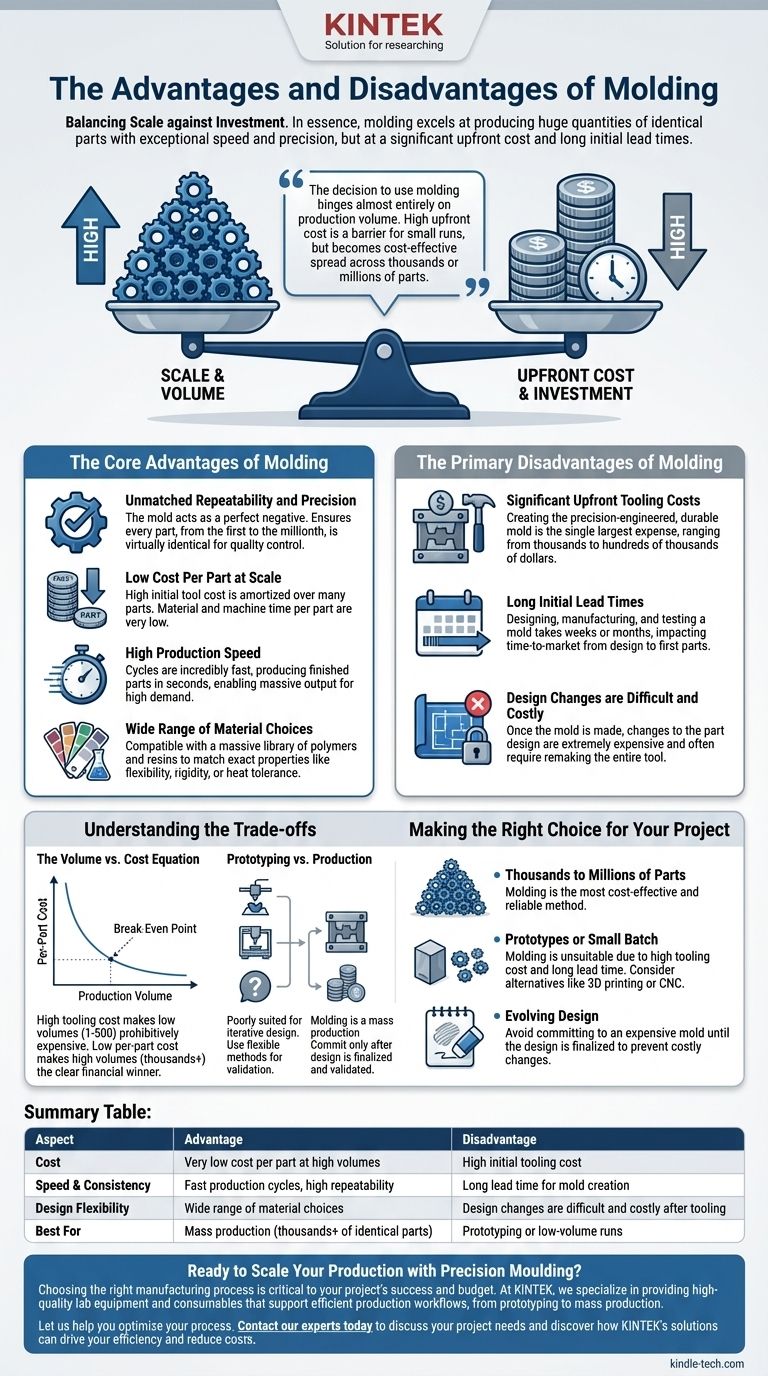
In essence, molding is a process of balancing scale against investment. It excels at producing huge quantities of identical parts with exceptional speed and precision, but this efficiency comes at the price of a significant upfront cost and long initial lead times. The primary advantages are high repeatability, a low cost-per-part at scale, and a vast selection of materials, while the main disadvantages are the high initial tooling costs and the time required to create the mold.
The decision to use molding hinges almost entirely on production volume. The high upfront cost of creating the mold is a major barrier for small runs, but that investment becomes increasingly cost-effective as it is spread across thousands or millions of parts.

The Core Advantages of Molding
Molding, particularly injection molding, is the backbone of modern mass production for a reason. Its benefits are most pronounced when manufacturing at scale.
Unmatched Repeatability and Precision
Once a high-quality mold (the "tool") is created, it acts as a perfect negative of your final part. This ensures that every single unit produced—from the first to the millionth—is virtually identical, which is critical for quality control and product consistency.
Low Cost Per Part at Scale
The most significant cost in molding is the creation of the mold itself. While this initial investment is high, the cost of materials and the automated machine time for each individual part is very low. As you produce more parts, the initial tooling cost is amortized, drastically reducing the effective cost per part.
High Production Speed
Molding cycles are incredibly fast, often taking only a matter of seconds to produce a finished part. This high-speed, automated process allows for massive output in a short amount of time, making it ideal for meeting high consumer demand.
Wide Range of Material Choices
The process is compatible with a massive library of polymers and resins. This allows you to select a material with the exact properties you need, whether it's flexibility, rigidity, impact resistance, UV stability, or heat tolerance.
The Primary Disadvantages of Molding
The drawbacks of molding are concentrated at the very beginning of the production process. These upfront hurdles are significant and must be carefully considered.
Significant Upfront Tooling Costs
Creating the mold is a highly specialized process that requires precision engineering and durable materials like hardened steel. This tooling is the single largest expense and can range from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the part's complexity.
Long Initial Lead Times
Designing, manufacturing, and testing a production-ready mold is not a quick process. The lead time from a finalized design to the first parts coming off the line can take weeks or even months, which can impact your time-to-market.
Design Changes are Difficult and Costly
A mold is a solid piece of metal. Once the steel is cut, making changes to the part design is extremely difficult and expensive. It often requires remaking the mold entirely, making it critical that the design is finalized and thoroughly validated before tooling begins.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a manufacturing process is never about finding a "perfect" solution; it's about understanding which set of trade-offs best aligns with your project's goals.
The Volume vs. Cost Equation
The central trade-off is initial cost vs. per-part cost. For a low number of parts (e.g., 1-500), the high tooling cost makes molding prohibitively expensive. Processes like 3D printing or CNC machining are far more economical here. However, as the required volume enters the thousands, molding's low per-part cost quickly creates a break-even point and becomes the clear financial winner.
Prototyping vs. Production
Molding is a mass production technology. It is poorly suited for the iterative design and testing phases of prototyping. A design flaw discovered after the mold is made is a costly mistake. Use more flexible methods to validate your design first, then commit to molding for the final production run.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Evaluate your project's needs to determine if molding is the appropriate manufacturing path.
- If your primary focus is producing thousands (or millions) of the same part: Molding is almost certainly the most cost-effective and reliable method available.
- If your primary focus is creating a few prototypes or a small batch: The high tooling cost and long lead time make molding unsuitable; consider alternatives like 3D printing or CNC machining.
- If your design is still evolving: Avoid committing to an expensive mold until your design is finalized and validated, as subsequent changes are exceptionally difficult and costly.
By correctly identifying your production volume and design maturity, you can confidently determine if molding is the right tool to bring your product to market.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Very low cost per part at high volumes | High initial tooling cost |
| Speed & Consistency | Fast production cycles, high repeatability | Long lead time for mold creation |
| Design Flexibility | Wide range of material choices | Design changes are difficult and costly after tooling |
| Best For | Mass production (thousands+ of identical parts) | Prototyping or low-volume runs |
Ready to Scale Your Production with Precision Moulding?
Choosing the right manufacturing process is critical to your project's success and budget. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support efficient production workflows, from prototyping to mass production.
Let us help you optimize your process. Whether you're evaluating materials or scaling up, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for exceptional results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your efficiency and reduce costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What are the different types of press machines? Choose the Right Heating Tech for Your Application
- What is the hot press molding method? A Guide to Shaping Materials with Heat & Pressure



















