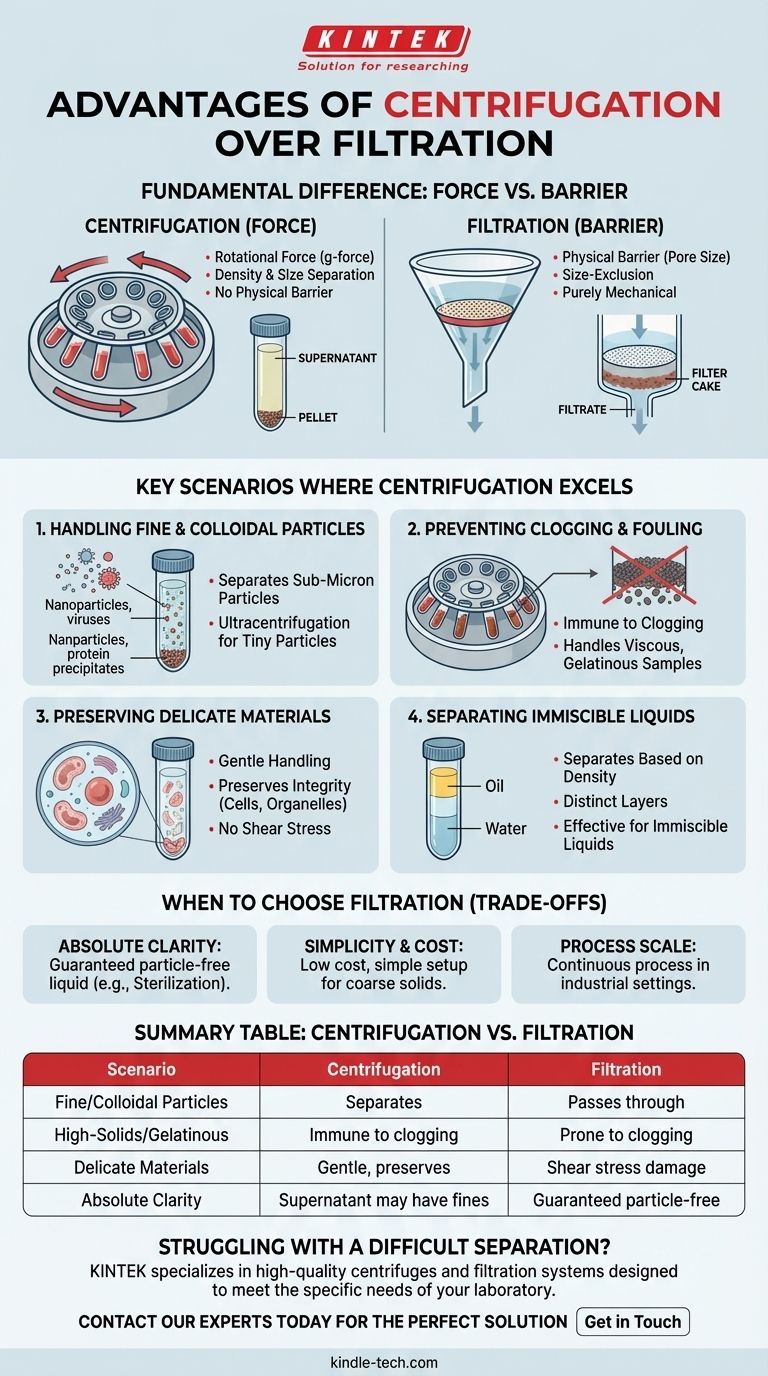
In separation science, the primary advantages of centrifugation over filtration lie in its ability to separate very fine particles that would pass through most filters, its effectiveness with high-solids or gelatinous samples that would cause immediate filter clogging, and its gentle handling of delicate biological materials. It separates components based on density and size using centrifugal force, rather than relying on a physical barrier.
Choosing between centrifugation and filtration is not a matter of one being universally superior. The decision hinges on the physical properties of your mixture—primarily particle size and concentration—and your ultimate goal: a clarified liquid (supernatant) or a collected solid (pellet/retentate).

The Fundamental Difference: Force vs. Barrier
To understand the advantages, you must first grasp the different principles at work. These methods are not interchangeable; they solve different classes of problems.
How Centrifugation Works
Centrifugation subjects a sample to immense rotational force, measured in multiples of gravity (g-force). This force accelerates the natural process of sedimentation.
Denser or larger particles move away from the center of rotation faster than less dense or smaller particles, forming a compact solid (a pellet) at the bottom of the tube. The remaining clarified liquid is called the supernatant.
How Filtration Works
Filtration uses a physical barrier—a filter medium with a defined pore size—to separate solids from a fluid.
Fluid and any particles smaller than the pores pass through to become the filtrate. Particles larger than the pores are retained on the filter, forming a filter cake. It is a purely mechanical size-exclusion process.
Key Scenarios Where Centrifugation Excels
Centrifugation is the superior choice when the physical properties of the mixture make filtration impractical or impossible.
Handling Very Fine or Colloidal Particles
Many separations involve particles that are sub-micron in size, such as nanoparticles, viruses, or protein precipitates. These are too small to be captured by standard filters and will simply pass through into the filtrate.
Centrifugation, especially ultracentrifugation, can generate enough force to pellet these tiny particles, achieving a separation that is impossible with conventional filtration.
Preventing Clogging and Fouling
This is arguably the most common practical advantage. Samples that are viscous, gelatinous, or have a high concentration of solids will instantly clog a filter membrane, halting the process.
Because centrifugation does not rely on a physical pore, it is immune to clogging. It efficiently handles "difficult" samples, like cell lysates or environmental sludges, that would be a nightmare to filter.
Preserving Delicate Materials
The shear forces involved in forcing a liquid through a filter can damage or destroy fragile materials. This is a critical concern when working with whole cells, organelles, or large protein complexes.
A centrifuge can be precisely controlled to gently pellet these materials without lysis or denaturation, preserving their structural and functional integrity for downstream analysis.
Separating Immiscible Liquids
Filtration is completely ineffective for separating two liquids that do not mix, such as oil and water. A centrifuge, however, will rapidly separate them based on their density differences, forming distinct layers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Choose Filtration
Acknowledging the strengths of filtration is key to making an informed decision. Centrifugation is not a universal solution.
The Need for Absolute Clarity
If your goal is a sterilized or completely particle-free liquid, filtration is the definitive choice. A filter with a specific pore size (e.g., 0.22 μm for sterilization) provides an absolute guarantee that no particle larger than that size is present in the filtrate.
A centrifuge's supernatant may appear clear, but it can still contain a small number of the smallest, least dense particles that did not have time to pellet.
Simplicity and Cost
For separating coarse, well-defined solids from a liquid, nothing beats the simplicity and low cost of gravity filtration with filter paper and a funnel.
While centrifuges are standard lab equipment, they represent a significant capital investment and have ongoing maintenance costs, especially high-speed and ultracentrifuge models.
Process Scale and Throughput
Filtration can be easily configured as a continuous process, which is highly advantageous in industrial settings where large volumes must be processed consistently.
Most centrifugation is a batch process. You must load the rotor, run the cycle, unload the samples, and repeat. While continuous-flow centrifuges exist, they are complex and expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sample
Your decision should be driven by your sample's characteristics and your final objective.
- If your primary focus is clarifying a liquid with very fine particles or avoiding clogs: Choose centrifugation for its ability to handle challenging samples without fouling.
- If your primary focus is achieving a guaranteed particle-free liquid: Choose filtration with a membrane of the appropriate absolute pore size.
- If your primary focus is gently harvesting intact cells or organelles: Choose centrifugation to avoid shear stress and preserve sample integrity.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost separation of coarse solids: Choose filtration for its operational simplicity and minimal equipment cost.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific separation challenge.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Centrifugation Advantage | Filtration Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Fine/Colloidal Particles | Separates sub-micron particles | Particles pass through standard filters |
| High-Solids/Gelatinous Samples | Immune to clogging | Prone to immediate membrane clogging |
| Delicate Biological Materials | Gentle, preserves integrity | Shear stress can cause damage |
| Absolute Clarity/Sterility | Supernatant may contain fines | Guaranteed particle-free filtrate |
| Operational Simplicity/Cost | Requires significant equipment | Simple, low-cost for coarse solids |
Struggling with a difficult separation? The right lab equipment is crucial for your results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality centrifuges and filtration systems designed to meet the specific needs of your laboratory.
Whether you're processing viscous samples, harvesting delicate cells, or require absolute sterility, we can help you select the ideal equipment for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your separation challenges and find the perfect solution: Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a hydraulic press with heating plates in copper welding tests? Analyze Stress & Thermal Cycles
- What is a hydraulic hot press? Unlock the Power of Heat and Pressure for Advanced Materials
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for LGVO synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Solid Electrolytes
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing



















