieves certified to a specific standard (like ASTM E11) and reference the exact opening size in micrometers (µm) or millimeters (mm).
- If your primary focus is scientific research or compliance: Rely exclusively on standardized sieve series and ensure your equipment is regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy and traceability.
Understanding how mesh size relates to both wire diameter and standardized openings empowers you to control particle separation with confidence.

Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Number of openings in one linear inch of the sieve screen. |
| Core Principle | Higher mesh number = smaller openings = finer particle separation. |
| Critical Factor | Wire diameter affects the actual opening size; standards ensure consistency. |
| Common Standard | ASTM E11 defines mesh numbers, wire diameters, and opening sizes. |
Achieve precise and reliable particle sizing in your laboratory.
The correct sieve is fundamental to quality control, research, and process efficiency. KINTEK specializes in high-quality, certified lab sieves and equipment that meet ASTM and ISO standards, ensuring your results are accurate and reproducible.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sieve for your specific material and application.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation and enhance your particle analysis workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research



















