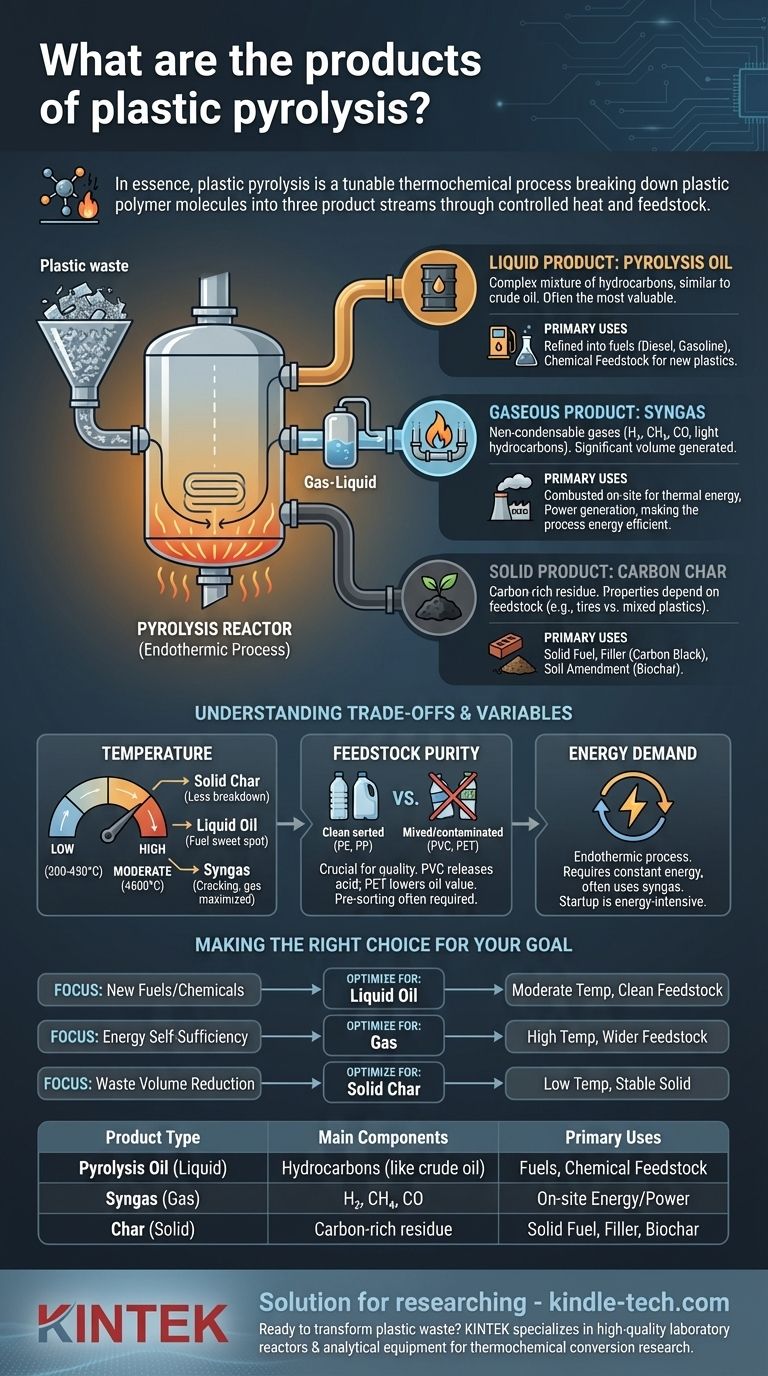
In essence, plastic pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that breaks down large plastic polymer molecules into three distinct product streams. These products consist of a liquid hydrocarbon mixture known as pyrolysis oil, a non-condensable synthetic gas (syngas), and a solid carbonaceous residue called char.
Think of plastic pyrolysis not as a single, fixed reaction, but as a tunable process. By carefully controlling the temperature, feedstock, and process duration, you can strategically shift the output to favor gas, liquid, or solid products, thereby determining the ultimate economic and environmental value of the operation.

Deconstructing the Pyrolysis Outputs
The distribution and specific composition of the products are not accidental. They are a direct result of the type of plastic being processed and the precise conditions within the reactor.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil
The primary liquid output is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, often called pyrolysis oil or plastic oil. This is typically the most valuable product stream.
This oil is compositionally similar to crude oil but can contain a wide variety of compounds depending on the input plastic.
It can be refined through processes like distillation and hydrotreating to produce transportation fuels such as diesel and gasoline, or it can serve as a chemical feedstock for producing new plastics.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
Pyrolysis also generates a significant volume of non-condensable gases, collectively known as syngas.
This gas is a mixture of combustible components like hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), carbon monoxide (CO), and other light hydrocarbons (C₂-C₄), along with inert components like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and nitrogen (N₂).
In most commercial operations, this syngas is not sold. Instead, it is captured and combusted on-site to provide the thermal energy required to heat the pyrolysis reactor, making the process more energy-efficient and economically viable.
The Solid Product: Carbon Char
The final product is a solid, carbon-rich residue known as char or, in some contexts, carbon black.
Its properties depend heavily on the feedstock. For example, pyrolysis of tires yields a product very similar to commercial carbon black, which can be used as a pigment or a reinforcing filler in rubber products.
Char from mixed plastics has lower purity but can still be used as a solid fuel, similar to coal, or as a soil amendment (biochar), though its quality for this purpose must be carefully verified.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
Achieving a desired product slate is a balancing act. The process is sensitive to several key factors, each presenting a trade-off.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the single most important variable for determining the product yield.
- Low Temperatures (300-450°C): These conditions favor the production of solid char, as the polymer chains are broken down less completely.
- Moderate Temperatures (450-600°C): This is the typical range for maximizing the yield of liquid pyrolysis oil, representing the "sweet spot" for fuel production.
- High Temperatures (>600°C): At very high temperatures, the liquid hydrocarbons "crack" further into smaller molecules, maximizing the yield of syngas.
The Challenge of Feedstock Purity
The type and cleanliness of the plastic feedstock dramatically impact the quality of the final products, especially the oil.
Plastics like PVC (polyvinyl chloride) release corrosive hydrochloric acid when heated, which can damage equipment and contaminate the oil. PET (polyethylene terephthalate) contains oxygen, which ends up in the oil and lowers its fuel value.
For this reason, high-quality oil production often requires extensive pre-sorting of plastic waste to isolate desirable feedstocks like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).
The Inherent Energy Demand
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a constant input of energy to break the chemical bonds in the plastic.
As mentioned, a well-designed system mitigates this by using its own byproduct (syngas) as the primary fuel source. However, the initial startup and process control still demand significant energy, which is a key factor in the overall economic viability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal approach to pyrolysis depends entirely on your end objective.
- If your primary focus is creating new fuels or chemical feedstocks: Optimize for liquid oil production by using moderate temperatures (450-600°C) and a clean, sorted polyolefin feedstock (PE, PP).
- If your primary focus is energy self-sufficiency or on-site power generation: Optimize for gas production by using higher temperatures (>600°C), which allows you to process a wider and potentially less pure range of feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction and creating a stable solid: Utilize lower temperatures to maximize the yield of carbon char, which can be used as a solid fuel, filler, or soil amendment.
Ultimately, mastering plastic pyrolysis is about controlling these variables to transform a complex waste problem into a set of predictable, valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Main Components | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil (Liquid) | Hydrocarbons similar to crude oil | Refined into fuels (diesel, gasoline) or chemical feedstock |
| Syngas (Gas) | Hydrogen (H₂), Methane (CH₄), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Combusted on-site to power the pyrolysis process |
| Char (Solid) | Carbon-rich residue | Used as a solid fuel, filler (e.g., carbon black), or soil amendment |
Ready to transform plastic waste into valuable resources?
The right lab equipment is critical for researching and optimizing your plastic pyrolysis process. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory reactors, temperature control systems, and analytical equipment tailored for thermochemical conversion research.
We help our laboratory customers:
- Accurately simulate pyrolysis conditions to predict product yields.
- Analyze the composition and quality of pyrolysis oil, syngas, and char.
- Scale up your process from bench-top experiments to pilot plants.
Let our expertise in lab equipment support your innovation in waste-to-energy and circular economy solutions. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific pyrolysis research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















