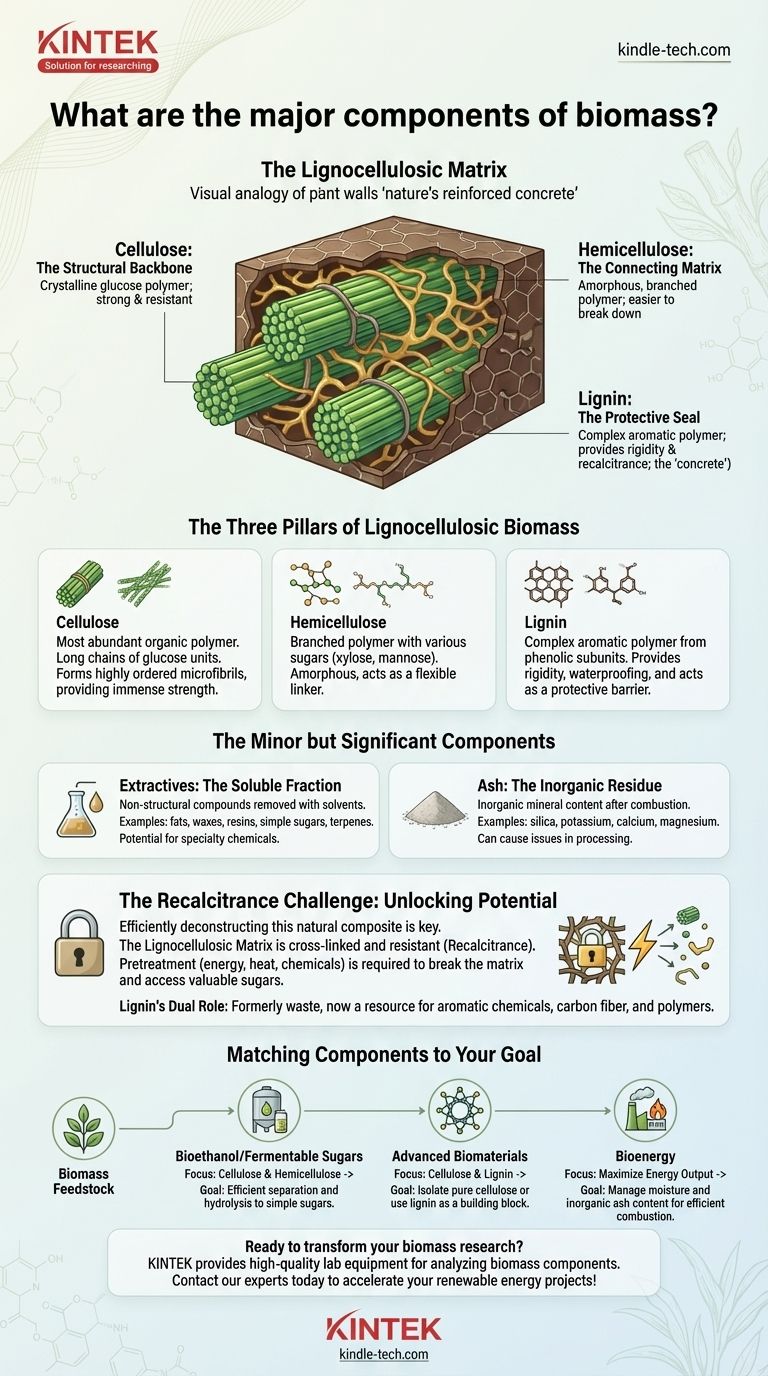
At its core, biomass is a complex composite material primarily made of three major organic polymers: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. These components are organized into a durable matrix, with smaller amounts of non-structural materials called extractives and inorganic minerals known as ash. The specific ratio of these components varies significantly depending on the biomass source, such as wood, grass, or agricultural waste.
The fundamental challenge—and opportunity—of using biomass lies not just in knowing its components, but in understanding that they are intricately locked together. Efficiently deconstructing this natural composite is the key to converting raw biomass into valuable fuels, chemicals, and materials.
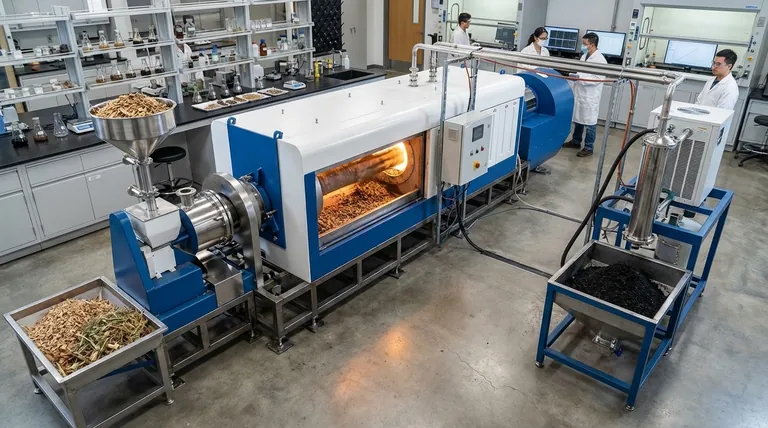

The Three Pillars of Lignocellulosic Biomass
Most plant biomass is referred to as lignocellulosic biomass. This name points directly to its three main structural components, each with a distinct chemical nature and function.
Cellulose: The Structural Backbone
Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, forming the primary structural framework of plant cell walls. It is a long-chain polymer composed exclusively of glucose units linked end-to-end.
These chains bundle together into highly ordered, crystalline structures called microfibrils. This crystalline arrangement gives cellulose its immense strength and makes it highly resistant to chemical and biological breakdown.
Hemicellulose: The Connecting Matrix
Hemicellulose is a branched polymer made up of various five-carbon and six-carbon sugars, including xylose, mannose, galactose, and arabinose, in addition to glucose.
Unlike the crystalline and uniform nature of cellulose, hemicellulose is amorphous and has a lower molecular weight. This makes it significantly easier to break down (hydrolyze) into its constituent sugars compared to cellulose. It acts as a flexible linker, connecting cellulose microfibrils to each other and to lignin.
Lignin: The Protective Seal
Lignin is a highly complex and irregular aromatic polymer, fundamentally different from the carbohydrate-based structures of cellulose and hemicellulose. It is built from phenolic subunits.
Functionally, lignin provides structural rigidity, stiffness, and waterproofing to the plant cell wall. In the context of biorefining, lignin is the most recalcitrant component, acting as a physical barrier that protects carbohydrates from enzymatic attack and often releasing inhibitory compounds during processing.
The Minor but Significant Components
While making up a smaller fraction of the total mass, these other components have a major impact on how biomass can be processed and utilized.
Extractives: The Soluble Fraction
This group includes a wide variety of non-structural organic compounds that can be removed with solvents. Examples include fats, waxes, resins, simple sugars, and terpenes.
The presence and composition of extractives can be a source of high-value specialty chemicals or, conversely, a contaminant that complicates downstream processing.
Ash: The Inorganic Residue
Ash is the inorganic mineral content that remains after complete combustion of the biomass. It consists of elements like silica, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
High ash content is often undesirable, as it can lead to slagging and fouling in combustion equipment and may deactivate catalysts used in chemical conversion processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Recalcitrance Challenge
The primary obstacle in most biomass conversion pathways is overcoming its natural resistance to deconstruction, a property known as recalcitrance.
The Lignocellulosic Matrix
Cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin are not simply mixed; they are physically and chemically cross-linked into a robust natural composite. Think of it as nature's version of reinforced concrete: cellulose acts as the high-strength rebar, while hemicellulose and lignin form the surrounding matrix that holds everything together.
The Cost of Deconstruction
To access the valuable cellulose and hemicellulose for conversion into fermentable sugars, this matrix must be broken apart. This step, known as pretreatment, often requires significant inputs of energy, heat, and chemicals.
The efficiency and cost of pretreatment are the most critical economic factors determining the viability of a biorefinery.
Lignin's Dual Role
Historically viewed as a problematic waste product, lignin is increasingly seen as a potential resource. While it hinders the conversion of carbohydrates, its aromatic structure makes it a potential renewable source for producing aromatic chemicals, carbon fiber, and advanced polymers. However, developing cost-effective methods for lignin valorization remains a major area of research.
Matching Components to Your Goal
The optimal strategy for using biomass depends entirely on which components you want to leverage and what end product you desire.
- If your primary focus is bioethanol or fermentable sugars: Your goal is to efficiently separate and hydrolyze cellulose and hemicellulose into simple sugars while minimizing the inhibitory effects of lignin.
- If your primary focus is advanced biomaterials: Your goal may be to isolate highly pure cellulose for applications like nanocrystalline cellulose or to use lignin as a building block for new functional polymers.
- If your primary focus is direct combustion for bioenergy: Your goal is to maximize energy output, which means you must carefully manage moisture and inorganic ash content to ensure efficient and clean combustion.
Unlocking the immense potential of biomass begins with a clear understanding of its fundamental chemical composition.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Structural backbone | Crystalline glucose polymer; strong & resistant |
| Hemicellulose | Connecting matrix | Amorphous, branched polymer; easier to break down |
| Lignin | Protective seal | Complex aromatic polymer; provides rigidity & recalcitrance |
| Extractives | Soluble compounds | Fats, waxes, resins; source of specialty chemicals |
| Ash | Inorganic minerals | Silica, potassium; can complicate processing |
Ready to transform your biomass research or production process? Understanding the composition of your feedstock is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for analyzing and processing biomass components like cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Whether you're developing biofuels, biomaterials, or optimizing combustion, our solutions help you achieve accurate and efficient results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and accelerate your renewable energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Polyethylene Separator for Lithium Battery
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process






