Yes, sputtering is a primary method of physical vapor deposition (PVD). It is a specific mechanism that falls under the broader PVD category, where solid material is converted into a vapor phase and then deposited as a thin film onto a substrate. Sputtering achieves this by ejecting atoms from a source material through energetic particle bombardment.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is the family of processes used to deposit thin films in a vacuum. Sputtering is a specific member of that family, distinguished by its use of ion bombardment to "knock" atoms off a source target, offering exceptional control and producing highly durable coatings.

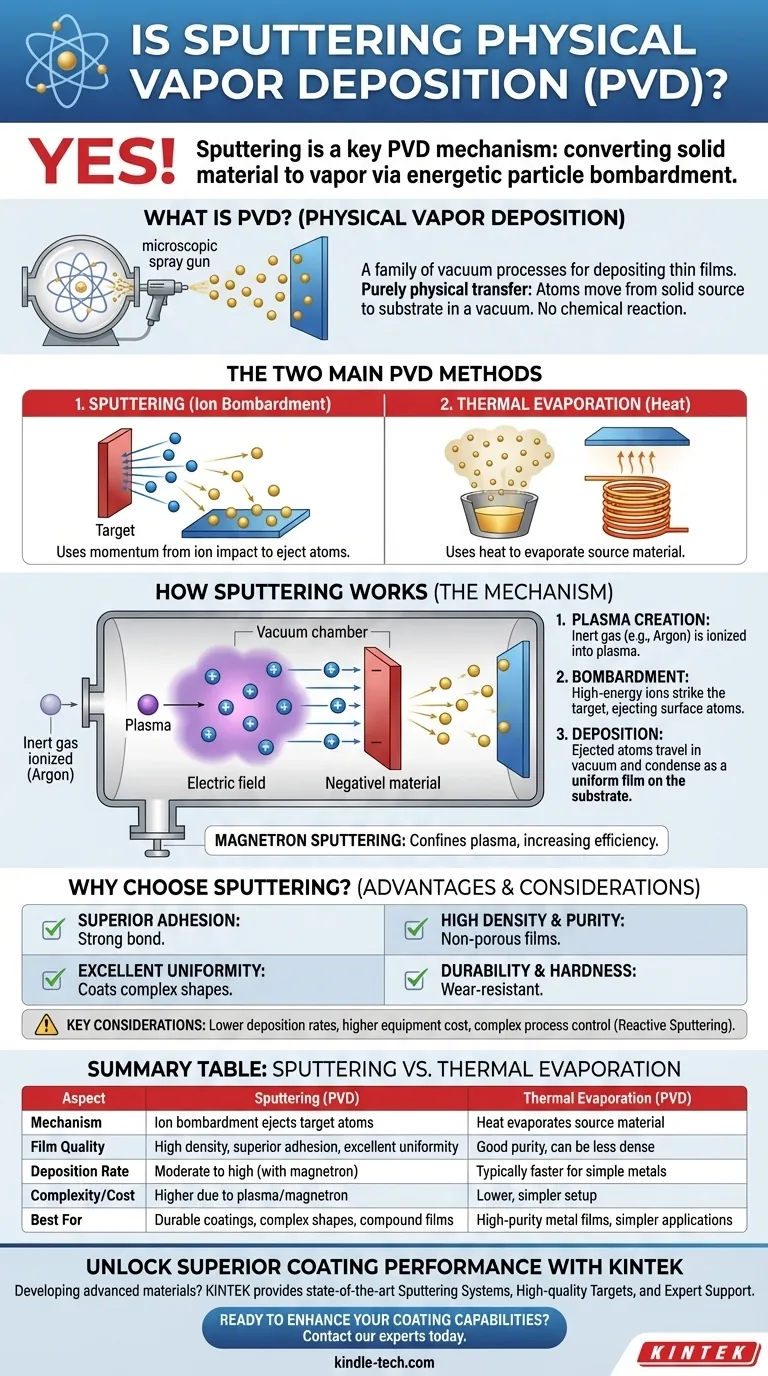
What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
To understand sputtering's role, we must first define the category it belongs to. PVD encompasses a set of vacuum deposition processes that involve a purely physical transition of material.
The Core Principle: A Physical Process
PVD moves atoms from a solid source to a substrate without a chemical reaction. Think of it as a microscopic form of spray painting, but instead of paint, you are spraying individual atoms or molecules inside a vacuum chamber.
This physical transfer is the key differentiator from processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which relies on chemical reactions on the substrate surface to form the film.
The Two Main PVD Methods
The PVD family is primarily divided into two major techniques based on how they generate the vapor:
- Sputtering: Uses momentum transfer from ion bombardment to dislodge atoms from the source.
- Thermal Evaporation: Uses heat to raise the vapor pressure of a source material until it evaporates.
How Sputtering Works as a PVD Process
Sputtering is a highly controlled and versatile PVD technique. The process relies on creating a plasma and using it to bombard a source material, known as the "target."
The Bombardment Mechanism
The process begins by introducing an inert gas, typically Argon, into a vacuum chamber. A strong electric field is applied, which ignites the gas into a plasma—a state of matter containing positively charged ions and free electrons.
These high-energy positive ions are then accelerated toward the negatively charged target material. When the ions strike the target, they transfer their momentum and energy, ejecting surface atoms from the target. This is the core "sputtering" effect, acting like a microscopic sandblaster.
The Deposition Step
The ejected atoms travel through the vacuum chamber until they strike the substrate (the part being coated). Upon arrival, they condense and build up, layer by layer, to form a dense and uniform thin film. A shutter is often used to block the material flow until conditions are stable, ensuring a high-quality initial layer.
The Role of Magnetrons
Modern systems often use magnetron sputtering. This technique uses powerful magnets behind the target to trap electrons near its surface. This confinement intensifies the plasma, dramatically increasing the rate of ion bombardment and making the sputtering process much more efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
Sputtering is chosen for its specific benefits, but like any engineering process, it involves trade-offs.
Why Choose Sputtering?
Films deposited via sputtering are known for their superior quality. They typically exhibit:
- Superior Adhesion: The high energy of sputtered atoms helps them embed slightly into the substrate surface, creating a very strong bond.
- High Density and Purity: The process creates dense, non-porous films with low gas incorporation.
- Excellent Uniformity: Sputtering can coat large and complex shapes with exceptional thickness uniformity.
- Durability and Hardness: Sputtered films are often very hard and provide excellent resistance to corrosion and wear.
Key Considerations
While powerful, sputtering has limitations. The deposition rates can be lower than some thermal evaporation methods, especially for certain materials. The equipment is also more complex and expensive than that used for simple evaporation.
Furthermore, reactive sputtering, where a gas like oxygen or nitrogen is added to form compounds (e.g., oxides or nitrides), adds another layer of process control complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the distinction between the general category and the specific method is crucial for clear communication and process selection.
- If your primary focus is describing the general class of vacuum coating: Use the term "Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)," as this correctly includes both sputtering and evaporation.
- If your primary focus is the specific mechanism using ion bombardment: Use the term "sputtering" to accurately describe how the atoms are liberated from the source.
- If your primary focus is a dense, durable, and highly adherent coating: Sputtering is often the superior PVD method for achieving these specific material properties.
Recognizing sputtering as a distinct and powerful PVD technique is the first step toward leveraging it for advanced material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Sputtering (PVD Method) | Thermal Evaporation (PVD Method) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Ion bombardment ejects target atoms | Heat evaporates source material |
| Film Quality | High density, superior adhesion, excellent uniformity | Good purity, can be less dense |
| Deposition Rate | Moderate to high (with magnetron) | Typically faster for simple metals |
| Complexity/Cost | Higher due to plasma and magnetron systems | Lower, simpler setup |
| Best For | Durable coatings, complex shapes, compound films (reactive sputtering) | High-purity metal films, simpler applications |
Unlock Superior Coating Performance with KINTEK
Are you developing advanced materials or products that require durable, high-purity thin films? Sputtering PVD technology delivers the exceptional adhesion, uniformity, and durability your laboratory or production needs.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for all your PVD requirements. Our expertise helps researchers and engineers achieve breakthrough results in sectors from microelectronics to medical devices.
We provide:
- State-of-the-art sputtering systems and components
- High-quality targets and consumables
- Expert technical support for process optimization
Ready to enhance your coating capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss how our sputtering solutions can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















