At its core, a sieving machine is a system designed for precision particle separation. While designs vary, they are all built around a few fundamental components: a vibrating motor that provides motion, one or more screens that perform the actual filtering, a frame to hold everything together, and a system of inlets and outlets to manage material flow. The interaction of these parts dictates the machine's efficiency, accuracy, and capacity.
A sieving machine's performance is not defined by any single component, but by the synergy between them. The motor generates the force, the screen provides the precision, and the frame ensures structural integrity, with each part being engineered to match the specific material being processed.

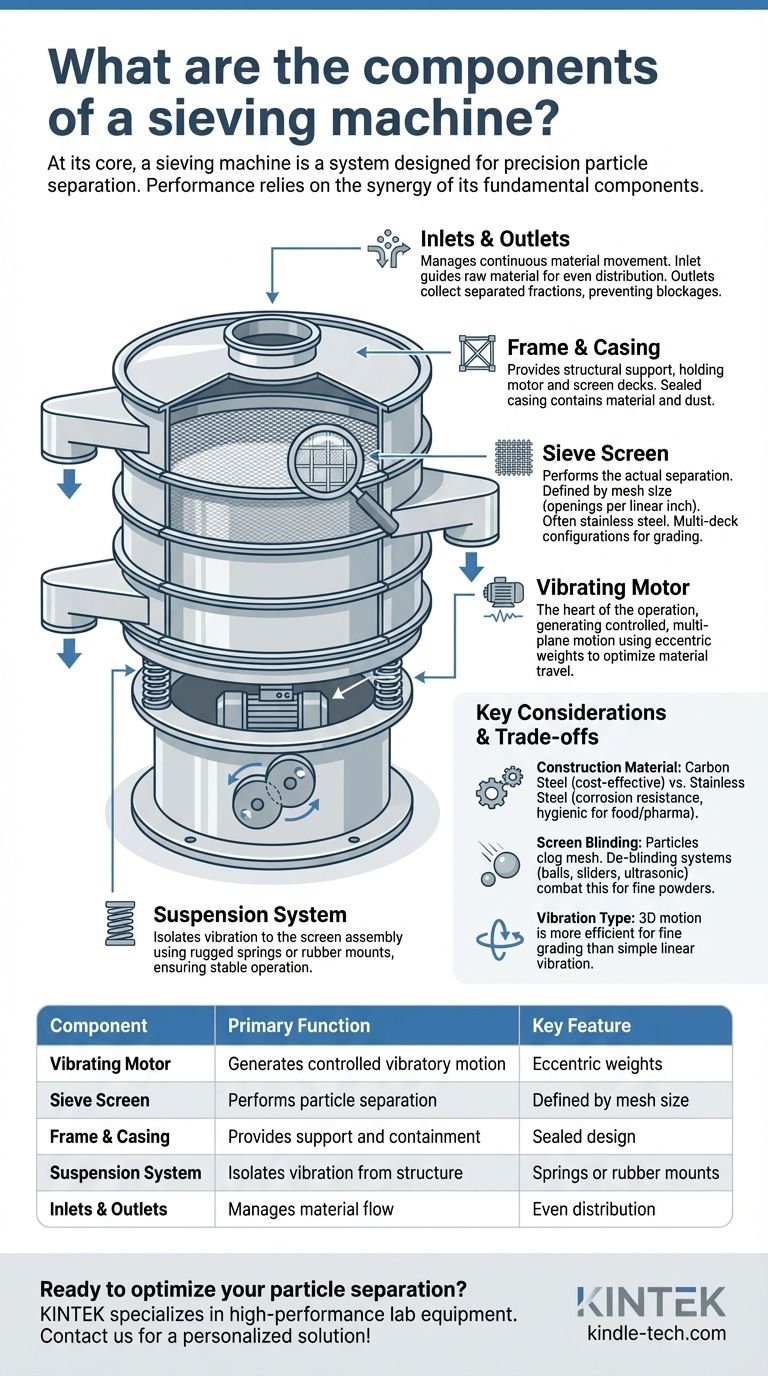
The Anatomy of a Sieving Machine
To truly understand how these machines function, we must examine each core component and the specific role it plays in the separation process.
The Vibrating Motor: The Heart of the Operation
The motor is the prime mover, responsible for generating the vibratory motion necessary to separate particles. It doesn't just shake the machine; it creates a controlled, multi-plane motion.
This is typically achieved using eccentric weights attached to the motor shaft. By adjusting these weights, operators can control the amplitude and pattern of vibration (both horizontal and vertical), optimizing the material's travel time across the screen for maximum efficiency.
The Sieve Screen: The Precision Tool
The screen, or sieve mesh, is the element that performs the actual separation. Its quality and specifications directly determine the accuracy of the final product.
Screens are defined by their mesh size, which refers to the number of openings per linear inch. A higher mesh number indicates finer openings for separating smaller particles. They are most often made from stainless steel for its durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for food-grade or pharmaceutical applications.
Many machines utilize a multi-deck configuration, stacking multiple screens with progressively finer mesh to grade a material into several different sizes in a single pass.
The Frame and Casing: The Structural Foundation
The frame provides the necessary support for the entire assembly, holding the motor and screen decks securely in place. It must be robust enough to withstand constant vibration without failing.
The casing encloses the screens, containing the material and any dust generated during the process. Proper sealing with gaskets is critical, especially in environments where contamination or dust exposure is a concern.
The Suspension System: Managing Vibration
To be effective, the vibration must be isolated to the screen assembly. This is the job of the suspension system, which typically consists of rugged springs or rubber mounts.
These components absorb the vibratory energy, preventing it from transferring to the floor or the machine's support structure. This ensures stable operation and a safer working environment.
Inlets and Outlets: The Flow Path
A well-designed sieving machine manages the continuous movement of material. The inlet guides raw material to the center of the top screen for even distribution.
The outlets, or discharge spouts, are positioned to collect the separated fractions from each screen deck (oversized particles) and the bottom pan (undersized particles). Their design is crucial for preventing material blockages and ensuring a smooth, uninterrupted flow.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Selecting the right components involves more than just knowing what they do. It requires understanding the critical trade-offs that impact performance and cost.
Construction Material: Stainless Steel vs. Carbon Steel
The most common choice is between carbon steel and stainless steel. A carbon steel frame is a cost-effective solution for applications involving non-corrosive materials like minerals or aggregates.
However, for food, pharmaceutical, or chemical applications, 304 or 316L stainless steel is mandatory. It provides necessary corrosion resistance and a hygienic, easy-to-clean surface that prevents contamination.
Screen Blinding and Clogging
Screen blinding is a common operational issue where particles become lodged in the mesh openings, reducing the screen's effective area and decreasing efficiency. This is especially problematic with fine or slightly sticky powders.
To combat this, many machines incorporate de-blinding systems. These can include bouncing rubber balls or plastic sliders installed beneath the screen that continuously tap it from below, dislodging trapped particles. More advanced systems use ultrasonic frequencies to achieve the same effect with even greater efficiency.
Vibration Type and Control
While all machines vibrate, the type of motion matters. Simple linear vibrators are effective for basic scalping, but gyratory or 3D motion is far more efficient for fine grading. This complex motion spreads material evenly and keeps it in contact with the screen longer, improving separation accuracy and throughput.
Matching Components to Your Application
The ideal configuration of your sieving machine depends entirely on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity separation (e.g., pharmaceuticals): Prioritize full stainless steel construction, a dust-tight sealed design, and easily disassembled parts for thorough cleaning.
- If your primary focus is high-volume scalping (e.g., aggregates): Choose a machine with a robust carbon steel frame, a powerful motor, and a heavy-duty, abrasion-resistant screen built for throughput.
- If your primary focus is fine powder grading (e.g., flour or spices): Select a multi-deck machine with an effective de-blinding system (balls or ultrasonic) to maintain efficiency and prevent screen clogging.
Understanding how these core components function and interact empowers you to select, operate, and maintain a sieving machine for optimal performance.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Vibrating Motor | Generates controlled vibratory motion | Eccentric weights for amplitude control |
| Sieve Screen | Performs particle separation by size | Defined by mesh size and material (e.g., stainless steel) |
| Frame & Casing | Provides structural support and containment | Sealed design for dust control and hygiene |
| Suspension System | Isolates vibration from the structure | Springs or rubber mounts for stability |
| Inlets & Outlets | Manages material flow into and out of the machine | Designed for even distribution and blockage prevention |
Ready to optimize your particle separation process? The right sieving machine is critical for accuracy, efficiency, and product quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including sieving machines tailored for pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, and aggregates. Our experts will help you select the perfect configuration—from material choice to de-blinding systems—to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution! Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis



















