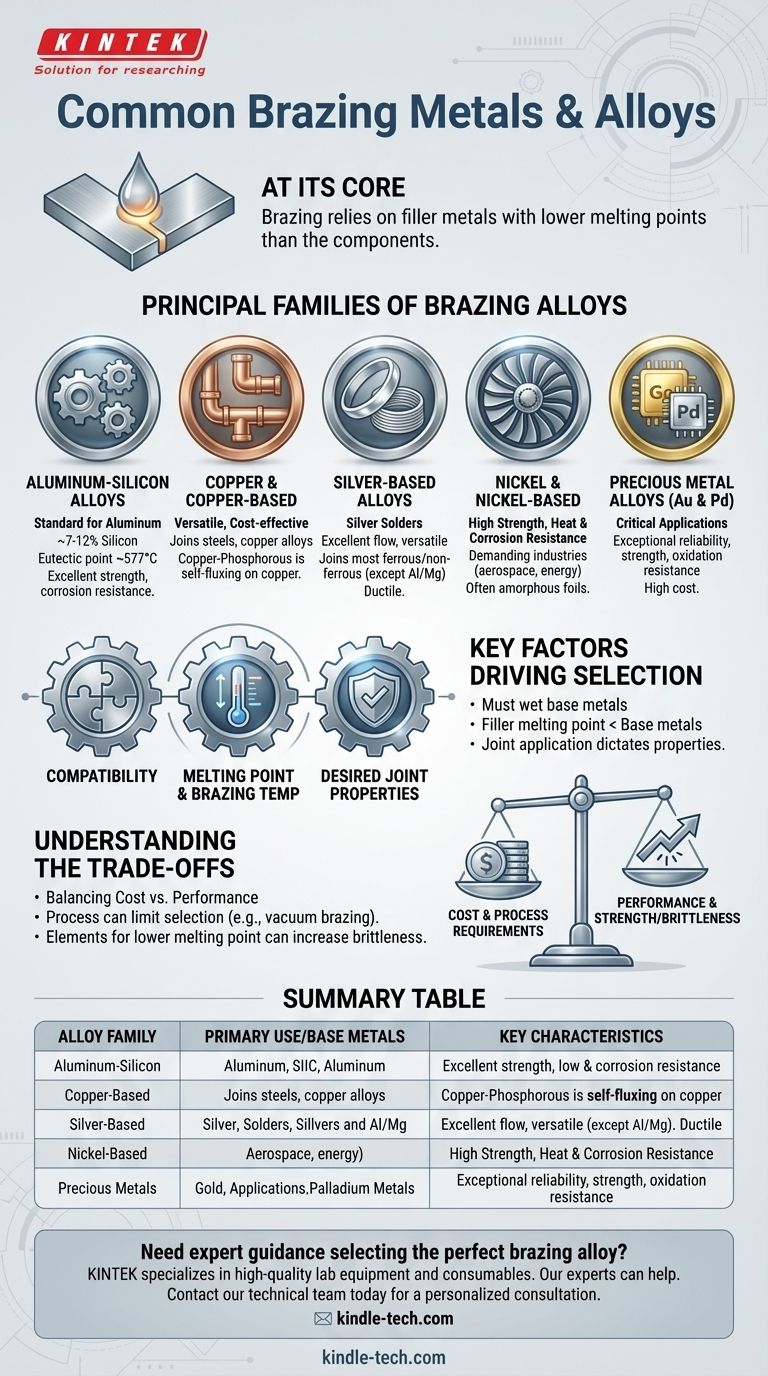
At its core, brazing relies on a select group of filler metals designed to melt at a lower temperature than the components they join. The most common families of these alloys are based on aluminum-silicon, copper, silver, nickel, and precious metals like gold and palladium, each chosen for specific properties and applications.
The selection of a brazing alloy is a critical engineering decision, not a simple choice of material. It is dictated by the base metals being joined, the required service temperature and strength of the final joint, and the specific brazing process being used.

The Principal Families of Brazing Alloys
Brazing filler metals are categorized into families based on their primary elemental composition. Each family offers a unique combination of melting point, strength, and compatibility with different base materials.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
These are the standard for brazing aluminum components. Most alloys in this family contain between 7% and 12% silicon, which significantly lowers the melting point.
The Al-Si system with 11.7% silicon is a eutectic alloy, meaning it has a single, sharp melting point of 577°C. This makes it ideal for brazing many aluminum alloys with higher melting points. These fillers provide excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and a good color match with the parent material.
Copper and Copper-Based Alloys
This broad category includes pure copper, copper-silver, copper-zinc (brass), copper-tin (bronze), and copper-phosphorous alloys.
Due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness, they are widely used for joining steels, copper, and copper alloys. Copper-phosphorous alloys are particularly useful for joining copper to copper without the need for a separate flux.
Silver-Based Alloys
Commonly known as "silver solders," these alloys offer a range of melting temperatures and excellent flow characteristics.
They are extremely versatile and capable of joining most ferrous and non-ferrous metals, with the notable exception of aluminum and magnesium. Their ductility makes them suitable for joints that will experience vibration or thermal cycling.
Nickel and Nickel-Based Alloys
When high strength and superior resistance to heat and corrosion are required, nickel alloys are the preferred choice.
These fillers are essential in demanding industries like aerospace and energy for applications such as turbine blade assembly. They are often supplied as amorphous foils containing elements like boron, silicon, and phosphorus to lower their melting point.
Precious Metal Alloys (Gold & Palladium)
Alloys based on gold and palladium are reserved for the most critical applications where performance and reliability are paramount.
While expensive, their exceptional strength, ductility, and resistance to oxidation make them indispensable for high-reliability electronic components, medical implants, and aerospace systems.
Key Factors Driving Alloy Selection
Choosing the correct filler metal involves a careful analysis of the entire engineering system. Three primary factors guide the decision.
Compatibility with Base Metals
The filler metal must be metallurgically compatible with the base metals. It needs to wet and flow across their surfaces to create a continuous, strong bond without eroding or detrimentally alloying with the parent material.
Melting Point and Brazing Temperature
A fundamental rule of brazing is that the filler metal's melting point must be significantly lower than that of the base metals. The brazing temperature is always set above the filler's melting point but below the base metals' melting point.
Desired Joint Properties
The final application dictates the required properties of the joint. This includes mechanical strength, ductility (the ability to deform without fracturing), corrosion resistance, thermal and electrical conductivity, and even aesthetics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every filler metal choice involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these compromises is the mark of a sound technical decision.
Cost vs. Performance
The most significant trade-off is often between cost and performance. Copper-based alloys are economical for many general-purpose applications, while nickel and precious metal alloys provide superior performance at a much higher material cost.
Process Requirements
The brazing process itself can limit alloy selection. For example, in vacuum brazing, alloys containing volatile elements like zinc or cadmium are generally avoided as they can vaporize and disrupt the process.
Strength vs. Brittleness
Some elements added to lower an alloy's melting point, such as phosphorus or boron, can form brittle phases in the final joint. This can increase strength but reduce ductility, making the joint more susceptible to failure under impact or vibration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the appropriate alloy, begin with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum components: Aluminum-silicon alloys are the industry standard and your most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose joining of steels or copper: Start by evaluating cost-effective copper-based alloys or versatile silver-based alloys.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance: Nickel-based alloys are engineered specifically for these demanding environments.
- If your primary focus is absolute reliability in a critical system: Precious metal alloys based on gold or palladium provide the highest performance, justifying their cost.
Ultimately, selecting the correct brazing alloy is the foundational step in creating a strong, reliable, and durable joint.
Summary Table:
| Alloy Family | Primary Use/Base Metals | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum-Silicon | Aluminum components | Excellent strength & corrosion resistance, melts at ~577°C |
| Copper-Based | Steels, copper alloys | Cost-effective, versatile, some are self-fluxing on copper |
| Silver-Based | Most ferrous & non-ferrous metals (except Al/Mg) | Excellent flow, ductile, good for thermal cycling |
| Nickel-Based | High-temp & corrosive environments | Superior strength, heat & corrosion resistance |
| Precious Metals | Critical applications (aerospace, medical) | Exceptional reliability, strength, and oxidation resistance |
Need expert guidance selecting the perfect brazing alloy for your specific materials and performance requirements?
The right filler metal is critical for joint strength, durability, and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material joining processes. Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of alloy selection to ensure optimal results for your laboratory or production needs.
Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the considerations for autoclave? Ensure Sterilization Success and Safety
- What are the requirements for an autoclave machine? Achieve Sterile Confidence for Your Lab
- What is the temperature effective for sterilization using autoclave? Achieve Sterile Conditions for Your Lab
- Which factors contribute to successful sterilization using an autoclave? Master the 3 Keys to Sterility
- What are the 4 principles of autoclave? Master Steam Sterilization for Your Lab















