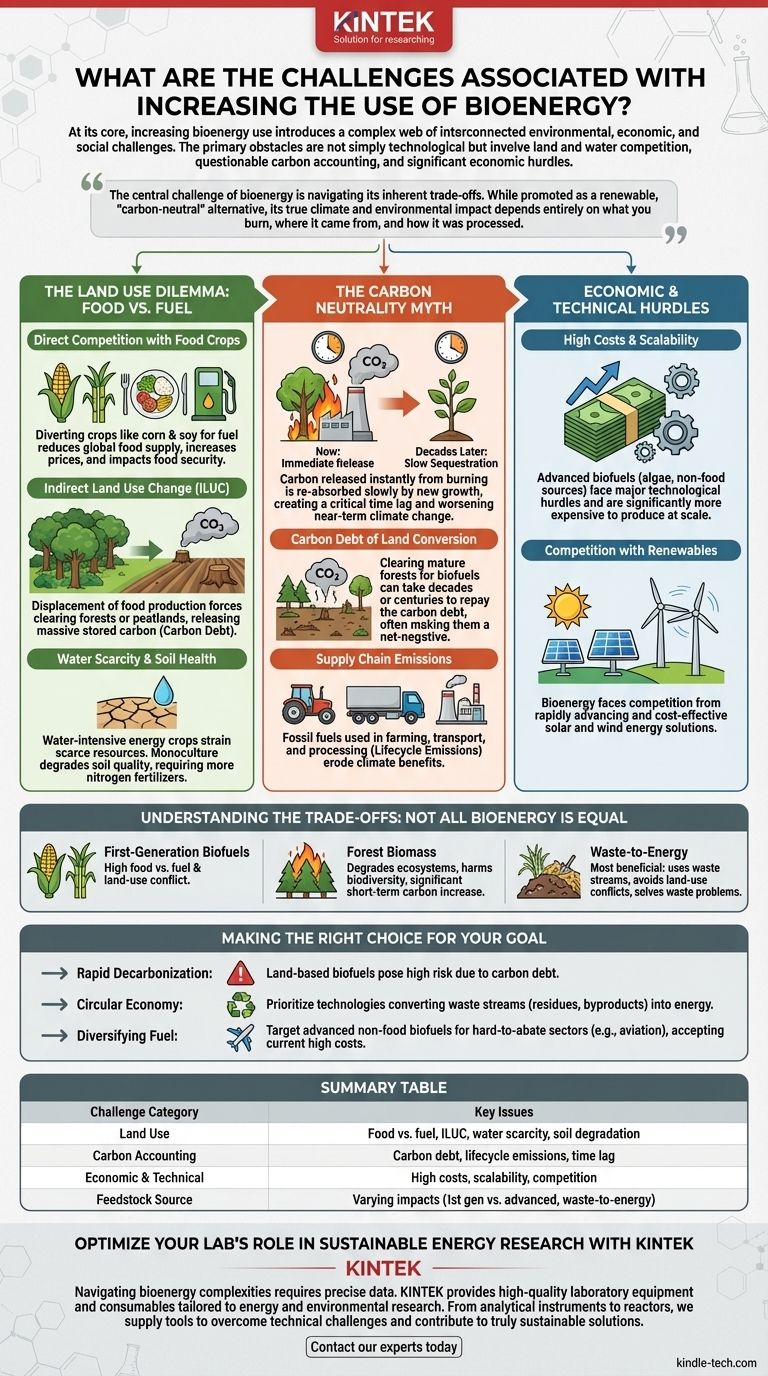
At its core, increasing the use of bioenergy introduces a complex web of interconnected challenges that span environmental, economic, and social domains. The primary obstacles are not simply technological; they involve intense competition for land and water, questionable carbon accounting, and significant economic hurdles that challenge its scalability as a global energy solution.
The central challenge of bioenergy is navigating its inherent trade-offs. While promoted as a renewable, "carbon-neutral" alternative, its true climate and environmental impact depends entirely on what you burn, where it came from, and how it was processed.

The Land Use Dilemma: Food vs. Fuel
The most significant and immediate challenge of scaling up bioenergy is its demand for land. This creates direct and indirect consequences for global food systems and natural ecosystems.
Direct Competition with Food Crops
First-generation biofuels are derived directly from food crops like corn, sugarcane, and soy.
Diverting these crops to produce fuel directly reduces the global food supply, putting upward pressure on food prices and impacting food security, particularly in developing nations.
Indirect Land Use Change (ILUC)
This is a more subtle but critically important effect. When existing agricultural land is converted to grow energy crops, the food production that once happened there is displaced.
This displacement often forces farmers to clear forests, grasslands, or peatlands to create new farmland. This conversion releases massive amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere, often creating a "carbon debt" that the biofuel may never repay.
Water Scarcity and Soil Health
Cultivating energy crops is a water-intensive process. In many regions, this places an additional strain on already scarce freshwater resources, competing with water for drinking and traditional agriculture.
Intensive monoculture farming of energy crops can also degrade soil quality over time, requiring increased use of nitrogen fertilizers, which have their own significant carbon footprint and can pollute waterways.
The Carbon Neutrality Myth
The popular claim that bioenergy is "carbon neutral" is a dangerous oversimplification. This idea assumes that the carbon released when biomass is burned is perfectly balanced by the carbon absorbed by new plant growth. The reality is far more complex.
The "Carbon Debt" of Land Conversion
As mentioned, ILUC is the single biggest factor undermining bioenergy's climate benefits. Clearing a mature forest to plant switchgrass for biofuel releases centuries of stored carbon instantly.
It can take decades, or even over a century, for the "carbon savings" from the biofuel to pay back this initial carbon debt. In the short-term window we have to fight climate change, this makes many biofuels a net-negative for the climate.
Supply Chain Emissions
The entire bioenergy lifecycle consumes energy. Fossil fuels are often used to power farm machinery, produce fertilizers, transport the biomass to a processing facility, and refine it into a usable fuel.
These "lifecycle emissions" are frequently underestimated and can significantly erode any potential climate benefits.
The Time Lag of Sequestration
When a tree is cut down and burned for energy in a power plant, its stored carbon is released into the atmosphere immediately.
While a new tree can be planted to re-absorb that CO2, this process takes many decades. This timing mismatch is critical; we are adding carbon to the atmosphere now with only a promise of removing it much later, worsening near-term climate change.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Bioenergy is Equal
It is a mistake to treat all forms of bioenergy as a single category. The source of the biomass is the single most important factor in determining whether it is a net benefit or a net harm.
First-Generation vs. Advanced Biofuels
First-generation biofuels, derived from food crops like corn ethanol, present the most severe conflicts with food security and land use.
Advanced biofuels, derived from non-food sources like algae, jatropha, switchgrass, or agricultural waste, hold more promise. However, they currently face major technological hurdles and are far more expensive to produce at scale.
The Problem with Forest Biomass
Burning wood pellets, often from whole trees, is one of the most controversial forms of bioenergy. While technically renewable, large-scale harvesting can degrade forest ecosystems, harm biodiversity, and result in a significant short-term increase in atmospheric carbon.
Classifying forest biomass as a zero-carbon fuel source is a flawed accounting method that ignores the decades-long carbon sequestration cycle of a forest.
The Promise of Waste-to-Energy
The most beneficial and least controversial form of bioenergy comes from using genuine waste streams.
This includes converting agricultural residues (corn stover, wheat straw), municipal solid waste, and landfill gas into energy. This approach avoids land-use conflicts, solves a waste management problem, and provides a reliable energy source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to invest in or support bioenergy must be based on a clear understanding of its different forms and the specific goal you aim to achieve.
- If your primary focus is rapid, large-scale decarbonization: Relying heavily on land-based biofuels is a high-risk strategy that could be counterproductive due to the carbon debt from land use change.
- If your primary focus is creating a circular economy: Prioritize investments in technologies that convert true waste streams—agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and municipal solid waste—into valuable energy.
- If your primary focus is diversifying fuel for specific sectors: Target advanced, non-food biofuels for hard-to-abate sectors like aviation, but remain realistic about their current high costs and technological immaturity.
Ultimately, the value of bioenergy lies not in its potential for massive scale, but in its strategic and careful application to solve specific problems within a diversified energy portfolio.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Land Use | Food vs. fuel competition, Indirect Land Use Change (ILUC), water scarcity, soil degradation |
| Carbon Accounting | Carbon debt from land conversion, lifecycle emissions, time lag in carbon sequestration |
| Economic & Technical | High costs of advanced biofuels, scalability issues, competition with other renewables |
| Feedstock Source | Varying impacts of first-generation vs. advanced biofuels and waste-to-energy systems |
Optimize Your Lab's Role in Sustainable Energy Research with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of bioenergy requires precise and reliable data. Whether you're analyzing feedstock composition, testing conversion processes, or monitoring emissions, the right lab equipment is critical for accurate, reproducible results.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to energy and environmental research. From analytical instruments for biomass characterization to reactors for biofuel synthesis, we supply the tools you need to overcome the technical challenges outlined in this article and contribute to truly sustainable bioenergy solutions.
Let us equip your lab for success. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific research goals and help you make informed decisions in the bioenergy landscape.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions


