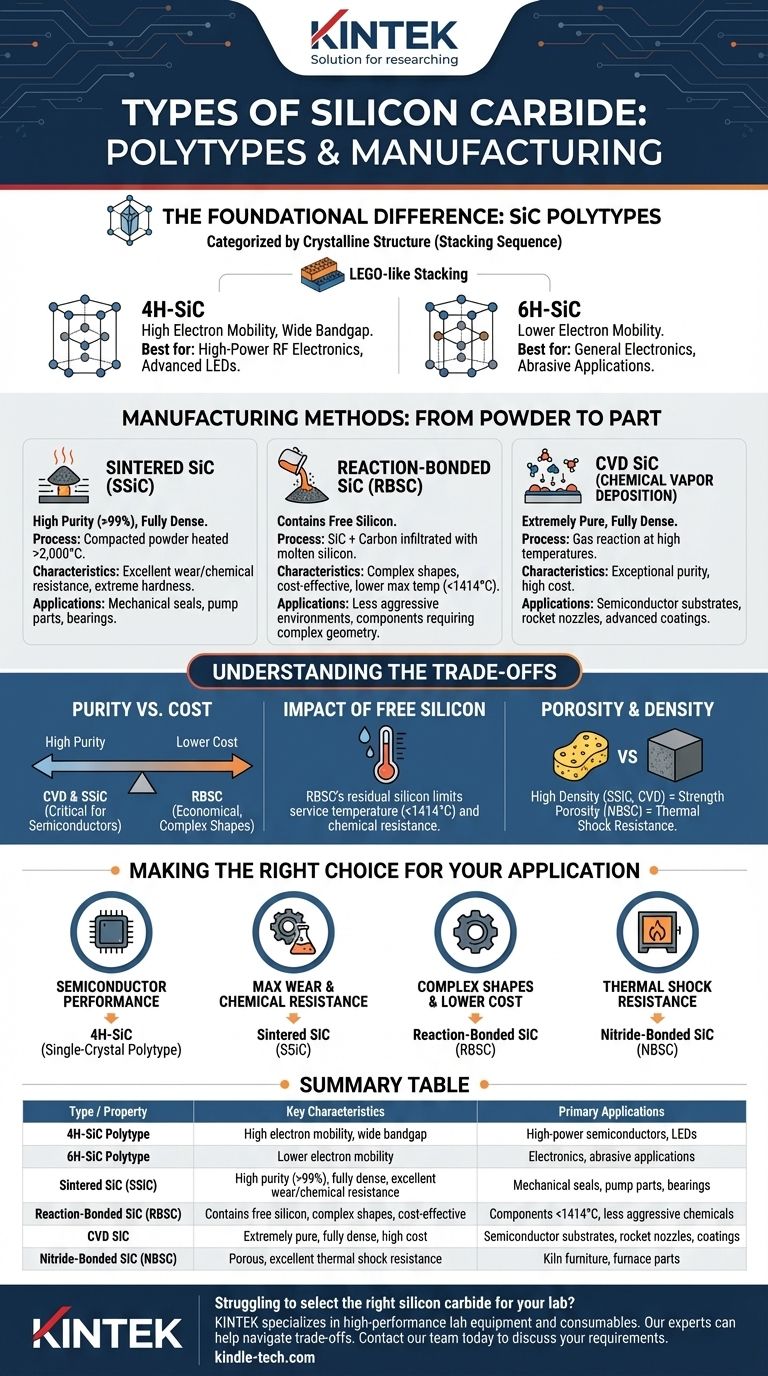
At a fundamental level, silicon carbide (SiC) is categorized in two primary ways: by its crystalline structure, known as polytypes (like 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC), and by its manufacturing process, which results in forms like sintered, reaction-bonded, and CVD SiC. These distinctions are critical as they dictate the material's final properties, from electrical conductivity to mechanical strength and thermal stability.
Understanding the types of silicon carbide is not about memorizing names; it's about matching a specific manufacturing method and crystal structure to a desired outcome. The right choice for a high-wear pump part is fundamentally different from the one needed for an advanced semiconductor.

The Foundational Difference: SiC Polytypes
The most basic distinction in silicon carbide lies in its crystal structure. While chemically identical (one silicon atom, one carbon atom), the way these atoms are stacked in layers can vary.
What is a Polytype?
A polytype refers to one of the many possible stacking sequences of the Si-C bilayers. Think of it like stacking LEGO blocks—you can stack them directly on top of each other or offset them in different repeating patterns.
These different patterns result in materials with distinct electronic properties, even though their mechanical and thermal properties remain broadly similar.
Common Polytypes: 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC
While over 250 polytypes exist, two dominate commercial applications, particularly in electronics: 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC. The number refers to the number of layers in the repeating stacking sequence.
The key difference between them is electron mobility. 4H-SiC allows electrons to move much more freely, making it the preferred choice for high-frequency, high-power electronic devices.
Why Polytypes Matter for Electronics
The specific polytype determines the material's bandgap and electron mobility, which are crucial for semiconductor performance. This is why substrates for advanced LEDs or power transistors are made from a specific, carefully grown single-crystal polytype like 4H-SiC.
Manufacturing Methods: From Powder to Part
For most mechanical, thermal, and structural applications, the manufacturing method is the most important classification. This process dictates the material's purity, density, and final strength.
Sintered Silicon Carbide (SSiC)
Sintered SiC is produced by compacting fine SiC powder at very high temperatures (over 2,000°C) until the particles fuse together.
This method produces an extremely pure (>99%) and dense material with superb strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. It is often used for demanding applications like pump seals, bearings, and valve components.
Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide (RBSC)
Also known as silicon-infiltrated SiC (SiSiC), this type is made by mixing SiC powder with carbon and then infiltrating it with molten silicon. The silicon reacts with the carbon to form more SiC, which bonds the original particles.
The final product contains a network of SiC with some amount of free, unreacted silicon (typically 8-15%). This makes it slightly less robust at very high temperatures but allows for the creation of complex shapes with minimal shrinkage, often at a lower cost than SSiC.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) SiC
This process involves reacting gases at high temperatures to deposit a layer of extremely pure silicon carbide onto a surface.
CVD SiC is theoretically dense and exceptionally pure, making it ideal for coatings on rocket engine nozzles or for producing substrates for the semiconductor industry. It is generally the most expensive manufacturing method.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right type of SiC requires understanding the inherent compromises between different manufacturing processes. No single type is best for every situation.
Purity vs. Cost
CVD and Sintered SiC offer the highest purity, which is critical for semiconductor applications and extreme chemical environments. This purity comes at a significant cost.
Reaction-Bonded SiC is a more economical alternative, but its performance is limited by the presence of free silicon.
The Impact of Free Silicon
The residual silicon in RBSC is its primary trade-off. Silicon melts at around 1,414°C, limiting the maximum service temperature of RBSC parts well below that of pure SSiC. This free silicon is also more susceptible to chemical attack than SiC itself.
Porosity and Density
High density is directly linked to high mechanical strength and impermeability. SSiC and CVD SiC are fully dense materials.
Other forms, like nitride-bonded SiC (NBSC), have intentional porosity, which improves thermal shock resistance but reduces overall strength, making them suitable for kiln furniture and furnace parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor performance: You will need a specific single-crystal polytype, typically 4H-SiC, grown into a wafer for devices like LEDs and power electronics.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear and chemical resistance: Choose a dense, high-purity material like Sintered SiC (SSiC) for components like mechanical seals and pump parts.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes at a lower cost: Reaction-Bonded SiC (RBSC) is an excellent choice, provided your application's temperature and chemical environment can tolerate the presence of free silicon.
- If your primary focus is thermal shock resistance in furnaces: A bonded material like Nitride-Bonded SiC (NBSC) often provides the best balance of properties for applications like heating element supports.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can confidently select the precise type of silicon carbide engineered to meet your specific technical and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Type / Property | Key Characteristics | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 4H-SiC Polytype | High electron mobility, wide bandgap | High-power semiconductors, LEDs |
| 6H-SiC Polytype | Lower electron mobility | Electronics, abrasive applications |
| Sintered SiC (SSiC) | High purity (>99%), fully dense, excellent wear/chemical resistance | Mechanical seals, pump parts, bearings |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC (RBSC) | Contains free silicon, complex shapes, cost-effective | Components where temperature <1414°C, less aggressive chemicals |
| CVD SiC | Extremely pure, fully dense, high cost | Semiconductor substrates, rocket nozzles, coatings |
| Nitride-Bonded SiC (NBSC) | Porous, excellent thermal shock resistance | Kiln furniture, furnace parts |
Struggling to select the right silicon carbide for your lab's specific needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including silicon carbide components for furnaces, semiconductors, and mechanical applications. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between purity, cost, and performance to find the optimal solution for your research or production.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities with the right SiC materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is microwave sintering of ceramic materials? A Guide to Faster, More Efficient Processing
- What is meant by ceramic powder? The Engineered Blueprint for Advanced Ceramics
- What is sintered ceramic? A Durable, Non-Porous Material for Modern Surfaces
- Are ceramics chemically unreactive? Discover Their Remarkable Corrosion Resistance
- What functions do high-purity alumina support rods serve in sCO2 experiments? Ensure High-Temp Material Integrity
- What is ceramic sintering? A Guide to High-Performance Material Manufacturing
- Why are Boron Nitride Tubes selected as reaction vessels for Na3SbS4? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Synthesis
- Why is a hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) layer required for LATP? Protect Your Samples from Carbon Contamination



















