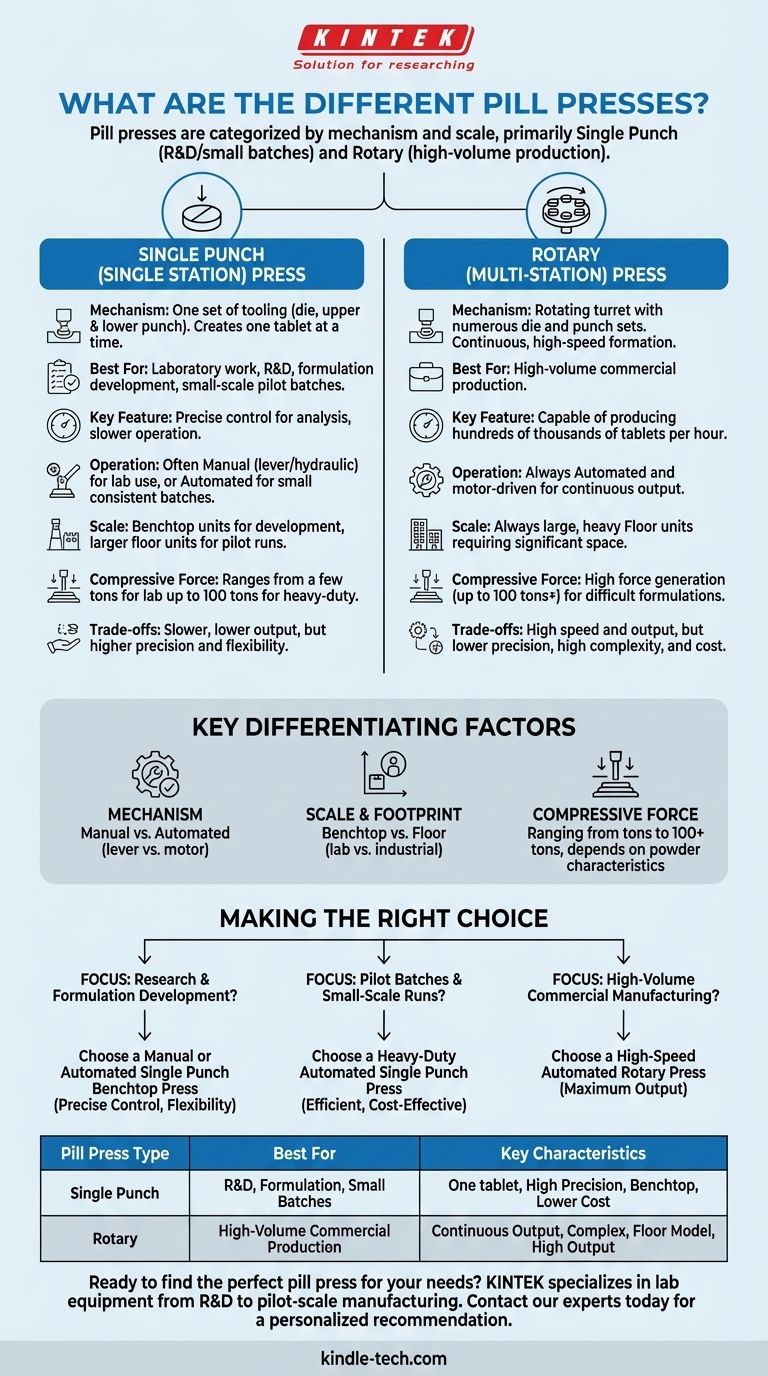
At their core, pill presses are categorized by their mechanism and scale of operation. The primary types are single punch (or single station) presses, which are ideal for development and small batches, and rotary (or multi-station) presses, which are built for high-volume commercial production.
The fundamental choice between a pill press comes down to its intended application. Single punch presses offer precision for research and development, while rotary presses provide the high-speed output required for large-scale manufacturing.

The Two Primary Categories of Pill Presses
Understanding the mechanical difference between the two main types of presses is the first step in selecting the right tool for your objective. Each is designed for a fundamentally different scale and purpose.
Single Punch (Single Station) Press
A single punch press is the simplest form of tablet compression machine. It uses one set of tooling—a die and a pair of upper and lower punches—to compress powder into a single tablet at a time.
This design is perfectly suited for laboratory work, research and development (R&D), and small-scale pilot batches. Its slower, methodical operation allows for precise control and analysis during the formulation stage.
Rotary (Multi-Station) Press
A rotary press, also known as a multi-station press, is the standard for commercial manufacturing. It features a rotating turret that holds numerous sets of dies and punches.
As the turret spins, the dies are filled with powder, and the punches pass between compression rollers, forming tablets in a continuous, high-speed process. This design can produce hundreds of thousands of tablets per hour.
Key Differentiating Factors
Beyond the core mechanical design, several key features define a press's capabilities and intended use. These factors determine its footprint, operation, and power.
Mechanism of Operation (Manual vs. Automated)
Manual presses, typically single-station designs, require an operator to apply force using a lever or a hydraulic jack. They offer maximum control for individual tablet creation in a lab setting.
Automated presses are motor-driven for continuous operation. While this is a defining feature of all rotary presses, many single punch presses are also automated to produce small, consistent batches.
Scale and Footprint (Benchtop vs. Floor)
Benchtop units are smaller presses designed to fit in a laboratory environment. The vast majority of these are single punch models used for formulation development.
Floor units are larger, heavier machines. This category includes heavy-duty single punch presses and all commercial-scale rotary presses, which require significant space and robust foundations.
Compressive Force
The compressive force a press can generate is critical for creating a hard, stable tablet that won't crumble. This force can range from a few tons for small lab presses up to 100 tons or more for industrial machines handling difficult formulations.
The required force depends entirely on the characteristics of the powder being compressed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a press involves balancing speed, cost, and flexibility. The machine that excels in one area often makes a compromise in another.
Speed vs. Precision
Single punch presses are inherently slower, but they provide granular control over the compression cycle. This precision is invaluable when developing a new product formulation.
Rotary presses are built for one thing: maximum output. They achieve this by sacrificing the individual tablet control found in a lab-scale press.
Cost and Complexity
A single punch press represents a much lower capital investment. It is also simpler to operate, clean, and maintain due to having only one set of tooling.
A rotary press is a complex piece of industrial machinery that is expensive to purchase, requires highly skilled operators, and has demanding maintenance and tooling management requirements.
Flexibility
Single punch presses offer excellent flexibility. Changing from one product to another is a relatively quick process of swapping out a single die and punch set.
Rotary presses are designed for long, dedicated production runs of a single product. Tooling changeovers are time-consuming and complex, making them inefficient for frequent product switches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct press is about aligning the machine's capabilities with your specific production or development needs.
- If your primary focus is research and formulation development: A manual or automated single punch benchtop press provides the necessary control and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is producing pilot batches or small-scale runs: A heavy-duty automated single punch press is the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-volume commercial manufacturing: A high-speed, automated rotary press is the only viable option to meet output demands.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental differences in design and scale empowers you to select the precise tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Pill Press Type | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Single Punch (Single Station) | R&D, Formulation, Small Batches | One tablet at a time, high precision, benchtop, lower cost |
| Rotary (Multi-Station) | High-Volume Commercial Production | Continuous high-speed output, complex, floor model, high output |
Ready to find the perfect pill press for your needs?
Whether you are developing new formulations in the lab or scaling up to full production, selecting the right equipment is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs from R&D to pilot-scale manufacturing.
Our experts can help you navigate the choice between a precise single punch press for development or a high-speed rotary press for production, ensuring you get the performance and reliability you require.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and get a personalized recommendation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- What do you press pills with? The Essential Guide to Tablet Press Machines
- What size are pellet mill die sizes? Master the L/D Ratio for Perfect Pellets
- What is the principle of a single punch tablet press machine? A Guide to Precision Lab-Scale Production
- What are pill presses called? The Correct Term is Tablet Press for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- What are pill presses used for? Transforming Powders into Precise Tablets for Medicine, Supplements, and More
- What is the process of pelleting biomass? Transform Raw Biomass into High-Value, Energy-Dense Fuel
- How does a rotary tablet press work? A Guide to High-Speed Tablet Manufacturing
- Which type of tablet press is more suitable for large scale production? Rotary Presses for High-Volume Efficiency



















