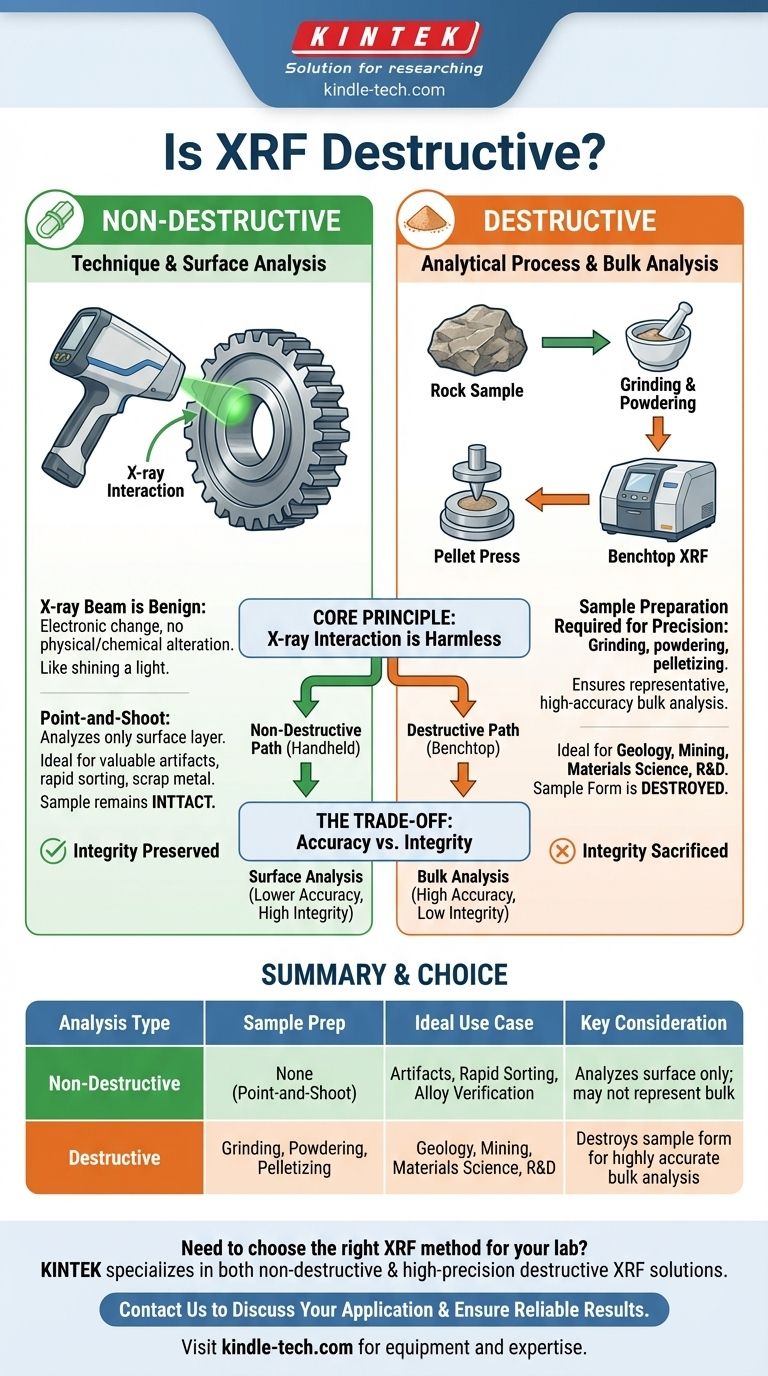
To be precise, the technique of X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is fundamentally non-destructive, as the X-ray beam itself does not damage or alter the sample's chemical composition. However, the overall analytical process can be destructive depending on the sample preparation required to achieve the desired level of accuracy for a specific material.
The core distinction lies between the measurement technique and the analytical method. While the X-ray interaction is harmless, preparing a sample for a high-precision benchtop XRF often involves destructive steps like grinding or powdering to ensure a representative analysis.

The Core Principle: How XRF Works Without Damage
The X-ray Interaction
XRF works by directing a primary X-ray beam at a sample. This energy excites atoms within the material, causing them to eject an inner-shell electron.
To regain stability, an electron from a higher energy shell drops down to fill the vacancy. This transition releases a specific amount of energy in the form of a secondary (or fluorescent) X-ray.
A Benign Measurement
The instrument’s detector measures the unique energy of this secondary X-ray, which acts as a fingerprint for a specific element.
This entire process of excitation and fluorescence is an electronic, not a physical or chemical, change. It is akin to shining a special light on an object to see its color; the light reveals information without altering the object itself.
The Destructive Variable: Sample Preparation
The question of whether the XRF process is destructive hinges entirely on how the sample must be prepared to get a meaningful result. This depends on the type of analyzer and the nature of the sample.
Truly Non-Destructive Analysis
For large, uniform (homogenous) materials, handheld XRF analyzers offer a completely non-destructive solution.
Operators can simply point the device at a metal alloy, a large mineral, or a consumer product to get an elemental reading from its surface in seconds. No sample is taken, and the object is left entirely intact.
When Preparation Becomes Necessary (Destructive)
For many scientific and quality control applications, analyzing only the surface is insufficient and can be misleading.
To obtain a precise and representative analysis of the entire material, destructive preparation is often required. This typically involves taking a small but representative fragment of the object and grinding it into a fine, homogenous powder. This powder is then often pressed into a pellet for analysis in a more powerful benchtop XRF spectrometer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between a destructive and non-destructive approach is a classic trade-off between sample integrity and analytical accuracy.
Accuracy vs. Integrity
A perfectly prepared, homogenous powder sample will yield vastly more accurate and precise results than a point-and-shoot surface analysis. This is critical in geology, mining, and materials science, where small variations in composition are significant.
However, this level of accuracy comes at the cost of destroying a portion of the original sample's form.
The Surface vs. The Bulk
Handheld, non-destructive XRF only analyzes a very thin layer of the material's surface.
If the sample is corroded, coated, painted, or naturally non-uniform, the surface reading will not represent the bulk composition. Destructive sampling is the only way to bypass this surface layer and analyze what lies beneath.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a destructive or non-destructive XRF method must be aligned with your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving a valuable artifact (e.g., artwork, jewelry, archaeological find): A handheld XRF is the only choice, accepting that you are only analyzing the immediate, accessible surface.
- If your primary focus is rapid sorting or quality verification (e.g., scrap metal, alloy confirmation): A handheld XRF provides the necessary speed and is perfectly suited for this non-destructive task.
- If your primary focus is high-precision scientific analysis (e.g., geological surveys, research): You must use a method involving destructive sample preparation to ensure your data is accurate and representative of the entire sample.
Ultimately, your analytical goal determines whether the XRF process you employ preserves or consumes your sample.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Type | Sample Preparation | Ideal Use Case | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Destructive | None (point-and-shoot) | Artifact analysis, scrap metal sorting, alloy verification | Analyzes surface only; may not represent bulk material |
| Destructive | Grinding, powdering, pelletizing | Geology, mining, materials science, high-precision R&D | Destroys sample form but provides accurate, representative bulk analysis |
Need to choose the right XRF method for your laboratory?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need for both non-destructive and high-precision destructive XRF analysis. Whether you're analyzing precious artifacts or conducting rigorous material science research, our experts can help you select the right solution to balance sample integrity with analytical accuracy.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and ensure you get the most reliable and representative results. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with a specialist!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
People Also Ask
- What equation do you use to calculate the heat required to melt a sample? Master the Heat of Fusion Formula
- What are pellet dies made of? Choose the Right Material for Accurate XRF Analysis
- What size are XRF pellets? A Guide to Standard Dimensions and Preparation
- What are the samples for XRF analysis? A Guide to Preparing Solids, Powders, and Liquids
- What are the five key considerations when designing a sample preparation recipe for pressed pellets in XRF analysis?













