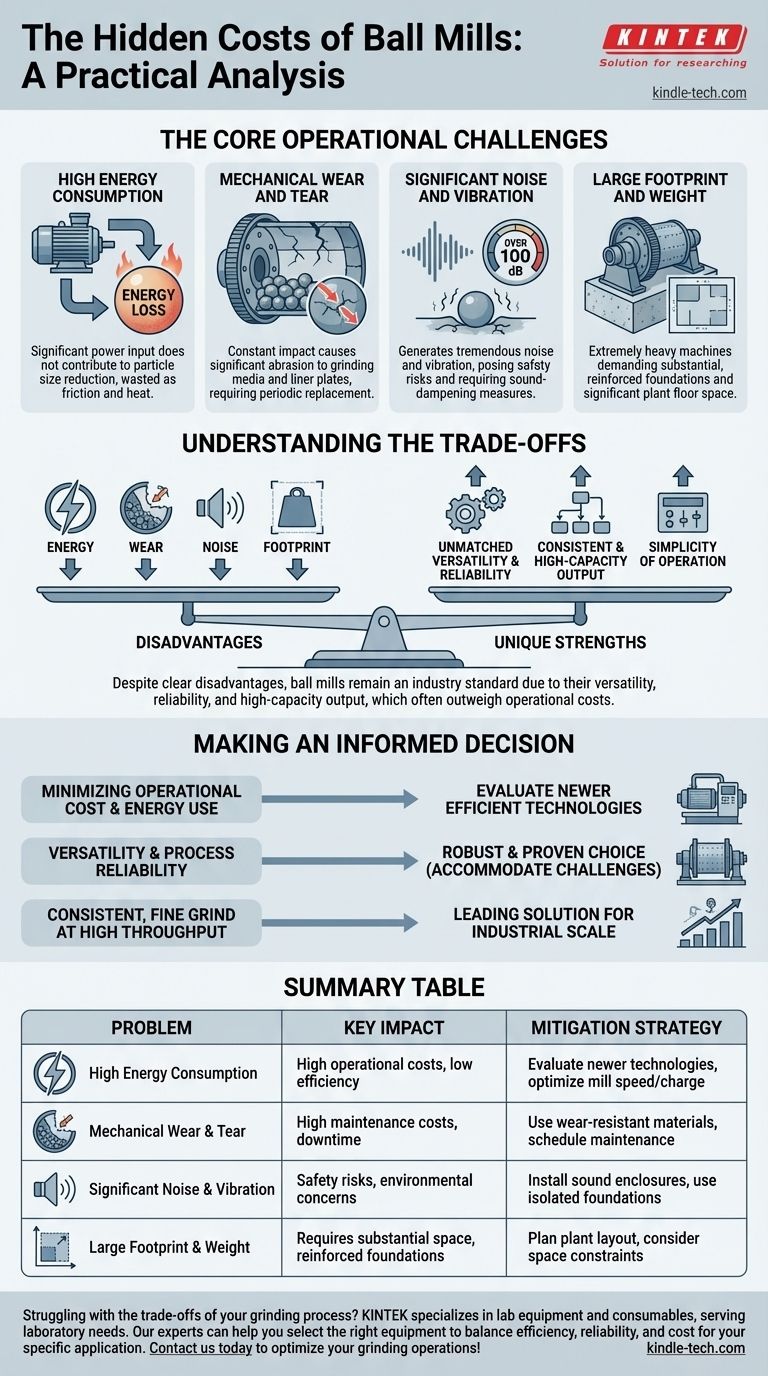
From a practical standpoint, the primary problems with ball mills are their significant energy consumption, high operational noise, and the considerable wear and tear on their internal components. These issues are a direct result of their fundamental grinding mechanism, which relies on the brute-force impact and attrition of heavy grinding media.
While ball mills are known for their operational challenges, particularly in energy use and noise, these are often accepted trade-offs. Their disadvantages are weighed against their exceptional reliability, versatility, and ability to produce a consistently fine product at high capacities.

The Core Operational Challenges
A ball mill is a simple, powerful tool, but its simplicity comes with inherent inefficiencies. Understanding these challenges is key to managing them effectively.
High Energy Consumption
A ball mill is not an energy-efficient machine. A significant portion of the electrical energy supplied to the motor does not contribute to particle size reduction.
This energy is instead lost as friction between the grinding media, heat generated within the slurry or powder, and the noise and vibration of the tumbling charge.
Mechanical Wear and Tear
The constant tumbling and impact of the grinding media (the balls) against the material and the mill's inner lining causes significant abrasion.
This means both the grinding media and the liner plates are consumable parts. They must be periodically replaced, adding to the operational cost and requiring scheduled downtime for maintenance.
Significant Noise and Vibration
The process of large, heavy steel balls cascading inside a rotating steel drum generates a tremendous amount of noise, often exceeding 100 decibels.
This is a major operational and safety concern, typically requiring sound-dampening enclosures, isolated foundations, and mandatory hearing protection for personnel.
Large Footprint and Weight
Ball mills are extremely heavy machines, requiring substantial, reinforced concrete foundations to support their weight and manage operational vibrations.
Their large physical size can dictate the layout of an entire processing plant, demanding significant floor space and vertical clearance for operation and servicing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Ball mills Remain an Industry Standard
Despite these clear disadvantages, ball mills have been an industrial staple for over a century. Their persistent use is a testament to their unique strengths, which often outweigh their operational costs.
Unmatched Versatility and Reliability
Ball mills are exceptionally versatile. They can be used to grind nearly any type of ore or industrial mineral, operating either wet or dry.
Their mechanical design is incredibly simple and robust. This leads to very high uptime and reliability, which is a critical factor in large-scale industrial operations where downtime is extremely costly.
Consistent and High-Capacity Output
Once a ball mill is operating under stable conditions, it produces a very consistent particle size distribution.
This permanence of fineness is crucial for downstream processes that depend on a predictable feed. They are also capable of handling immense throughput, making them ideal for high-capacity plants.
Simplicity of Operation
From a process control standpoint, ball mills are relatively simple to operate and service.
Adjusting performance is straightforward (e.g., changing media size, charge volume, or slurry density), and the maintenance procedures for replacing liners and media are well-established.
Making an Informed Decision
Choosing the right grinding technology requires balancing your primary objective against the inherent characteristics of the machine.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost and energy use: You should carefully evaluate newer, more efficient grinding technologies, as the high energy consumption of a ball mill will be a significant factor.
- If your primary focus is versatility and process reliability for a wide range of materials: A ball mill is a robust and proven choice, provided you can accommodate its energy, space, and noise requirements.
- If your primary focus is achieving a consistent, fine grind at high throughput: The ball mill remains a leading solution, as its design inherently delivers repeatable results at an industrial scale.
Ultimately, understanding these inherent challenges is the first step toward effectively managing them and leveraging the ball mill's proven strengths.
Summary Table:
| Problem | Key Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| High Energy Consumption | High operational costs, low efficiency | Evaluate newer grinding technologies, optimize mill speed/charge |
| Mechanical Wear & Tear | High maintenance costs, downtime for liner/media replacement | Use wear-resistant materials, schedule preventative maintenance |
| Significant Noise & Vibration | Safety risks, environmental concerns, requires hearing protection | Install sound enclosures, use isolated foundations |
| Large Footprint & Weight | Requires substantial space and reinforced foundations | Plan plant layout accordingly, consider space constraints |
Struggling with the trade-offs of your grinding process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to balance efficiency, reliability, and cost for your specific application. Contact us today to optimize your grinding operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What function does an industrial disc mill perform for energy sugarcane? Enhance Your Pretreatment Yields Today
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination
- What is the role of an industrial dry grinder in the surface modification of 304L stainless steel? Expert Insights
- What is the role of an agate mortar in LATP solid electrolyte preparation? Ensure Purity and Homogeneous Mixing
- What is the purpose of a colloid mill? Achieve Ultra-Fine Emulsions and Dispersions
- Why is an agate mortar used for manual grinding? Ensure Purity in LLZO Electrolyte Mixing
- What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a milling operation? Optimize Your Grinding Circuit for Peak Performance
- How does the use of grinding equipment benefit iron-substituted manganese oxide? Optimize Energy Storage Performance



















