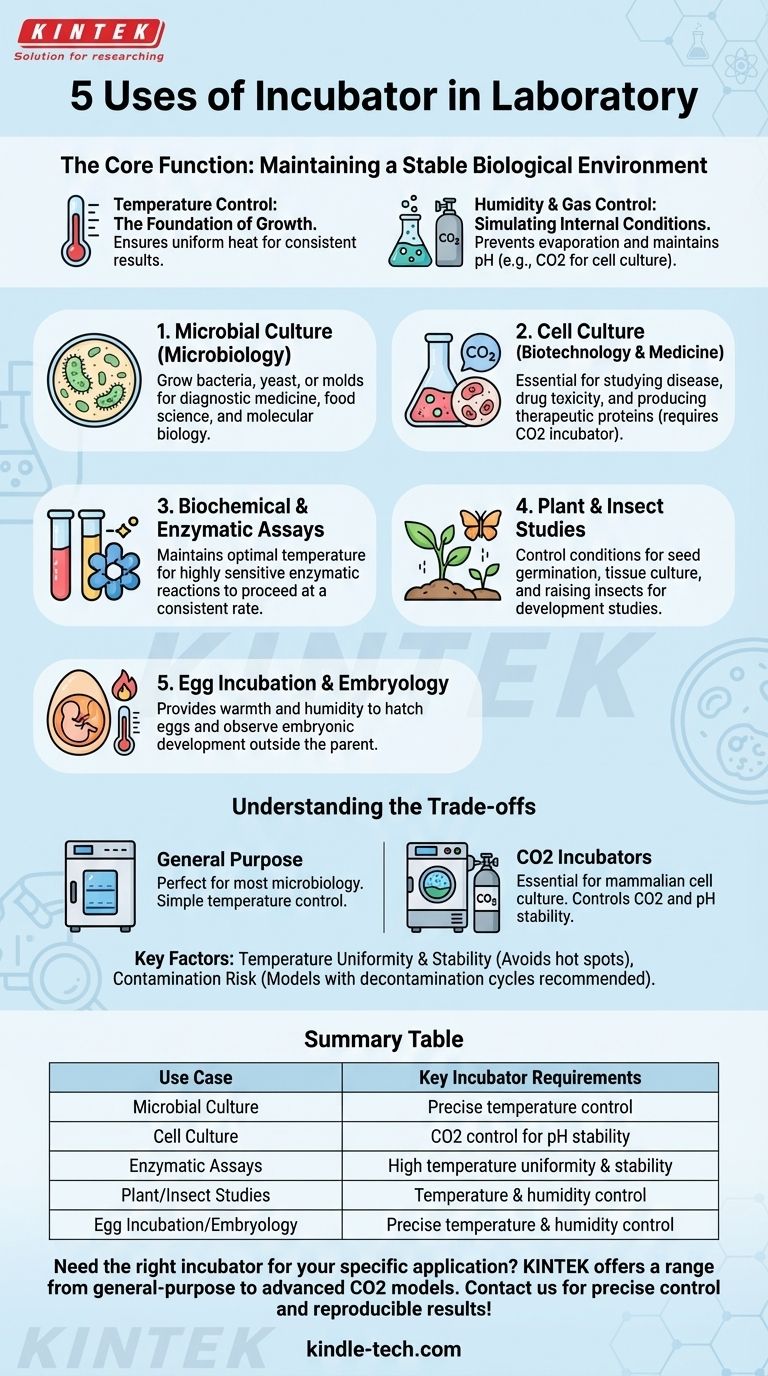
At its core, a laboratory incubator provides a controlled, contaminant-free environment for a wide range of scientific applications. The five most common uses are the cultivation of microorganisms like bacteria and yeast, the culture of eukaryotic cells (such as mammalian cells), conducting biochemical or enzymatic assays, incubating insect or plant life, and hatching eggs for embryology studies.
A laboratory incubator is more than just a heated box. It is a precision instrument designed to maintain a stable, predictable environment, allowing sensitive biological processes to occur reliably outside of a living organism.

The Core Function: Maintaining a Stable Biological Environment
The primary job of an incubator is to mimic the ideal physiological conditions required for a specific biological process to thrive. This control is what makes experiments reproducible and results trustworthy.
Temperature Control: The Foundation of Growth
Nearly all biological activity is temperature-dependent. Enzymes, which drive metabolic processes, have optimal temperature ranges.
An incubator provides constant, uniform heat, ensuring that all samples experience the exact same conditions. This is critical for achieving consistent growth rates in cell cultures or predictable reaction speeds in enzymatic assays.
Humidity and Gas Control: Simulating Internal Conditions
Many advanced incubators do more than just control heat. They also manage humidity to prevent sensitive liquid culture media from evaporating over days or weeks.
For mammalian cell culture, CO2 incubators are essential. They inject a specific percentage of CO2 (typically 5%) into the chamber to interact with the bicarbonate in the culture medium, creating a buffer system that maintains a stable physiological pH (around 7.2-7.4).
Key Laboratory Applications Explained
While the principle is simple—provide a stable environment—the applications are incredibly diverse.
1. Microbial Culture (Microbiology)
This is the most classic use. Incubators are used to grow bacteria, yeast, or molds on agar plates or in liquid broths. This is fundamental for diagnostic medicine (identifying pathogens), food science, and molecular biology research.
2. Cell Culture (Biotechnology & Medicine)
Growing lines of human or animal cells is a cornerstone of modern research. These cells are used to study disease, test the toxicity of new drugs, and produce therapeutic proteins like antibodies. This application almost always requires a CO2 incubator.
3. Biochemical and Enzymatic Assays
Many biochemical reactions, especially those catalyzed by enzymes, are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Placing these reactions in an incubator set to the enzyme's optimal temperature (e.g., 37°C for human enzymes) ensures the reaction proceeds at a consistent and maximal rate.
4. Plant and Insect Studies
Botanists and entomologists use incubators to control conditions for their subjects. This includes seed germination studies, plant tissue culture, and raising insects at specific temperatures to study their development, behavior, and genetics.
5. Egg Incubation and Embryology
For developmental biologists and zoologists, incubators provide the warmth and humidity needed to hatch eggs from birds, reptiles, or fish outside the parent. This allows for close observation of embryonic development.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Incubators Are Equal
Choosing an incubator depends entirely on the specific application, as a mismatch can ruin an experiment.
General Purpose vs. CO2 Incubators
A general-purpose incubator simply controls temperature. It is perfect for most bacteriological work but is completely unsuitable for mammalian cell culture, which requires the pH-buffering capability of a CO2 incubator.
Temperature Uniformity and Stability
Cheaper models may have "hot spots" or temperature fluctuations. For sensitive cell lines or quantitative assays, investing in a unit with high uniformity (same temperature everywhere) and stability (minimal fluctuation over time) is critical for reproducible data.
The Risk of Contamination
Because incubators are warm and often humid, they are ideal breeding grounds for unwanted contaminants like mold. Models with high-temperature decontamination cycles and easy-to-clean interiors help mitigate this constant risk. Water pans used for humidity are a common source of contamination if not properly maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right incubator is the one that reliably creates the specific environment your biological system needs.
- If your primary focus is basic microbiology: A simple, reliable general-purpose incubator is often sufficient for routine bacterial or yeast cultures.
- If your primary focus is mammalian cell culture: A CO2 incubator is non-negotiable to maintain the required pH of your growth media.
- If your primary focus is sensitive enzyme assays: Prioritize an incubator with documented high temperature uniformity and stability to ensure your results are consistent.
- If your primary focus is embryology or insect rearing: A model with precise humidity control may be just as important as temperature control.
Ultimately, using an incubator correctly is about precisely recreating the ideal biological conditions for your specific scientific question.
Summary Table:
| Use Case | Key Incubator Requirements |
|---|---|
| Microbial Culture | Precise temperature control |
| Cell Culture | CO2 control for pH stability |
| Enzymatic Assays | High temperature uniformity & stability |
| Plant/Insect Studies | Temperature & humidity control |
| Egg Incubation/Embryology | Precise temperature & humidity control |
Need the right incubator for your specific application? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment, offering a range of incubators from general-purpose to advanced CO2 models. Our experts can help you select the perfect unit to ensure precise temperature control, prevent contamination, and achieve reproducible results in your cell culture, microbiology, or biochemical work. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the carbon footprint of diamond mining? Uncovering the True Environmental and Ethical Cost
- What is the application of spark plasma sintering? Achieve Dense, High-Performance Materials in Minutes
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is the rule of 20 in rotavap? Master Efficient Solvent Evaporation & Recovery
- Are diamonds used in machines? Unlock Superior Performance with Diamond Tools
- What is abnormal grain growth during sintering? Understanding a Key Microstructural Defect
- What are the challenges of biomass utilization for biofuel production? Overcoming Logistical and Technical Hurdles
- How effective is electric heating? Uncover the Truth About Efficiency and Cost


















