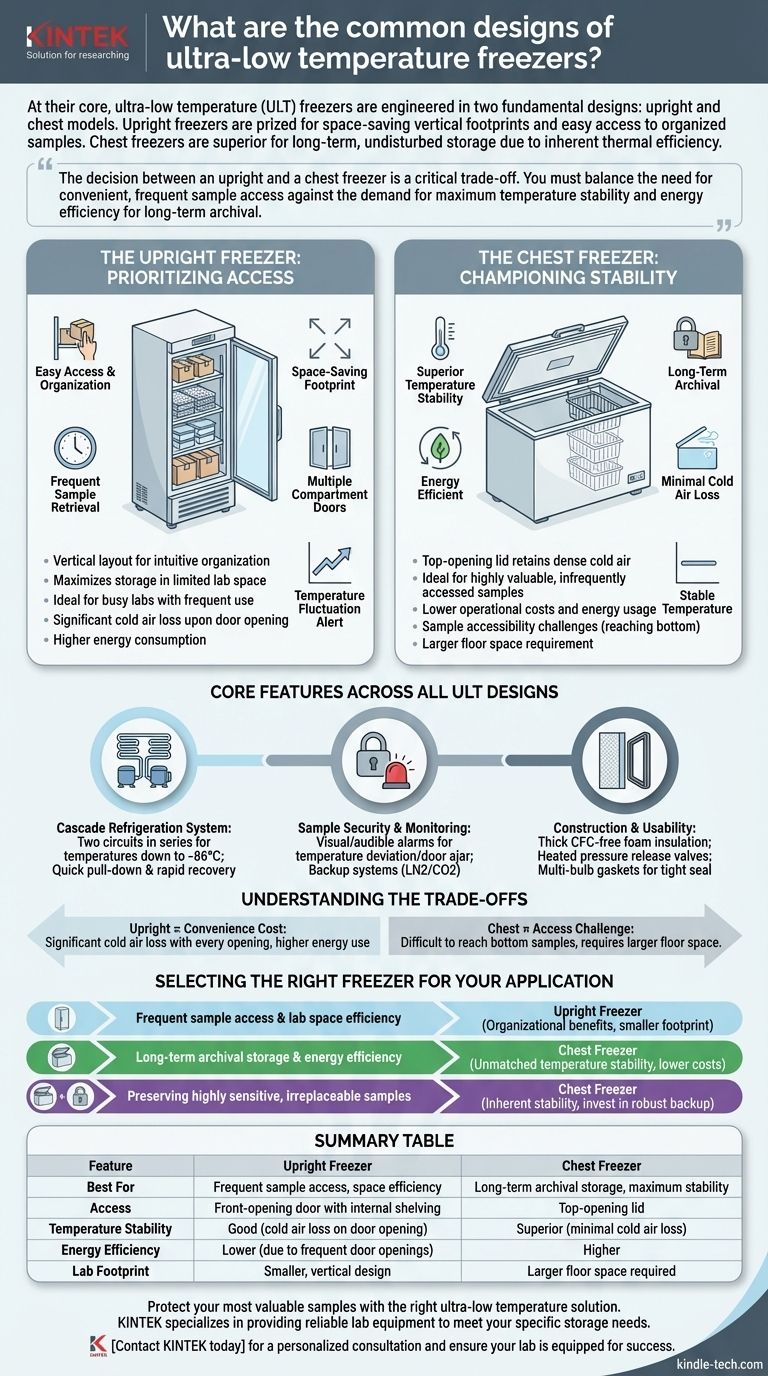
At their core, ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers are engineered in two fundamental designs: upright and chest models. Upright freezers are the most common choice in laboratory settings, prized for their space-saving vertical footprint and easy access to organized samples. Chest freezers, while requiring more floor space, are the superior option for long-term, undisturbed storage due to their inherent thermal efficiency.
The decision between an upright and a chest freezer is a critical trade-off. You must balance the need for convenient, frequent sample access against the demand for maximum temperature stability and energy efficiency for long-term archival.

Decoding the Two Primary Designs
While both designs achieve the same goal of extreme cold (typically -80°C to -86°C), their physical form dictates their ideal use case, efficiency, and impact on your daily workflow.
The Upright Freezer: Prioritizing Access
The upright freezer is designed like a standard refrigerator, with a front-opening door and internal shelving. This makes it the default choice for busy labs.
Its vertical layout allows for intuitive organization of samples in racks and boxes, making retrieval quick and straightforward.
Because of its smaller footprint, it maximizes storage capacity in labs where floor space is at a premium. Many models feature separate internal doors for each compartment to minimize cold air loss when the main door is opened.
The Chest Freezer: Championing Stability
The chest freezer is designed with a top-opening lid. This simple difference in orientation is its greatest strength.
When the lid is opened, the dense, cold air tends to remain inside the chamber, preventing the significant temperature fluctuations seen in upright models.
This superior temperature stability makes chest freezers the ideal solution for the long-term archival of highly valuable or irreplaceable samples that are accessed infrequently.
Core Features Across All ULT Designs
Regardless of the orientation, several key technological and safety features define a modern ultra-low temperature freezer. Understanding these is crucial for protecting your valuable assets.
The Refrigeration System
The heart of a ULT freezer is its cascade refrigeration system. This design uses two separate refrigeration circuits in series to efficiently reach and maintain temperatures as low as -86°C.
This system is also responsible for key performance metrics like quick temperature pull-down (how fast it gets cold initially) and rapid temperature recovery after a door opening.
Sample Security and Monitoring
Protecting the contents is paramount. All ULT freezers are equipped with visual and audible alarms that trigger if the temperature deviates from the set point or if a door is left ajar.
For enhanced protection, many labs opt for backup systems, such as liquid nitrogen (LN2) or carbon dioxide (CO2) injection, which automatically deploy if the primary cooling system fails.
Construction and Usability
ULT freezers are built with thick, CFC-free foam insulation to maintain thermal integrity.
Features like heated pressure release valves prevent vacuum formation, making the door easier to open, while multi-bulb gaskets create a tight seal to reduce frost buildup and maintain temperature homogeneity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a freezer design is not just about preference; it involves acknowledging fundamental compromises in performance and convenience.
Upright Freezers: The Cost of Convenience
The primary drawback of an upright freezer is significant cold air loss. Every time the door is opened, the cold, heavy air spills out and is replaced by warmer, ambient air.
This forces the compressors to work much harder to return to the set temperature, consuming more energy and placing greater stress on the system over time.
Chest Freezers: The Access Challenge
The main limitation of a chest freezer is sample accessibility. Reaching items at the bottom can be difficult, requiring careful inventory management and potentially unpacking upper layers.
Their larger physical footprint also makes them impractical for smaller or more crowded laboratory spaces, despite their superior efficiency.
Selecting the Right Freezer for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by your primary application and workflow.
- If your primary focus is frequent sample access and lab space efficiency: An upright freezer is the clear choice for its organizational benefits and smaller footprint.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival storage and energy efficiency: A chest freezer provides unmatched temperature stability and lower operational costs for samples you rarely need to access.
- If your primary focus is preserving highly sensitive, irreplaceable samples: Prioritize a chest freezer for its inherent stability and invest in robust backup and monitoring systems.
Ultimately, making an informed choice is about aligning the freezer's design strengths with the specific demands of your research.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Upright Freezer | Chest Freezer |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Frequent sample access, space efficiency | Long-term archival storage, maximum stability |
| Access | Front-opening door with internal shelving | Top-opening lid |
| Temperature Stability | Good (cold air loss on door opening) | Superior (minimal cold air loss) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (due to frequent door openings) | Higher |
| Lab Footprint | Smaller, vertical design | Larger floor space required |
Protect your most valuable samples with the right ultra-low temperature solution.
Choosing between an upright and chest freezer is critical for your lab's efficiency and sample integrity. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including ultra-low temperature freezers, to meet your specific storage needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect model to ensure optimal temperature stability, energy efficiency, and sample security for your research.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your lab is equipped for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
- 938L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Advanced Laboratory Storage
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are commonly stored in ultra low temperature freezers? Preserving Cells, Vaccines & Biomolecules
- What are the different types of ultra-low temperature freezers available? Choose the Right ULT Freezer for Your Lab
- How should frost be removed from Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers? Protect Your Samples and Equipment
- What is convection-based cooling in ultra-low temperature freezers? Achieve Superior Temperature Stability for Your Samples
- How is temperature controlled in ultra low temperature freezers? A Guide to Stable -80°C Storage



















