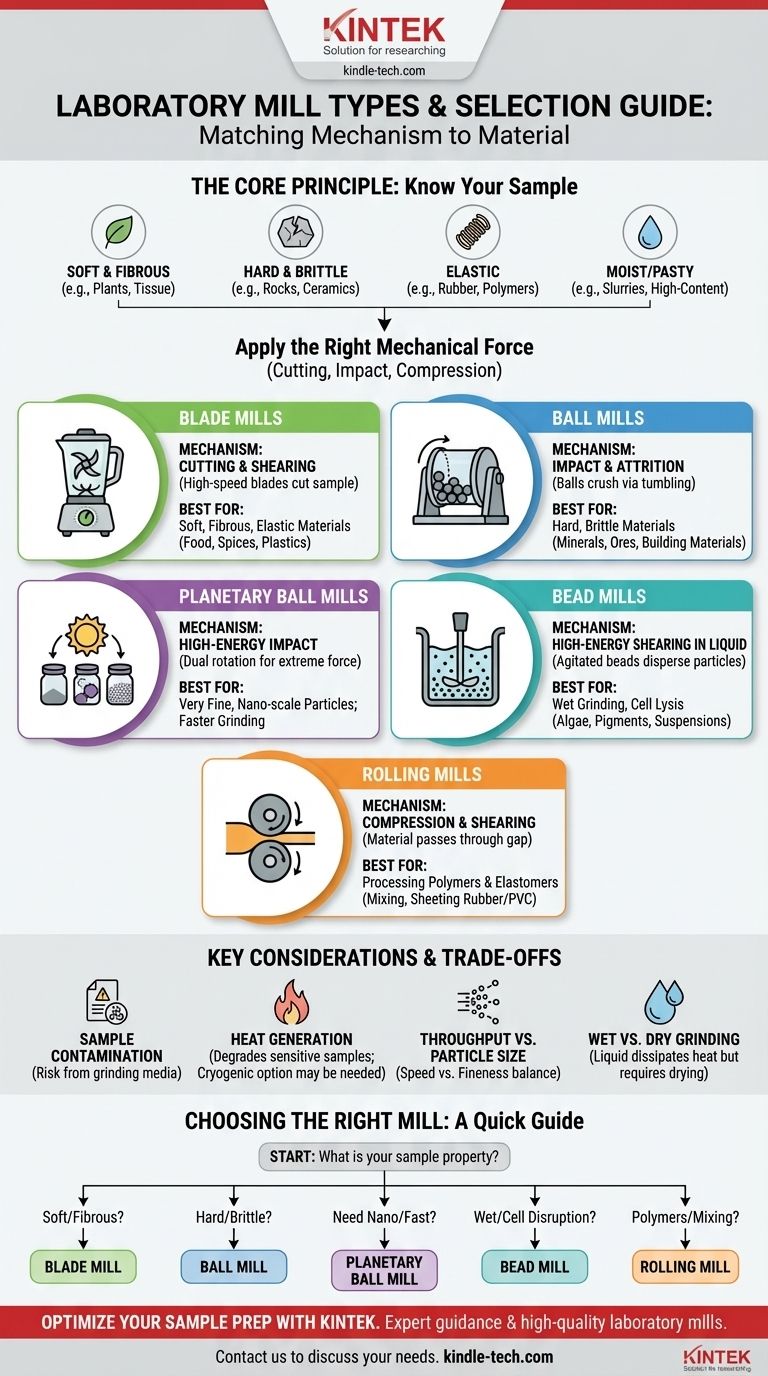
In short, the main types of laboratory mills are categorized by their grinding mechanism, with the most common being blade mills (for cutting), ball mills (for impact), and specialized high-energy variants like planetary or bead mills. These are used to reduce the size of solid samples for analysis. Other, more specialized types like rolling mills are used for processing polymers rather than general sample grinding.
The most critical factor in selecting a laboratory mill is not the mill itself, but the properties of your sample. The goal is to match the mill's mechanical action—cutting, impact, or compression—to your material's characteristics, whether it is soft, hard, fibrous, or brittle.

The Core Principle: Matching Mechanism to Material
Before choosing a mill, you must first characterize your sample. The effectiveness of any grinding process depends entirely on applying the right kind of force to the material you need to break down.
Understanding Material Properties
Every sample responds differently to force. Key properties include:
- Soft & Fibrous: Materials like plant leaves, animal tissue, or paper. These tend to tear or deform rather than shatter, requiring a cutting or shearing action.
- Hard & Brittle: Materials like rocks, minerals, ceramics, or glass. These fracture easily under sharp impact.
- Elastic: Materials like rubber or many polymers. These absorb impact and deform, requiring specialized compression or cryogenic (frozen) grinding to make them brittle.
- Moist or Pasty: Materials with high water or oil content. These can clog certain mills and often require wet grinding methods.
Common Types of Laboratory Mills Explained
Each type of mill employs a distinct mechanical principle designed for a specific category of material.
Blade Mills (Cutting & Shearing)
Also known as rotor or knife mills, these operate like a high-speed kitchen blender. A set of rotating blades cuts and shears the sample material.
These are the ideal choice for soft, elastic, or fibrous samples like plants, spices, food products, and some plastics.
Ball Mills (Impact & Attrition)
A ball mill is a rotating cylinder partially filled with grinding media, typically ceramic or steel balls. As the cylinder turns, the balls cascade from the top, crushing the sample material through impact and attrition (friction).
They are highly effective for hard, brittle materials such as minerals, ores, building materials, and some chemical compounds.
Planetary Ball Mills (High-Energy Impact)
This is an enhanced version of the traditional ball mill. Grinding jars are mounted on a rotating "sun" wheel and simultaneously spin on their own axis, like planets orbiting the sun.
This combination of forces creates extremely high-energy impacts, allowing for much faster grinding and the ability to achieve very fine, nano-scale particles.
Bead Mills (High-Energy Shearing in Liquid)
Bead mills are used for wet grinding and dispersing particles in a liquid suspension. The chamber is filled with tiny grinding beads (zirconia, glass) which are agitated at high speed.
This creates intense shear forces ideal for breaking down cells (cell lysis), algae, pigments, and creating stable nano-particle suspensions.
Rolling Mills (Compression & Shearing)
Mentioned for polymer processing, these mills use two or more counter-rotating rollers. Material is passed through the gap between them and processed by intense compression and shear.
In a lab setting, they are primarily used for mixing and processing polymers and elastomers, such as rubber, silicone, or PVC, not for general-purpose sample grinding.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Choosing a mill involves balancing performance with potential drawbacks.
Sample Contamination
Any mill that uses grinding media (like ball or bead mills) risks introducing trace amounts of the media material into your sample. This is a critical concern for high-purity applications or trace element analysis.
Heat Generation
High-energy mills, especially planetary and bead mills, generate significant heat. This can degrade heat-sensitive samples like pharmaceuticals, biological tissues, or certain polymers. For these, cryogenic grinding (using liquid nitrogen to make the sample brittle) is often necessary.
Throughput vs. Particle Size
There is often a trade-off between how quickly you can process a sample and the final particle size you can achieve. Achieving nano-scale particles in a planetary mill, for instance, takes more time than a coarse grind in a blade mill.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Some materials are easier to grind when wet, as the liquid helps dissipate heat and prevent clogging. However, wet grinding requires a mill designed for liquids and adds a subsequent drying or separation step to your workflow.
Choosing the Right Mill for Your Application
Use your sample's properties and your analytical goal as your guide.
- If your material is soft or fibrous (e.g., plants, food, paper): Your best choice is a blade mill for its efficient cutting action.
- If your material is hard and brittle (e.g., rocks, ceramics, gypsum): Use a standard ball mill for effective impact grinding.
- If you need extremely fine particles or rapid results on hard materials: A planetary ball mill provides the necessary high energy.
- If you are working with wet suspensions or cell disruption (e.g., algae, microbes): A bead mill is specifically designed for this purpose.
- If you are processing polymers like rubber or PVC: A laboratory rolling mill is the appropriate tool for mixing and sheeting.
Ultimately, a successful sample preparation begins with correctly identifying your material and selecting the tool designed to break it down effectively.
Summary Table:
| Mill Type | Grinding Mechanism | Best For Sample Type |
|---|---|---|
| Blade Mill | Cutting & Shearing | Soft, fibrous, elastic materials (plants, food, plastics) |
| Ball Mill | Impact & Attrition | Hard, brittle materials (minerals, ceramics, ores) |
| Planetary Ball Mill | High-Energy Impact | Hard materials requiring very fine or nano-scale particles |
| Bead Mill | High-Energy Shearing | Wet suspensions, cell disruption (algae, pigments) |
| Rolling Mill | Compression & Shearing | Polymers and elastomers (rubber, PVC) |
Optimize Your Sample Preparation with KINTEK
Choosing the right laboratory mill is critical for achieving consistent, contamination-free results. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of mills designed for various sample types and applications.
Let our experts help you select the perfect mill for your specific needs. We can guide you through the trade-offs and considerations to ensure your sample preparation is efficient and effective.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's reliable lab solutions can enhance your workflow and support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Micro Horizontal Jar Mill for Precision Sample Preparation in Research and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding tools like agate mortars? Optimize LTO Electrode Performance
- What is a mortar and pestle used for in a lab? A Guide to Precision Grinding and Mixing
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination



















