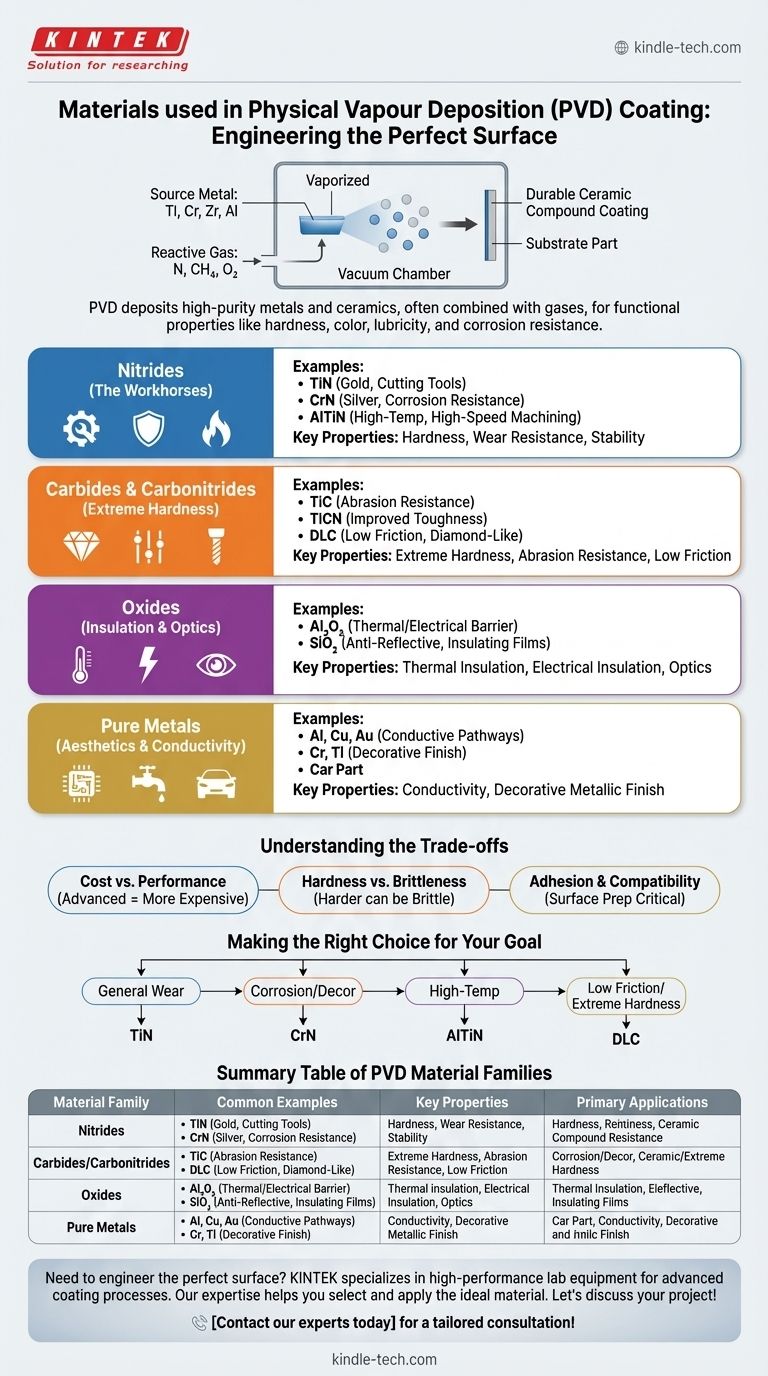
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a process that can deposit a wide variety of materials, primarily metals and ceramics. The most common materials used for PVD coatings are high-purity, solid metals like titanium, chromium, zirconium, and aluminum. These are often combined with reactive gases like nitrogen or methane during the deposition process to form extremely hard and durable ceramic compound coatings directly on a part's surface.
The specific material chosen for a PVD coating is not an arbitrary decision. It is a deliberate engineering choice driven entirely by the desired functional properties of the final product, such as hardness, color, lubricity, or corrosion resistance.

The Core Families of PVD Materials
To understand the options, it's best to think of PVD materials in terms of their primary chemical families. Each family offers a distinct profile of performance characteristics.
Nitrides (The Workhorses)
Nitride coatings are formed by introducing nitrogen gas into the vacuum chamber, which reacts with the vaporized source metal. They are the most common PVD coatings due to their excellent balance of hardness, wear resistance, and stability.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): Often considered the industry standard. It's known for its gold color, general-purpose hardness, and good lubricity, making it ideal for cutting tools and decorative finishes.
- Chromium Nitride (CrN): Offers superior corrosion resistance compared to TiN and has a silver, metallic appearance. It is frequently used in high-humidity environments or for components that require a combination of wear and rust protection.
- Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN): This advanced composite coating is designed for high-temperature applications. The aluminum forms a protective oxide layer at high heat, making AlTiN a top choice for high-speed machining and dry cutting tools.
Carbides and Carbonitrides (For Extreme Hardness)
By introducing carbon-containing gases (like methane or acetylene), even harder coatings can be formed. These are specified for the most demanding wear applications.
- Titanium Carbide (TiC): One of the hardest ceramic materials, offering exceptional abrasion resistance.
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN): This coating combines the properties of TiN and TiC, resulting in higher hardness than TiN but with less internal stress than TiC, improving toughness.
- Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC): A unique class of amorphous carbon material that exhibits some of the properties of natural diamond. DLC coatings provide an unmatched combination of low friction and high hardness.
Oxides (For Insulation and Optics)
While less common for wear resistance, oxide coatings are critical in other fields. They are formed by introducing oxygen as the reactive gas.
- Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃): Used as a thermal barrier or electrical insulator due to its high stability and low conductivity.
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂): A key material in optics and electronics for creating anti-reflective layers or insulating films.
Pure Metals (For Aesthetics and Conductivity)
Sometimes, the goal is simply to deposit a thin layer of a pure metal without any reactive gases.
- Aluminum, Copper, Gold: Commonly deposited in the electronics industry to create conductive pathways on circuits.
- Chromium and Titanium: Used in decorative applications for a bright, durable metallic finish on everything from automotive parts to household fixtures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PVD material involves balancing performance requirements with practical limitations. There is no single "best" coating for every situation.
Cost vs. Performance
More complex, multi-layered, or advanced composite coatings like AlTiN or DLC require more sophisticated equipment and process controls. This makes them significantly more expensive to apply than a standard, general-purpose TiN coating.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
There is often a direct trade-off between a coating's hardness and its toughness. Extremely hard coatings can sometimes be brittle, making them susceptible to chipping or flaking if the underlying part flexes or is subjected to sharp impacts.
Adhesion and Substrate Compatibility
The success of any PVD coating depends on its ability to adhere to the base material (the substrate). Some coatings adhere better to certain materials than others, and proper surface preparation of the part before it enters the coater is absolutely critical to the final result.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary requirement should guide your material selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose wear resistance and a classic gold finish: Titanium Nitride (TiN) is the most proven and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance or a chrome-like decorative finish: Chromium Nitride (CrN) is the ideal choice for its toughness and chemical stability.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance, such as for dry machining: Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) provides the necessary thermal barrier to protect the tool.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction and extreme hardness: A Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating is the premium choice for high-performance components.
Ultimately, understanding these material options empowers you to engineer a surface with specific, predictable, and highly optimized properties for your exact need.
Summary Table:
| Material Family | Common Examples | Key Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrides | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) | Hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance (CrN), high-temp stability (AlTiN) | Cutting tools, decorative finishes, high-speed machining |
| Carbides/Carbonitrides | Titanium Carbide (TiC), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Extreme hardness, abrasion resistance, low friction (DLC) | Demanding wear applications, high-performance components |
| Oxides | Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Thermal insulation, electrical insulation, anti-reflective | Electronics, optics, thermal barriers |
| Pure Metals | Aluminum, Chromium, Gold, Copper | Conductivity, decorative metallic finish | Electronics (circuits), decorative coatings |
Need to engineer the perfect surface for your application?
The right PVD coating can dramatically enhance your product's performance, durability, and aesthetics. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables for advanced coating processes. Our expertise helps you select and apply the ideal material—whether it's TiN for general wear resistance, CrN for superior corrosion protection, or DLC for extreme hardness and low friction.
Let's discuss your project requirements and how our solutions can bring your specifications to life. Contact our experts today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control
- How much does CVD diamond equipment cost? A Breakdown of Investment from Lab to Production
- How thick is diamond coating? Achieve Unprecedented Precision with Ultra-Thin Films
- What are the applications of CVD diamonds? From Jewelry to High-Tech Tools
- What are the advantages of the CVD diamond growing process compared to the HPHT process? Master Precision & Efficiency



















