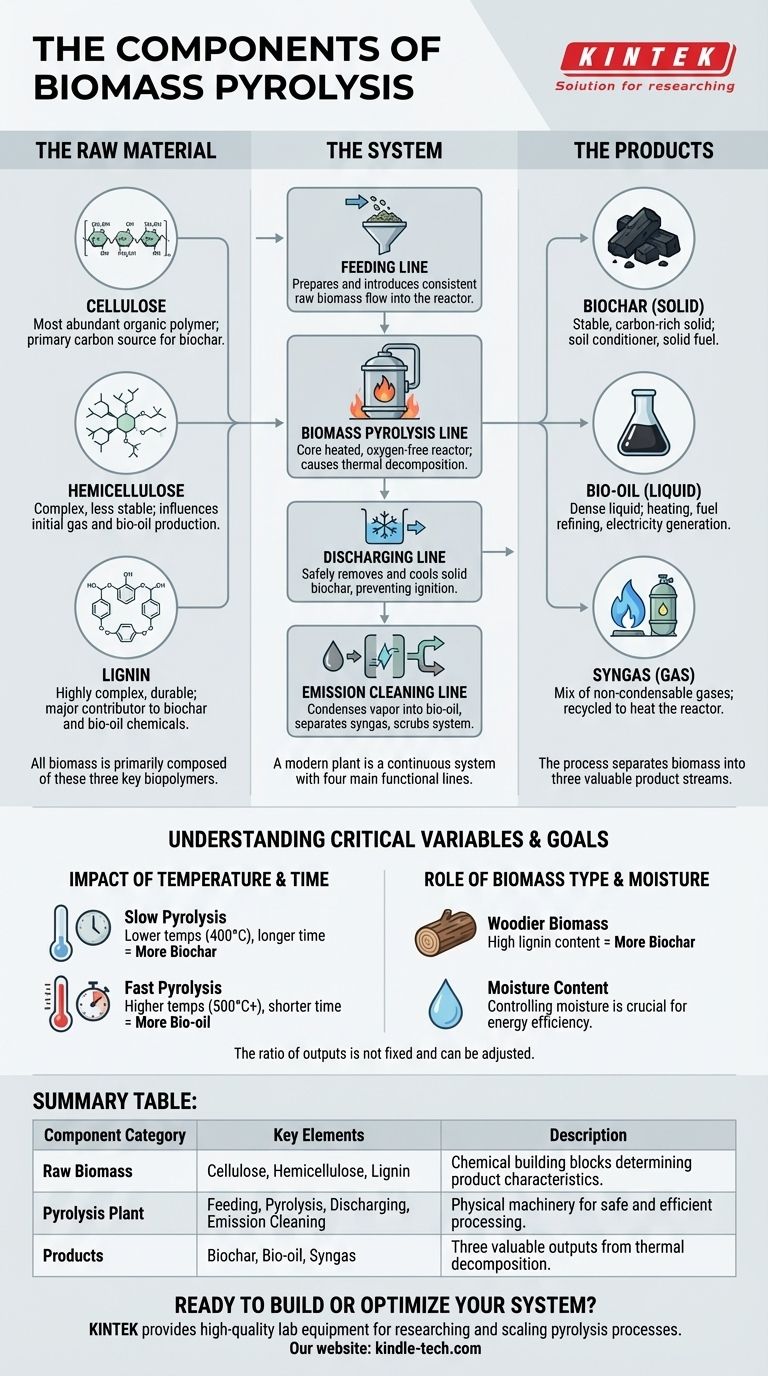
Understanding the components of biomass pyrolysis requires looking at the process from three distinct angles. The term "components" can refer to the chemical makeup of the raw biomass itself (cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin), the physical machinery of a pyrolysis plant (feeding, pyrolysis, and discharge systems), or the valuable products created by the process (biochar, bio-oil, and syngas). Each perspective is critical to understanding the system as a whole.
Biomass pyrolysis is best understood not as a single action, but as a complete system. It transforms the core chemical components of organic matter within a structured industrial plant to create a predictable set of valuable outputs.

The Raw Material: What Biomass is Made Of
The characteristics of the final products are determined by the chemical composition of the initial feedstock. All biomass is primarily composed of three key biopolymers.
Cellulose
Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, forming the main structural component of plant cell walls. Its long, stable chains are a primary source of carbon for creating biochar.
Hemicellulose
Hemicellulose is a more complex and less stable polymer that binds cellulose fibers together. It breaks down at lower temperatures than cellulose, influencing the initial production of gases and bio-oil.
Lignin
Lignin is a highly complex aromatic polymer that provides rigidity and durability to plant cell walls, essentially acting as a glue. It is the most difficult component to break down and is a major contributor to the final yield of biochar and certain chemicals in bio-oil.
The System: How a Pyrolysis Plant is Structured
A modern biomass pyrolysis plant is a continuous system engineered with four main functional lines to manage the material flow from input to output safely and efficiently.
The Feeding Line
This is the intake system where raw biomass is prepared and introduced into the reactor. It must be designed to handle various forms of feedstock, from wood chips and rice husks to sewage sludge, ensuring a consistent flow into the pyrolysis chamber.
The Biomass Pyrolysis Line
This is the core of the plant, containing the heated, oxygen-free reactor. Here, the biomass is subjected to high temperatures, causing it to thermally decompose into solids, liquids, and gases without combustion.
The Discharging Line
This system safely removes the solid product, biochar, from the reactor. It often involves a water-cooling mechanism to prevent the hot char from igniting upon contact with oxygen in the air.
The Emission Cleaning Line
This crucial line processes the outputs. It condenses the hot vapor into liquid bio-oil and wood vinegar, separates the non-condensable syngas, and scrubs the system to ensure environmental compliance. The collected syngas is often recycled to heat the pyrolysis reactor, making the process more energy-efficient.
The Products: What Pyrolysis Creates
The process systematically separates the biomass into three valuable product streams: one solid, one liquid, and one gas.
Biochar (The Solid Component)
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after pyrolysis. It is an exceptional soil conditioner that improves water retention and nutrient availability. It can also be used as a solid fuel or a base material for activated carbon.
Bio-oil (The Liquid Component)
Also known as pyrolysis oil or tar, this is a dense liquid created by cooling and condensing the pyrolysis vapors. It can be used directly for heating, refined into transportation fuels and specialty chemicals, or used to generate electricity.
Syngas (The Gaseous Component)
This is a mix of non-condensable gases, primarily carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane. While it can be collected, its most common use is to be immediately cycled back to provide the heat that drives the pyrolysis reaction, creating a self-sustaining energy loop.
Understanding the Critical Variables
The ratio of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas is not fixed. It is determined by several key operational factors that can be adjusted to target specific outcomes.
Impact of Temperature and Time
The temperature inside the reactor and the residence time of the biomass are the most critical factors.
- Slow Pyrolysis: Lower temperatures (around 400°C) and longer residence times favor the production of biochar.
- Fast Pyrolysis: Higher temperatures (over 500°C) and very short residence times (a few seconds) maximize the yield of bio-oil.
Role of Biomass Type and Moisture
The feedstock's composition directly impacts the output. Woodier biomass with high lignin content will generally produce more biochar. The moisture content must also be controlled, as evaporating water consumes significant energy and reduces overall efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding these components, you can tune the pyrolysis process to meet specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment: Prioritize slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures and use a feedstock with high lignin content, like wood or nut shells.
- If your primary focus is generating bio-oil for fuel: Implement a fast pyrolysis system with high temperatures and rapid quenching of vapors, using feedstocks like agricultural residues.
- If your primary focus is waste management and energy self-sufficiency: Design a robust system that can handle diverse, moist inputs and efficiently recycles syngas to power the plant.
Ultimately, mastering biomass pyrolysis means seeing it as an integrated system where the material, the machinery, and the process variables all work together to produce your desired result.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Biomass | Cellulose, Hemicellulose, Lignin | The chemical building blocks that determine the final product characteristics. |
| Pyrolysis Plant | Feeding, Pyrolysis, Discharging, Emission Cleaning Lines | The physical machinery that safely and efficiently processes the biomass. |
| Products | Biochar (Solid), Bio-oil (Liquid), Syngas (Gas) | The three valuable outputs created by the thermal decomposition process. |
Ready to build or optimize your biomass pyrolysis system?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for researching and scaling pyrolysis processes. Whether you are developing new feedstocks, optimizing product yields, or ensuring process efficiency, our reliable equipment is designed to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific biomass conversion goals with precision equipment and expert consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















