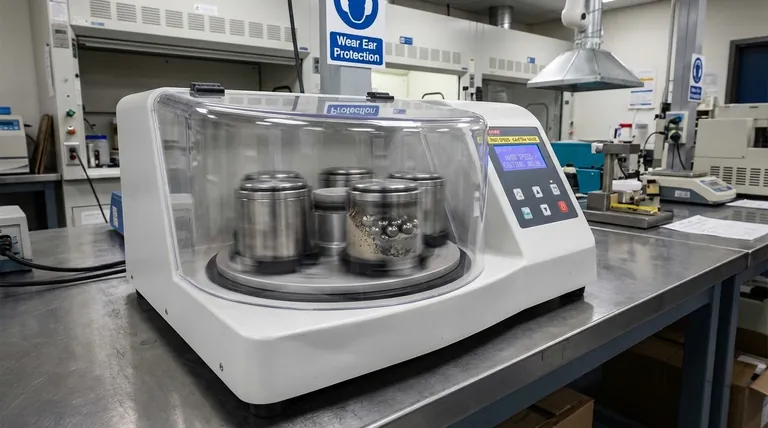
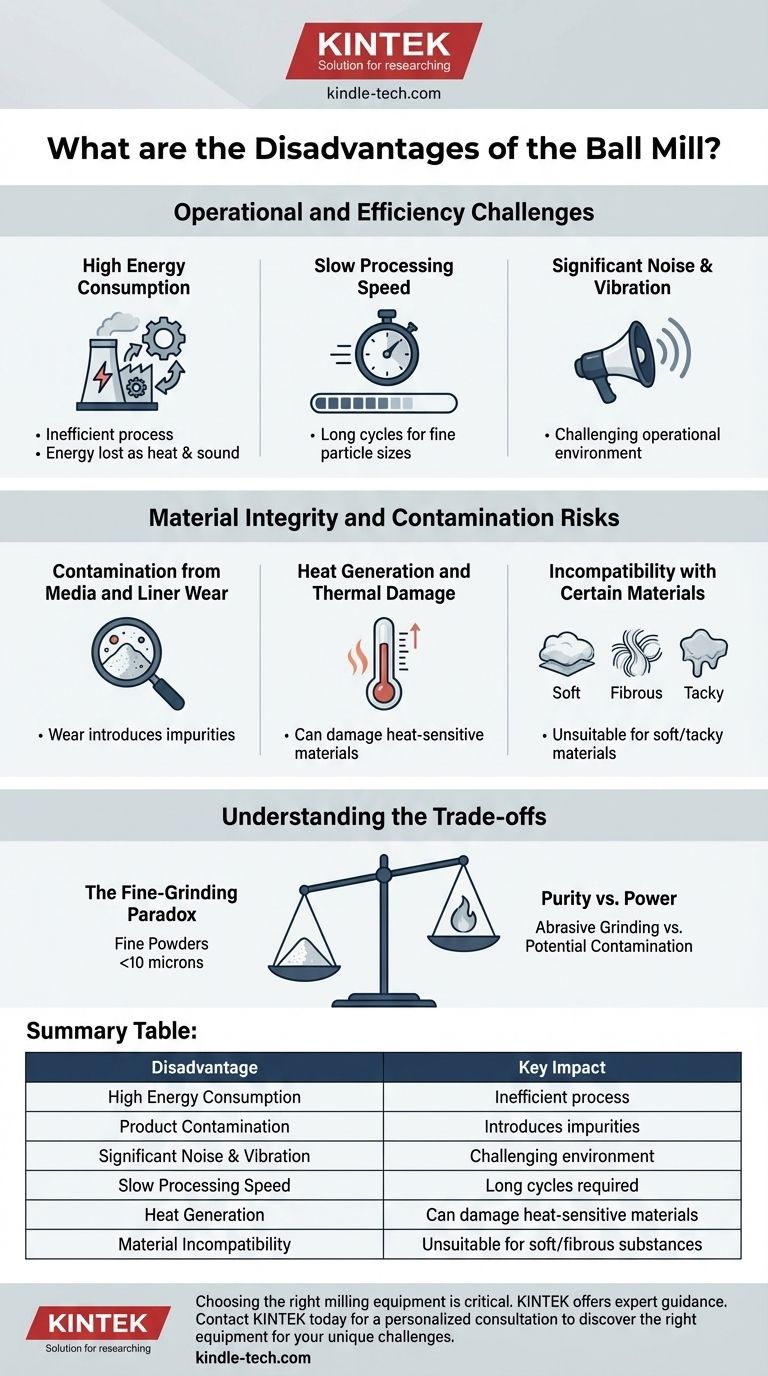
The primary disadvantages of a ball mill are its high energy consumption, significant noise output, and the potential for product contamination from the wear of its grinding media and internal lining. Furthermore, it is a relatively slow process and is fundamentally unsuitable for grinding soft, fibrous, or tacky materials that tend to coat the grinding media rather than break apart.
A ball mill's effectiveness comes from a high-impact, brute-force grinding process. This mechanical reality means its key strengths—producing extremely fine powders and handling hard materials—are intrinsically linked to its main drawbacks: inefficiency, noise, heat generation, and material contamination.

Operational and Efficiency Challenges
A ball mill operates through a simple but intense mechanical action, which brings several inherent operational hurdles. Understanding these is the first step in evaluating its suitability for a given task.
High Energy Consumption
The process of continuously lifting and cascading heavy grinding media (steel or ceramic balls) to crush materials is mechanically intensive. A significant portion of the electrical energy consumed is converted into heat and sound rather than direct grinding force, making the process relatively inefficient.
Slow Processing Speed
Compared to other milling methods, ball milling is a process of attrition that takes time. Achieving a target particle size, especially in the micron range, can require long operational cycles, which impacts overall throughput.
Significant Noise and Vibration
The constant tumbling of heavy grinding balls inside a large metal drum creates substantial noise and vibration. This necessitates dedicated infrastructure, sound dampening measures, and can make the operational environment challenging.
Material Integrity and Contamination Risks
The most critical disadvantages often relate to the quality and purity of the final product. The grinding action itself can introduce undesirable elements and alter the material's properties.
Contamination from Media and Liner Wear
This is arguably the most significant drawback for high-purity applications. The abrasive action causes the grinding media and the cylinder's inner lining to wear down over time. These microscopic particles of steel, ceramic, or rubber are introduced directly into the product, causing contamination.
Heat Generation and Thermal Damage
The friction generated during the milling process creates considerable heat. For heat-sensitive materials, such as certain pharmaceuticals or polymers, this can lead to thermal degradation, altering the material's chemical structure and compromising product quality.
Incompatibility with Certain Materials
Ball mills excel at pulverizing hard, brittle materials. However, they are ineffective for processing soft, tacky, or fibrous substances. These materials tend to absorb the impact, flatten, or coat the grinding balls, preventing the fracturing action required for particle size reduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single piece of equipment is perfect for every job. The disadvantages of a ball mill must be weighed against its unique and powerful advantages.
The Fine-Grinding Paradox
The very mechanism that allows a ball mill to produce exceptionally fine powders (less than 10 microns) is the source of its main drawbacks. The intense, prolonged attrition required for this level of grinding is precisely what causes high energy use, component wear, and heat generation.
Purity vs. Power
A ball mill is a powerful tool for grinding abrasive materials that would quickly destroy other types of mills. However, this robustness comes at the cost of potential contamination. For applications where absolute purity is non-negotiable (like in high-grade pharmaceuticals or electronics), the risk of media contamination may require exploring alternative, often more complex, milling technologies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating these disadvantages in the context of your specific goal is crucial for making a sound technical decision.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest particle size with hard, abrasive materials: A ball mill is an excellent tool, but you must plan for noise mitigation, high energy costs, and routine maintenance to manage wear.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or heat-sensitive products: The risks of contamination and thermal damage are significant. You must carefully select liner and media materials or consider alternative technologies like a jet mill.
- If your primary focus is processing soft, fibrous, or tacky materials: A ball mill is unsuitable for your application, and you should investigate equipment designed for shearing or cutting, such as a knife mill.
Understanding these inherent limitations is the key to harnessing the powerful capabilities of a ball mill effectively.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Energy Consumption | Inefficient process; significant energy lost as heat and sound. |
| Product Contamination | Wear of grinding media and liners introduces impurities. |
| Significant Noise & Vibration | Creates a challenging operational environment. |
| Slow Processing Speed | Long cycles required to achieve fine particle sizes. |
| Heat Generation | Can damage heat-sensitive materials. |
| Material Incompatibility | Unsuitable for soft, fibrous, or tacky substances. |
Choosing the right milling equipment is critical for your lab's efficiency and product integrity. The disadvantages of a ball mill highlight the importance of matching the technology to your specific materials and purity requirements. At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to help you select the perfect solution—whether it's a ball mill for tough, abrasive materials or an alternative like a jet mill for high-purity applications. Let our expertise ensure your processes are efficient, cost-effective, and contamination-free. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the right equipment for your laboratory's unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- What is the primary function of the grinding process in LiCoO2/LSPS mixtures? Optimize Solid-State Battery Conductivity
- What is the preventive maintenance of ball mill? Ensure Maximum Uptime and Reliability
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- What affects ball mill efficiency? Optimize Grinding Speed, Media, and Material for Peak Performance



















