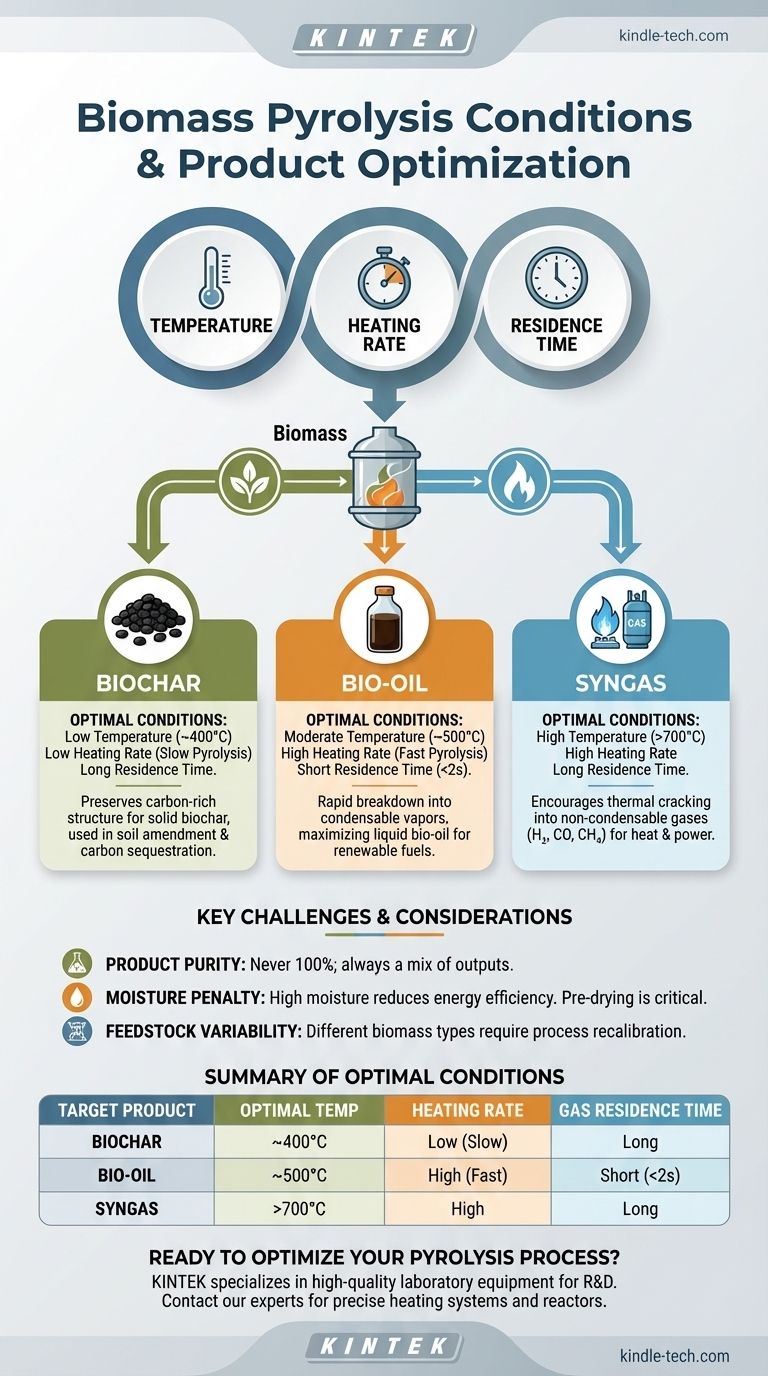
The essential conditions for biomass pyrolysis are the controlled variables that determine the final product. Primarily, these are temperature, heating rate, and the residence time of gases in the reactor. By precisely manipulating these three factors, you can steer the process to maximize the output of either solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible syngas.
Biomass pyrolysis is not a single, fixed process but a highly tunable technology. The key is to understand that you are not just running a reaction; you are deliberately choosing specific operating conditions to optimize the yield of your desired end-product, whether it's a stable solid, a liquid fuel, or a combustible gas.

The Core Variables Controlling Pyrolysis Outcomes
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material in the absence of oxygen. The "recipe" you use—the specific conditions inside the reactor—directly dictates what you create.
Temperature: The Primary Driver of Product Type
Temperature is the most critical factor. Different temperature ranges favor the formation of different products.
At low temperatures (around 400-500°C), the decomposition process is slow and incomplete. This environment preserves the carbon-rich solid structure, maximizing the yield of biochar.
At moderate temperatures (around 500-650°C), the biomass breaks down rapidly into smaller, condensable vapors. This is the optimal range for producing liquid bio-oil.
At high temperatures (above 700°C), the organic vapors produced during pyrolysis undergo further thermal cracking, breaking down into the simplest, non-condensable gas molecules like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This maximizes the yield of syngas.
Heating Rate: The Speed of Transformation
The rate at which the biomass is heated is nearly as important as the final temperature.
A low heating rate (slow pyrolysis) allows the biomass to heat gradually. This process favors the formation of stable biochar as volatile components are slowly driven off.
A high heating rate (fast pyrolysis) subjects the biomass to rapid thermal shock. This cracks the material quickly into vapors before they can form char, which is ideal for maximizing bio-oil production.
Gas Residence Time: How Long Vapors Remain Hot
This refers to the amount of time the hot vapors and gases stay within the heated reactor zone before being cooled or removed.
A short residence time (typically <2 seconds) is crucial for bio-oil production. Vapors are removed and cooled (quenched) quickly, preventing them from breaking down further into gas.
A long residence time gives the vapors more time at high temperatures. This encourages secondary reactions and thermal cracking, which converts condensable bio-oil vapors into non-condensable syngas.
Feedstock Characteristics: The Starting Material Matters
The type and condition of the biomass itself are foundational conditions. Key factors include its chemical composition (lignin, cellulose) and, most importantly, its moisture content.
High moisture content requires significant energy input just to evaporate the water before pyrolysis can even begin, reducing the overall efficiency of the process. Pre-drying the feedstock is a critical step for optimal performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Realities
No pyrolysis process is perfect. You are always managing a balance between competing reactions and products.
Product Purity is a Myth
You will never produce 100% of a single product. The goal is to create conditions that heavily favor one output over the others.
Running a system for maximum bio-oil will still produce some biochar and syngas. These are often used internally to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction itself, improving the system's energy balance.
The Moisture Content Penalty
High moisture is the enemy of efficient pyrolysis. Every percentage point of water in your feedstock must be boiled off, consuming valuable energy that could have been used for the pyrolysis reaction.
This reality makes feedstock sourcing and pre-treatment a critical operational consideration for any commercial-scale pyrolysis plant.
Feedstock Variability
Different types of biomass, from wood chips and corn stalks to sewage sludge, will behave differently even under identical conditions due to their unique chemical makeup.
Optimizing a process for one type of feedstock may require adjustments and re-calibration when switching to another.
Optimizing Conditions for Your Specific Goal
Your operational strategy must be driven by your end-product goal. The conditions are not "one size fits all" but are levers to be pulled to achieve a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar (for carbon sequestration or soil amendment): Use slow pyrolysis with low temperatures (around 400°C) and low heating rates.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil (for renewable fuel): Use fast pyrolysis with moderate temperatures (around 500°C), very high heating rates, and short gas residence times.
- If your primary focus is generating syngas (for heat and power): Use high temperatures (>700°C) and long gas residence times to encourage complete thermal cracking of the biomass and its vapors.
By mastering these conditions, you transform biomass pyrolysis from a simple reaction into a precise tool for creating valuable, sustainable products.
Summary Table:
| Target Product | Optimal Temperature | Heating Rate | Gas Residence Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar | ~400°C | Low (Slow Pyrolysis) | Long |
| Bio-Oil | ~500°C | High (Fast Pyrolysis) | Short (<2 seconds) |
| Syngas | >700°C | High | Long |
Ready to design or optimize your biomass pyrolysis process?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables for research and development. Whether you are developing new biochar soil amendments, optimizing bio-oil yields for renewable fuel, or scaling up syngas production, our precise heating systems and reactors can help you achieve reliable, repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific lab's needs. Let's turn your biomass into valuable products together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















