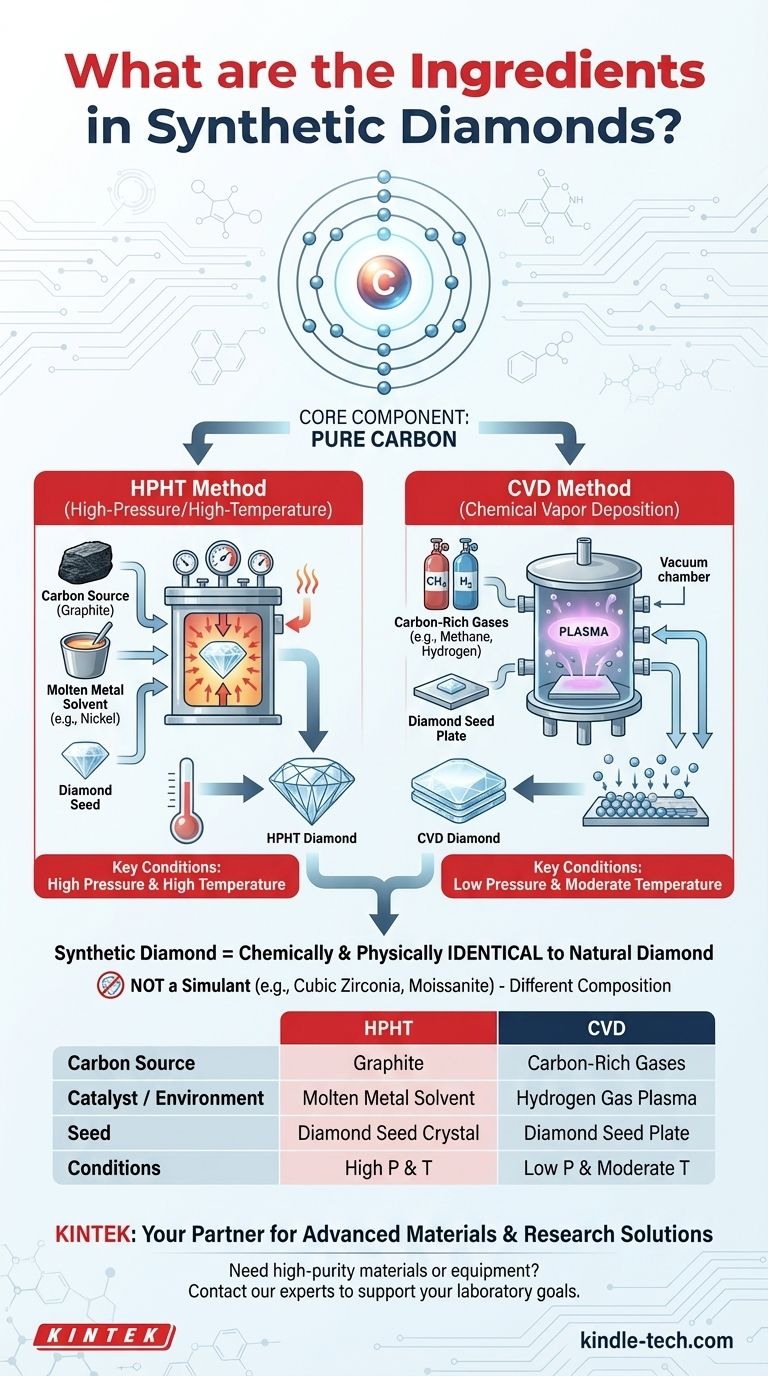
At their core, synthetic diamonds are made of a single ingredient: carbon. They are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds, sharing the same atomic structure. The difference is not in the substance but in the origin—synthetic diamonds are created in a laboratory, while natural diamonds are formed by geological processes.
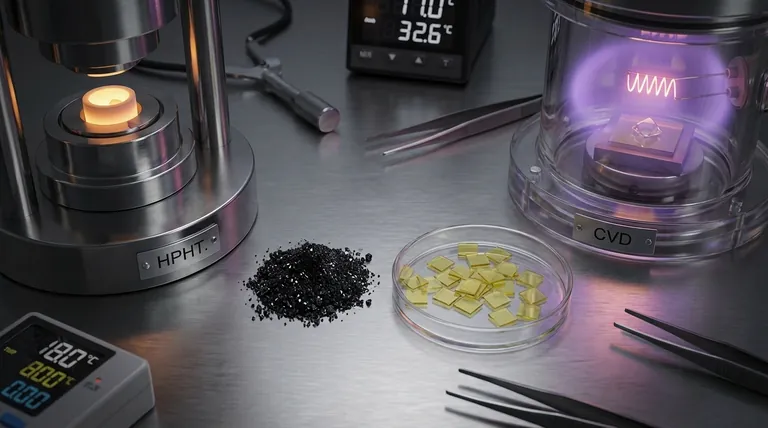
The term "synthetic" refers to the diamond's man-made origin, not its chemical makeup. The key "ingredients" are a source of pure carbon and a specific technological process, either high-pressure/high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), that forces that carbon to crystallize.

The Core Component: Pure Carbon
Identical Atomic Structure
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds are a crystalline allotrope of carbon. Their atoms are arranged in a rigid, tetrahedral lattice structure, which gives the diamond its exceptional hardness and brilliance.
The Starting Carbon Source
The carbon used to create synthetic diamonds can come from various sources. The method of synthesis determines the state of the starting carbon material.
The Two Primary "Recipes" for Diamond Synthesis
The vast majority of synthetic diamonds are created using one of two methods. Each uses a different set of "ingredients" and conditions to achieve the same result.
The HPHT Method (High-Pressure/High-Temperature)
This process mimics the natural geological conditions that form diamonds deep within the Earth.
The "ingredients" for HPHT are a carbon source (typically graphite), a molten metal solvent to act as a catalyst (like nickel), and a small, pre-existing diamond seed. These are placed in a chamber and subjected to immense pressure and heat, causing the carbon to dissolve and recrystallize onto the diamond seed.
The CVD Method (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
This method can be thought of as "growing" a diamond layer by layer in a controlled environment.
The "ingredients" for CVD are a diamond seed plate and carbon-rich gases (like methane and hydrogen). These gases are introduced into a vacuum chamber and heated, causing the carbon atoms to separate and deposit onto the cooler diamond seed plate, building up the crystal structure.
Understanding the "Synthetic" Distinction
What a Synthetic Diamond Is Not
A synthetic diamond is not a "fake" diamond or a simulant like cubic zirconia or moissanite. Those materials have entirely different chemical compositions and physical properties. A synthetic diamond is, by every scientific measure, a real diamond.
Traces of the Creation Process
While chemically identical, the different formation processes can leave behind microscopic clues to a diamond's origin.
Natural diamonds often contain tiny mineral inclusions—foreign materials trapped during their formation. In contrast, HPHT diamonds may contain trace metal inclusions from the solvent, and CVD diamonds can exhibit unique growth patterns or a specific type of fluorescence when exposed to UV light.
Alternative and Niche Methods
While HPHT and CVD dominate commercial production, a few other methods exist, primarily for industrial or research applications.
Detonation Synthesis
This method uses the detonation of carbon-containing explosives to create nanometer-sized diamond grains. These are primarily used for industrial abrasives and coatings, not for jewelry.
Ultrasonic Treatment
Researchers have demonstrated the ability to create diamonds by treating graphite with high-power ultrasound in a laboratory setting. However, this method currently has no commercial application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is chemical composition: Understand that synthetic and natural diamonds are fundamentally the same material—crystallized carbon.
- If your primary focus is identifying origin: The key is not the core ingredient but the subtle markers left by the manufacturing process, such as specific inclusions or fluorescence.
- If your primary focus is understanding value: The distinction lies entirely in their origin—one is a finite product of geology, the other a product of human technology.
Ultimately, the "ingredients" of a synthetic diamond are simply carbon atoms arranged in a perfect crystal, made possible by remarkable scientific processes.
Summary Table:
| Ingredient / Process | HPHT Method | CVD Method |
|---|---|---|
| Core Ingredient | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Carbon Source | Graphite | Carbon-Rich Gases (e.g., Methane) |
| Catalyst / Environment | Molten Metal Solvent (e.g., Nickel) | Hydrogen Gas Plasma |
| Seed | Diamond Seed Crystal | Diamond Seed Plate |
| Key Conditions | High Pressure & High Temperature | Low Pressure & Moderate Temperature |
Need high-purity materials or equipment for your research? Whether you're exploring advanced materials synthesis or require reliable lab consumables, KINTEK is your trusted partner. We specialize in providing the equipment and expertise to support your innovative work. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help achieve your laboratory goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- Are CVD diamonds better than HPHT? The Real Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Quality
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs














