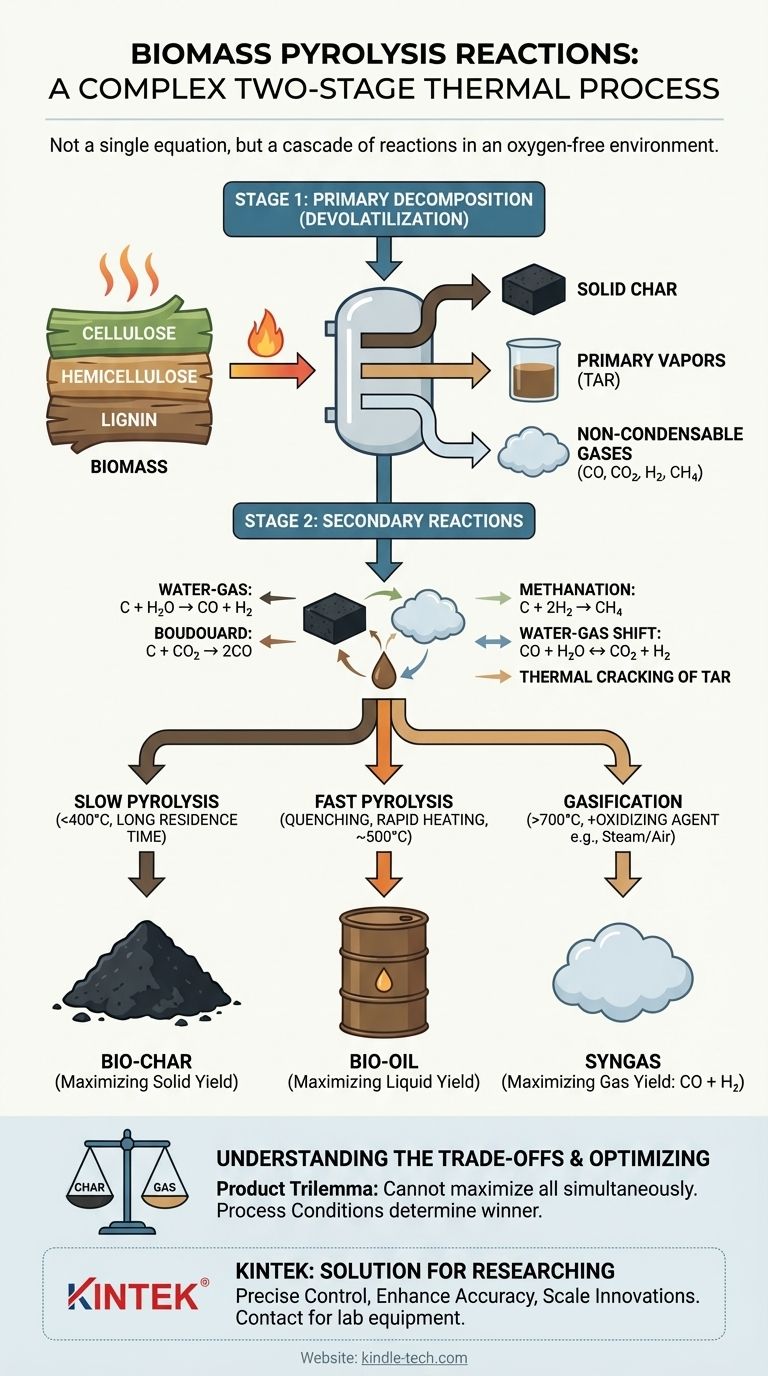
At its core, biomass pyrolysis is not a single chemical reaction but a complex, two-stage thermal process. First, heat breaks down the large organic polymers of biomass in an oxygen-free environment (a process called devolatilization), creating a mix of solid char, liquid vapors (tar), and gases. These initial products then undergo a series of secondary reactions, reacting with each other to form the final, stable products of bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas.
Pyrolysis is best understood as a cascade of reactions, not a single equation. The initial thermal cracking of biomass is followed by secondary reactions involving the resulting char and vapors. The final product yields—char, oil, or gas—are determined entirely by which of these secondary reaction pathways are favored by the process conditions like temperature and heating rate.

The Two Stages of Pyrolysis Reactions
To understand pyrolysis, you must separate the process into two distinct but interconnected stages. The first is the initial breakdown of the solid biomass, and the second is the subsequent transformation of the resulting products.
Stage 1: Primary Decomposition (Devolatilization)
This is the initial thermal "cracking" of the biomass itself. Heat energy breaks the chemical bonds within the primary components of biomass: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
This stage is not represented by a simple chemical equation. It is a complex web of simultaneous decomposition reactions that convert the solid biomass into three primary products:
- Solid Char: The carbon-rich solid residue left behind.
- Primary Vapors: A condensable aerosol of liquids, often called tar or bio-oil precursors.
- Non-condensable Gases: Light gases like CO, CO₂, H₂, and CH₄.
Stage 2: Secondary Reactions
Once the primary products are formed, they continue to react within the hot environment of the reactor. These secondary reactions are what ultimately determine the final composition and yield of your products. The most important of these involve the hot char reacting with the gases and vapors produced in Stage 1.
Key secondary reactions include:
- Water-Gas Reaction:
C (char) + H₂O (steam) → CO + H₂ - Boudouard Reaction:
C (char) + CO₂ → 2CO - Methanation:
C (char) + 2H₂ → CH₄ - Water-Gas Shift:
CO + H₂O ↔ CO₂ + H₂
Additionally, the heavy tar vapors can undergo thermal cracking at high temperatures, breaking down into lighter, non-condensable gases and depositing more carbon onto the char.
How Process Conditions Dictate the Outcome
The "winner" of the competition between these reactions is determined by the process conditions. By controlling temperature, heating rate, and residence time, you can steer the process to maximize the yield of char, liquid, or gas.
Slow Pyrolysis (Bio-char Focus)
In slow pyrolysis, low temperatures (<400°C) and slow heating rates give the secondary reactions ample time to occur. This environment favors char-forming reactions and allows some vapors to re-polymerize back into a solid, maximizing the bio-char yield.
Fast Pyrolysis (Bio-oil Focus)
In fast pyrolysis, high temperatures and extremely rapid heating rates break down the biomass almost instantly. The resulting vapors are immediately removed and quenched (cooled) to stop the secondary reactions. This "freezes" the process at the intermediate stage, maximizing the collection of condensable vapors as bio-oil.
Gasification (Syngas Focus)
It is critical to distinguish pyrolysis from gasification. While pyrolysis occurs in the complete absence of oxygen, gasification involves intentionally introducing a reactive agent like oxygen, steam, or air.
This introduction of an oxidizing agent at high temperatures promotes gas-producing reactions like partial combustion (C + ½O₂ → CO) and the water-gas reactions shown above. This fundamentally shifts the goal toward maximizing the yield of syngas (CO + H₂).
Understanding the Trade-offs
The chemistry of pyrolysis presents an unavoidable "product trilemma": you cannot simultaneously maximize the yield of char, oil, and gas from a single process.
The Inherent Product Conflict
Optimizing for one product comes at the expense of the others. A long residence time that favors char formation will destroy liquid yields as vapors crack or repolymerize. A rapid quench to save bio-oil prevents the secondary gas-forming reactions from proceeding fully.
The Complexity of Biomass
Biomass is not a uniform chemical. Its components—cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—decompose at different temperatures and produce different intermediate products. This inherent variability means that precise control and prediction of reaction pathways remain a significant technical challenge.
Optimizing Reactions for Your Goal
Your choice of pyrolysis conditions must be guided by your desired end product. The underlying reactions provide a clear roadmap for how to achieve your goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-char: Employ slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures (~400°C) and long residence times to favor solid formation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil: Use fast pyrolysis with rapid heating rates (>100°C/s), moderate temperatures (~500°C), and short vapor residence times followed by rapid quenching.
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas: Shift from pyrolysis to gasification by operating at higher temperatures (>700°C) and introducing an agent like steam or air to drive gas-producing reactions.
Understanding these reaction pathways is the key to transforming raw biomass into valuable, tailored products.
Summary Table:
| Reaction Stage | Key Process | Primary Products |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Primary Decomposition | Thermal cracking of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in an oxygen-free environment. | Solid Char, Primary Vapors (Tar), Non-condensable Gases (CO, CO₂, H₂) |
| Stage 2: Secondary Reactions | Char and vapors react further (e.g., Water-Gas, Boudouard, Cracking). | Final Bio-char, Bio-oil, and Syngas |
| Controlling Factor | Process Conditions (Temperature, Heating Rate, Residence Time) | Determines Final Product Yields |
Ready to Master Your Pyrolysis Process?
Understanding the complex reactions is the first step; precise control is the key to success. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for biomass research and analysis.
Whether you are developing a process to maximize bio-char for soil amendment, bio-oil for renewable fuel, or syngas for energy, the right equipment ensures accurate temperature control and reaction management.
Let KINTEK's expertise support your laboratory's mission:
- Achieve Precise Control: Optimize temperature and heating rates to steer secondary reactions toward your desired product.
- Enhance Research Accuracy: Reliable furnaces and reactors for reproducible results in pyrolysis studies.
- Scale Your Innovations: From lab-scale experimentation to process development.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can help you unlock the full potential of biomass pyrolysis for your specific application.
#ContactForm to get a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















