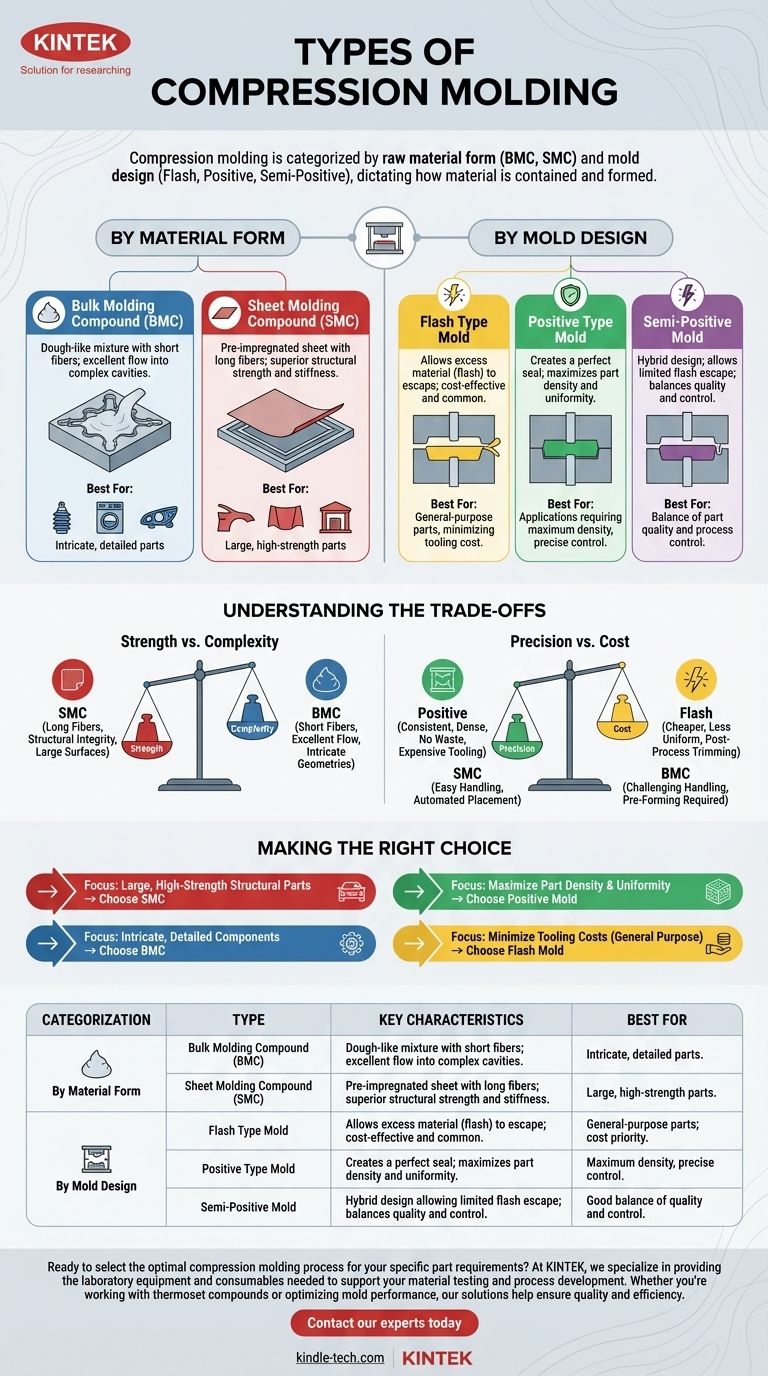
At its core, compression molding is categorized in two primary ways: by the form of the raw material used and by the design of the mold itself. The most common process distinctions are Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) and Sheet Molding Compound (SMC), which define the material. The mold design, such as flash, positive, or semi-positive, dictates how that material is contained and formed under pressure.
The choice between compression molding variations is not about which is "best," but which is the most appropriate fit. Your decision depends on a direct trade-off between the complexity of your part, the required structural strength, and your budget for tooling and process control.

Understanding the Primary Process Types: Material Form
The most significant distinction in compression molding is the state of the thermoset plastic before it enters the mold. This dictates the material's flow, fiber length, and ideal application.
Bulk Molding Compound (BMC)
Bulk Molding Compound is a dough-like or putty-like mixture. It combines thermosetting resin with various fillers, catalysts, and short reinforcing fibers (like chopped glass).
Because of its consistency, BMC flows easily into intricate and complex cavities. This makes it ideal for producing smaller, detailed parts such as electrical insulators, appliance components, and automotive headlight housings.
Sheet Molding Compound (SMC)
Sheet Molding Compound is a pre-impregnated, mat-like material. It consists of a layer of resin and fillers reinforced with longer fibers, sandwiched between two layers of carrier film.
The longer fibers in SMC provide superior structural strength and stiffness. This makes it the preferred material for large, relatively flat, high-strength parts like automotive body panels, truck hoods, and building fascias.
How Mold Design Influences the Process
The second way to categorize compression molding is by the tooling design. The mold determines how pressure is applied and whether excess material is allowed to escape.
Flash Type Molds
This is the most common and cost-effective mold design. It is built with a small gap or "land" area around the cavity, allowing excess material, known as flash, to escape as the mold closes.
While simple and forgiving of slight variations in material charge, this method offers less control over final part density and can require a secondary trimming operation to remove the flash.
Positive Type Molds
A positive mold is designed to create a perfect seal around the material charge. The male and female halves of the mold telescope together, leaving no path for excess material to escape.
This design forces all material into the part, resulting in maximum density and uniformity. However, it requires an extremely precise amount of material to avoid either an incomplete part or damagingly high pressures within the mold.
Semi-Positive Molds
Semi-positive molds offer a compromise between the flash and positive designs. They allow the mold to close completely like a positive mold but incorporate a small relief channel for a limited amount of flash to escape.
This hybrid approach provides better density control than a flash mold while being more forgiving than a true positive mold, offering a good balance of part quality and process control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right combination of material and mold design requires balancing competing priorities of cost, quality, and part geometry.
Strength vs. Complexity
SMC's long fibers provide excellent structural integrity for large surfaces but do not flow well into small, complex features. BMC's short fibers and putty-like nature allow it to fill intricate geometries with ease but at the cost of ultimate strength.
Precision vs. Cost
Positive molds produce highly consistent, dense parts with no waste but demand expensive, precision tooling and exact material measurements. Flash molds are cheaper to build and operate but result in less uniform parts and require post-process trimming.
Material Handling and Automation
SMC is easily handled in large sheets and lends itself to automated cutting and placement. BMC is more amorphous and can be more challenging to handle automatically, often requiring pre-forming into a specific shape before being placed in the mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Use these guidelines to select the best approach based on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is large, high-strength structural parts: Choose Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) for its superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is intricate, detailed components: Choose Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) for its excellent flow characteristics.
- If your primary focus is maximizing part density and minimizing waste: A positive mold is the ideal choice, but be prepared for higher tooling costs and stricter process control.
- If your primary focus is minimizing tooling costs for general-purpose parts: A flash-type mold is the most common and economical solution.
Ultimately, aligning the material characteristics and mold design with your part's specific requirements is the key to successful compression molding.
Summary Table:
| Categorization | Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| By Material Form | Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) | Dough-like mixture with short fibers; excellent flow into complex cavities. | Intricate, detailed parts (e.g., electrical insulators, appliance components). |
| Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) | Pre-impregnated sheet with long fibers; superior structural strength and stiffness. | Large, high-strength parts (e.g., automotive body panels, truck hoods). | |
| By Mold Design | Flash Type Mold | Allows excess material (flash) to escape; cost-effective and common. | General-purpose parts where minimizing tooling cost is a priority. |
| Positive Type Mold | Creates a perfect seal; maximizes part density and uniformity. | Applications requiring maximum density and minimal waste, with precise material control. | |
| Semi-Positive Mold | A hybrid design allowing limited flash escape; balances quality and control. | A good balance of part quality and process control, more forgiving than a positive mold. |
Ready to select the optimal compression molding process for your specific part requirements? The choice between BMC, SMC, and different mold designs directly impacts the strength, complexity, and cost of your final product.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables needed to support your material testing and process development. Whether you're working with thermoset compounds or optimizing mold performance, our solutions help ensure quality and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's compression molding projects and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What are the parameters to be considered for selecting the thin wall molding machine? Key Specs for High-Speed Production
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?



















