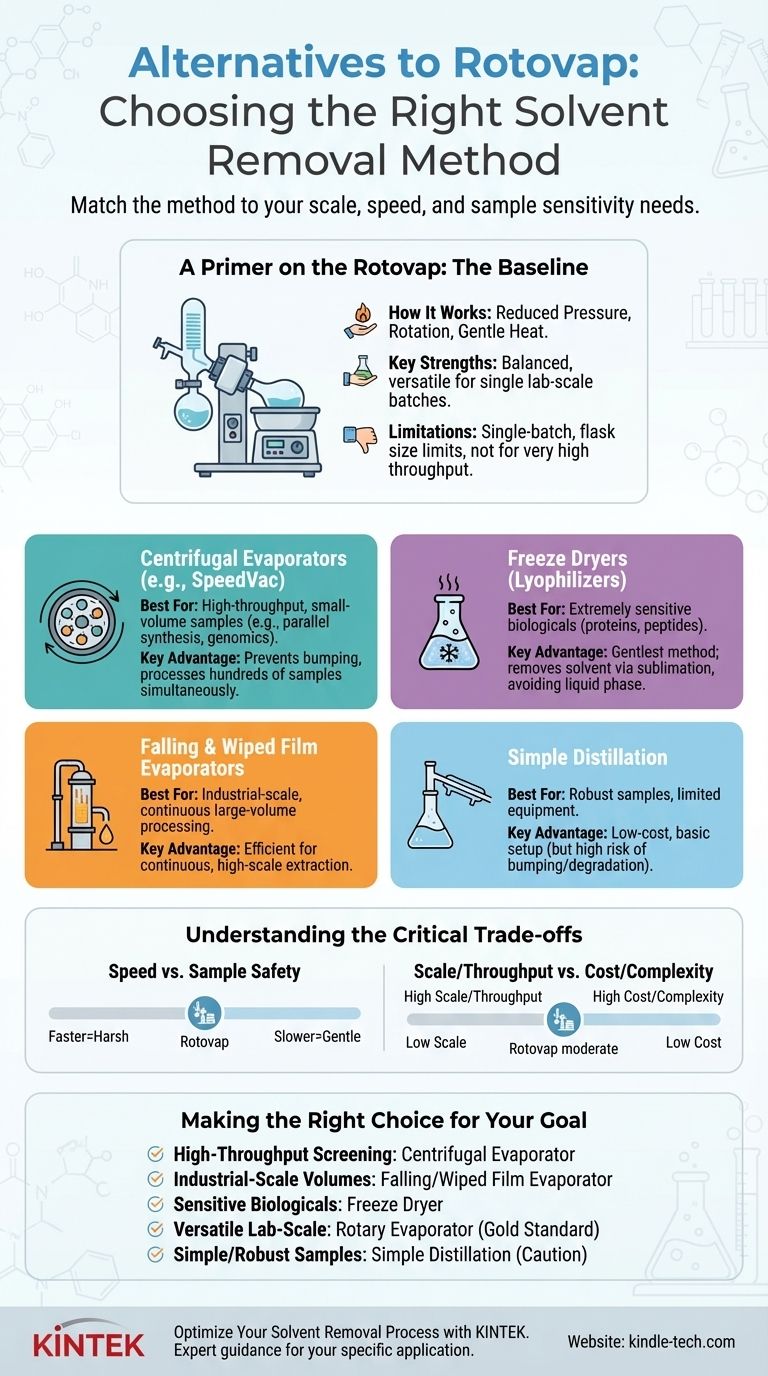
The primary alternatives to a rotary evaporator are centrifugal evaporators (like a SpeedVac or Genevac), freeze dryers (lyophilizers), and large-scale systems like falling or wiped film evaporators. For simpler, less sensitive applications, basic distillation setups can also be used. Each method is designed to solve a specific problem related to sample volume, throughput, sensitivity, or solvent properties.
The most effective alternative to a rotovap depends entirely on your core objective. The central challenge isn't simply removing a solvent, but doing so under the right conditions of scale, speed, and gentleness for your specific sample and workflow.

A Primer on the Rotovap: The Baseline for Comparison
To understand the alternatives, we must first establish the role of the rotary evaporator, or "rotovap." It is the most common workhorse for solvent removal in synthetic chemistry labs for good reason.
How It Works
A rotovap combines three key principles:
- Reduced Pressure (Vacuum): Lowering the pressure above a liquid reduces its boiling point, allowing for evaporation at a lower, less damaging temperature.
- Rotation: Spinning the flask spreads the sample into a thin film on the inner surface. This dramatically increases the surface area for evaporation and prevents violent boiling, or "bumping."
- Gentle Heat: A water or oil bath provides controlled, uniform energy to facilitate the evaporation process.
Key Strengths
The rotovap is popular because it offers a balanced, versatile solution for single-batch solvent removal on a typical lab scale (from a few milliliters to several liters). It provides good control over temperature and pressure, protecting most moderately sensitive compounds.
Key Limitations
The rotovap is not a universal solution. Its design creates bottlenecks that alternatives are designed to address, such as being a single-batch process, having limits on flask size, and being less efficient for very high-boiling point solvents or high-throughput applications.
Exploring the Alternatives: Method by Method
Each alternative method excels where the rotovap falls short, targeting a specific need for scale, sensitivity, or throughput.
Centrifugal Evaporators (e.g., SpeedVac, Genevac)
This is the go-to alternative for high-throughput and small-volume work. It places samples in vials or microtiter plates inside a rotor, which is then spun under vacuum with controlled heat.
The centrifugal force pins the liquid to the bottom of the container, preventing any bumping or cross-contamination, even when hundreds of samples are boiling simultaneously. It is ideal for parallel synthesis, genomics, and proteomics labs.
Freeze Dryers (Lyophilizers)
This is the gentlest method available, reserved for extremely sensitive materials, especially biologicals like proteins, peptides, or microorganisms.
The process involves first freezing the sample solid. A deep vacuum is then applied, causing the frozen solvent (usually water) to turn directly into a gas in a process called sublimation. This completely avoids the liquid phase and any thermal stress, resulting in a fine, stable, and easily re-dissolved powder.
Falling and Wiped Film Evaporators
These are industrial-scale solutions designed for continuous, large-volume processing. Instead of a rotating flask, the liquid is introduced at the top of a heated vertical column.
It flows down the inner walls as a very thin film, causing near-instantaneous evaporation. A "wiped film" system uses rotating blades to constantly spread the liquid, making it even more efficient. These are common in chemical manufacturing and large-scale extraction.
Simple Distillation
This is the most basic alternative, often used when equipment is limited or the sample is very robust. It involves simply heating a flask containing the solution, possibly under a slight vacuum from a water aspirator.
While simple and cheap, it offers poor control. There is a high risk of bumping, and localized overheating can easily decompose temperature-sensitive compounds. It is only suitable for high-boiling solutes and low-boiling, non-flammable solvents.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing your evaporation method is a balancing act. No single method is the "best"; it is always a matter of compromises based on your priorities.
Speed vs. Sample Safety
Faster evaporation requires more energy (heat), which increases the risk of thermal degradation. A falling film evaporator is incredibly fast but harsh. A freeze dryer is exceptionally gentle but can take many hours or even days. The rotovap sits in the middle of this spectrum.
Scale and Throughput
The physical design of the equipment dictates its capacity. A centrifugal evaporator is built for high throughput (many small samples). A falling film evaporator is for high scale (one massive batch). A rotovap is designed for single, medium-sized batches.
Cost and Complexity
A simple distillation setup costs very little. A rotovap represents a moderate capital investment for a lab. Centrifugal evaporators, freeze dryers, and especially industrial-scale evaporators are significantly more expensive and complex to operate and maintain.
Solvent Properties
Your choice of solvent is a critical factor. Freeze drying is most effective for solvents with a high freezing point, like water or benzene. Removing very high-boiling point solvents like DMSO or DMF efficiently requires deep vacuum and often higher heat, which may favor systems like a centrifugal evaporator that also prevent bumping under these aggressive conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct instrument begins with identifying your single most important constraint or goal.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening of many small samples: A centrifugal evaporator is the superior choice for its parallel processing capability.
- If you are working with large, industrial-scale volumes: A falling or wiped film evaporator provides the necessary continuous processing power.
- If you must preserve the structure of a highly sensitive biological sample: A freeze dryer (lyophilizer) is the only method that guarantees maximum gentleness through sublimation.
- If you have a simple, robust sample and very limited equipment: Simple distillation can work, but proceed with caution and awareness of the risks.
- If you need a versatile, all-around tool for typical lab-scale synthesis: The rotary evaporator remains the gold standard for its excellent balance of control, efficiency, and flexibility.
By matching the evaporation technique to your specific constraints, you ensure efficient solvent removal while protecting the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Alternative Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Evaporator | High-throughput, small-volume samples | Prevents bumping, processes many samples in parallel |
| Freeze Dryer (Lyophilizer) | Extremely sensitive biological samples | Gentlest method; removes solvent via sublimation |
| Falling/Wiped Film Evaporator | Industrial-scale, continuous processing | Handles large volumes efficiently |
| Simple Distillation | Robust samples, limited equipment | Low-cost, simple setup |
Optimize Your Solvent Removal Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right evaporation technology is critical for the efficiency and integrity of your work. Whether your lab requires the high-throughput capability of a centrifugal evaporator, the gentle processing of a freeze dryer, or the robust power of an industrial-scale system, KINTEK has the solution.
We provide expert guidance and reliable equipment to help you:
- Increase throughput without compromising sample safety.
- Scale up your processes efficiently and effectively.
- Protect sensitive materials with the gentlest available techniques.
Let our specialists help you select the perfect instrument for your specific application and budget.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our lab equipment can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the freeze drying or lyophilisation process? A Guide to Gentle, High-Quality Dehydration
- Why is freeze drying important for certain chemical products? Preserve Integrity & Extend Shelf Life
- What is the purpose of laboratory freeze drying? Preserve Sensitive Drugs & Biologics for Stability
- What are the key steps in the freeze drying process? A Guide to Mastering Sublimation
- Why is freeze drying a good method for preserving fruits and vegetables? Unlock Superior Food Preservation



















