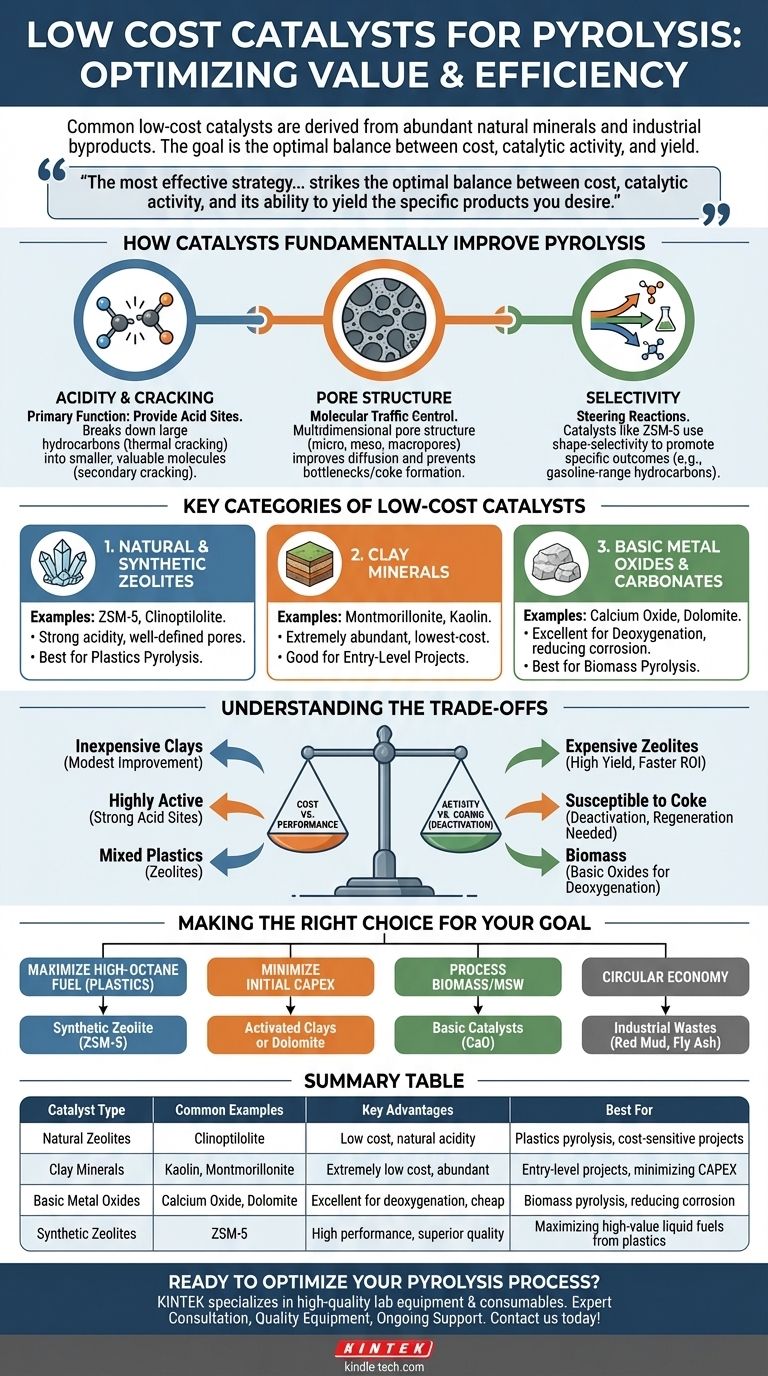
In practice, the most common low-cost catalysts for pyrolysis are derived from abundant natural minerals and industrial byproducts. These primarily include natural zeolites, various clay minerals like kaolin and montmorillonite, and basic metal oxides such as calcium oxide (from limestone). These materials are favored because they offer a significant performance boost over non-catalytic pyrolysis at a fraction of the cost of specialized commercial catalysts.
The most effective strategy for low-cost catalytic pyrolysis is not simply choosing the cheapest material, but selecting the one that strikes the optimal balance between cost, catalytic activity, and its ability to yield the specific products you desire from your particular feedstock.
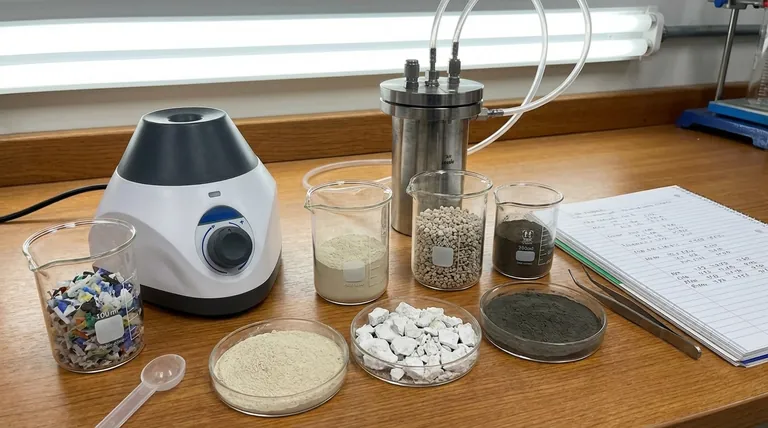

How Catalysts Fundamentally Improve Pyrolysis
Before comparing costs, it's crucial to understand what a catalyst is actually doing. In pyrolysis, catalysts create a more efficient chemical pathway for breaking down large, complex molecules (like plastics or biomass) into smaller, more valuable ones.
The Role of Acidity and Cracking
The primary function of many pyrolysis catalysts is providing acid sites. Large hydrocarbon chains from the initial thermal cracking are adsorbed onto these sites, where they are broken down further (secondary cracking) into smaller, more useful molecules, such as those found in gasoline or diesel. The strength and density of these acid sites heavily influence the final product distribution.
The Importance of Pore Structure
A catalyst's physical structure is as important as its chemical nature. The network of pores within a catalyst acts as a "molecular sieve," controlling which molecules can enter and react. A well-designed multidimensional pore structure (with micro-, meso-, and macropores) improves the diffusion of large molecules to the active sites and the escape of smaller product molecules, a concept known as improving molecular traffic control. This prevents bottlenecks that can lead to unwanted side reactions and coke formation.
Selectivity: Steering Toward Valuable Products
Different catalysts "steer" the chemical reactions toward different outcomes. For example, a catalyst like ZSM-5 is well-known for its shape-selectivity, promoting the formation of aromatic compounds and gasoline-range hydrocarbons due to its specific pore size. Others might be better suited for producing olefins (key chemical building blocks).
Key Categories of Low-Cost Catalysts
Low-cost options generally fall into three families, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages.
1. Natural and Synthetic Zeolites
Zeolites are crystalline aluminosilicates with a well-defined pore structure and strong acidity. They are the workhorses of the refining industry and are highly effective for plastics pyrolysis.
- ZSM-5: A synthetic zeolite, it is the benchmark for producing high-quality liquid fuels from plastics. While more expensive than natural options, its performance is often so superior that it justifies the cost.
- Natural Zeolites (e.g., Clinoptilolite): These are mined directly and are significantly cheaper than their synthetic counterparts. However, their performance can be less consistent due to impurities and a less ideal acid site distribution.
2. Clay Minerals
These are extremely abundant and represent one of the lowest-cost catalytic options available.
- Montmorillonite and Kaolin: These activated clays possess natural acidity and can enhance liquid yields and improve product quality compared to non-catalytic processes. They are a good entry-level choice where minimizing initial cost is the absolute priority. Their performance is generally modest compared to zeolites.
3. Basic Metal Oxides & Carbonates
These materials are particularly useful when pyrolyzing biomass, which has a high oxygen content.
- Calcium Oxide (CaO) & Calcium Carbonate (CaCO₃): Sourced from cheap limestone, these basic materials are excellent for deoxygenation. They neutralize acidic compounds (like acetic acid) formed during biomass pyrolysis, reducing equipment corrosion and upgrading the resulting bio-oil by removing oxygen.
- Dolomite: A naturally occurring mineral of calcium magnesium carbonate, it provides a mix of basic sites and acts as a mild cracking catalyst.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The "best" low-cost catalyst is entirely dependent on your specific goals and constraints. There is no single answer.
Cost vs. Performance
This is the central dilemma. An inexpensive natural clay might cost a few hundred dollars per ton, while a high-performance synthetic ZSM-5 zeolite could cost several thousand. The clay provides a marginal improvement, while the zeolite can dramatically increase the yield of high-value gasoline-range fuels, potentially offering a much faster return on investment.
Activity vs. Deactivation by Coking
Highly active catalysts with strong acid sites can sometimes be too effective, leading to excessive cracking that produces light gases instead of valuable liquids. They can also be more susceptible to coke formation—a layer of carbon that deposits on the catalyst's surface, blocking active sites and deactivating it. Managing regeneration cycles is a key operational challenge.
Feedstock Compatibility
The nature of your feedstock dictates your catalyst choice. Processing mixed plastic waste benefits greatly from the cracking power of zeolites. In contrast, pyrolyzing agricultural residue or wood waste almost demands the use of basic oxides like CaO to handle the high oxygen content.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on a clear understanding of your economic model and desired output.
- If your primary focus is maximizing high-octane liquid fuel from plastics: Invest in a synthetic zeolite like ZSM-5; the superior product quality and yield will likely justify the higher upfront cost.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital expenditure: Start with activated natural clays or mined dolomite, accepting a trade-off in liquid yield and quality.
- If your primary focus is processing biomass or municipal solid waste: Prioritize basic catalysts like calcium oxide (from limestone) to deoxygenate the pyrolytic vapors and protect your equipment.
- If your primary focus is a circular economy model: Explore using industrial wastes like red mud or fly ash as catalysts, but be prepared for extensive testing to manage their inherent variability.
Ultimately, selecting the right catalyst is a strategic engineering decision that directly balances process economics against product value.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst Type | Common Examples | Key Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Zeolites | Clinoptilolite | Low cost, natural acidity | Plastics pyrolysis, cost-sensitive projects |
| Clay Minerals | Kaolin, Montmorillonite | Extremely low cost, abundant | Entry-level projects, minimizing capital expenditure |
| Basic Metal Oxides | Calcium Oxide (from limestone), Dolomite | Excellent for deoxygenation, cheap | Biomass pyrolysis, reducing equipment corrosion |
| Synthetic Zeolites | ZSM-5 | High performance, superior product quality | Maximizing high-value liquid fuels from plastics |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process with the right catalyst?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Our experts can help you select the ideal catalyst for your specific feedstock and desired products, balancing performance with cost-effectiveness.
We offer:
- Expert Consultation: Get tailored advice on catalyst selection for plastics, biomass, or mixed waste.
- Quality Equipment: Reliable pyrolysis systems and analytical tools for testing catalyst performance.
- Ongoing Support: From initial setup to process optimization.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your pyrolysis efficiency and product yields. Let's build a solution that fits your budget and goals.
Get in touch with our pyrolysis experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- Can a horizontal furnace be installed vertically? The Critical Safety Risks Explained
- What is the role of vacuum annealing in a tube furnace for Cr-Al-C coatings? Optimize Phase Transformation Safely
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace? Optimize Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanomaterial Calcination
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What are the key functions of a laboratory tube furnace in perovskite studies? Mastering Atmospheric Stability Control
- What is RTA rapid temperature annealing? Achieve Precise Material Processing in Seconds
- What issues are addressed by using tube furnaces or muffle furnaces for the co-sintering of LLZO? Optimize Solid-State Battery Interfaces
- Will quartz dissolve in water? The truth about its durability for your home and lab.



















