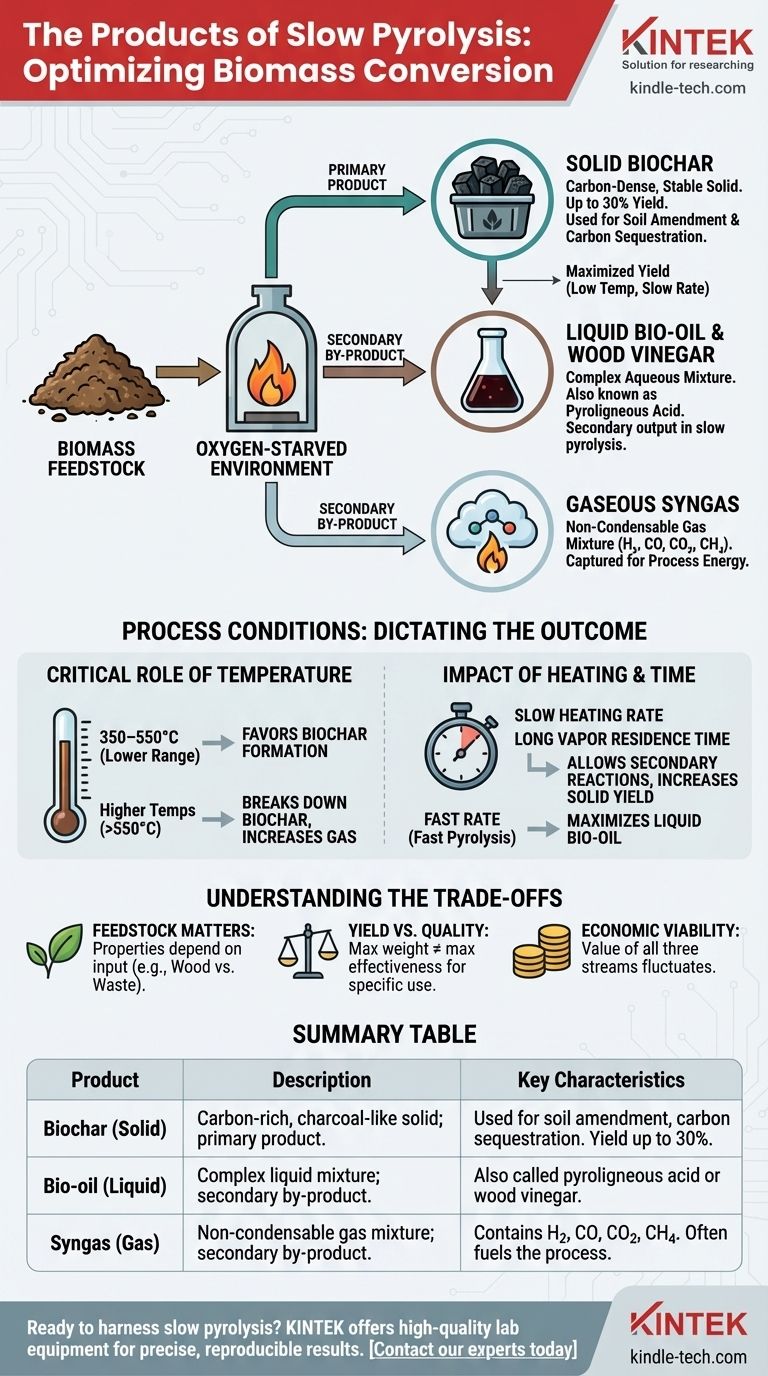
Slow pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that breaks down biomass in an oxygen-starved environment. Its primary products are a solid, carbon-rich material called biochar, a liquid mixture known as bio-oil or wood vinegar, and a collection of non-condensable gases often referred to as syngas. The exact proportion and characteristics of these products are not fixed; they are highly dependent on the process conditions and the initial biomass feedstock.
While slow pyrolysis produces solids, liquids, and gases, it is best understood as a process specifically engineered to maximize the yield of solid biochar. The liquid and gas fractions are typically considered secondary products, whose value and composition can be tuned but are not the primary goal.
Deconstructing the Three Product Categories
Slow pyrolysis systematically separates biomass into three distinct states of matter: a stable solid, a complex liquid, and a combustible gas.
The Primary Product: Solid Biochar
Biochar is the carbon-dense, charcoal-like solid that remains after the volatile components of the biomass have been driven off. This is the main target product of slow pyrolysis.
Yields are typically maximized under these conditions, often reaching up to 30% of the original feedstock's dry weight. The primary application for biochar is as a soil amendment to improve fertility and, critically, to act as a highly stable form of sequestered carbon.
The Liquid By-product: Bio-oil & Wood Vinegar
As the biomass heats, various organic compounds vaporize. When these hot vapors are cooled, they condense into a dark, aqueous liquid fraction.
This liquid is a complex mixture, sometimes called bio-oil, pyroligneous acid, or wood vinegar. While fast pyrolysis is optimized to maximize this liquid fuel, in slow pyrolysis, it is a secondary output.
The Gaseous Fraction: Syngas
Not all the vapors will condense into a liquid. The remaining non-condensable gases form a mixture known as syngas.
This gas includes hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and other light hydrocarbons. In many systems, this syngas is captured and combusted to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction, creating a more energy-efficient process.
Why Process Conditions Dictate the Outcome
You cannot simply "do" pyrolysis and get a standard result. The output is a direct function of how you control the reaction. Understanding these levers is crucial for producing a desired product.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The highest treatment temperature is the single most influential factor. Lower temperatures (e.g., 350–550°C) and slower heating rates favor the formation of solid biochar.
As temperatures increase beyond this range, the biochar itself begins to break down, which decreases the solid yield and significantly increases the gas yield.
The Impact of Heating Rate and Residence Time
Slow pyrolysis is defined by its slow heating rate and long vapor residence time. This allows for secondary reactions where volatile vapors can re-condense and polymerize onto the surface of the char, further increasing the solid yield.
This is the direct opposite of fast pyrolysis, which uses extremely rapid heating to "crack" the biomass molecules into smaller components that form the liquid bio-oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing for one product or characteristic often comes at the expense of another. Recognizing these compromises is key to designing an effective pyrolysis strategy.
Feedstock Is Not Interchangeable
The properties of the final products are highly dependent on the initial biomass. Woody biomass will produce a different type of biochar with a different yield compared to agricultural waste like corn stover or manure, even under identical process conditions.
Yield vs. Quality
Maximizing the sheer weight of biochar produced is not always the main goal. The objective is often to create "tailor-made" biochar with specific properties, such as high porosity or a particular pH, for a given application like soil remediation.
The process conditions that maximize yield might not be the same ones that produce the highest-quality or most effective biochar for a specific end-use.
Economic Viability
The value proposition for slow pyrolysis is not always clear-cut. The market price for biochar, bio-oil, and the value of the syngas can fluctuate and are highly dependent on local economies and regulations. An operation's success often hinges on finding value in all three product streams.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis setup depends entirely on your primary objective. Use these principles to guide your approach.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil amendment: Prioritize slow heating rates and lower-to-moderate temperatures to maximize the yield of stable, high-carbon biochar.
- If your primary focus is process energy efficiency: Design the system to capture and combust the syngas fraction, using its energy to power the decomposition and reduce external energy inputs.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels: Slow pyrolysis is the wrong tool; you must investigate fast pyrolysis, which is specifically optimized to maximize bio-oil yield.
Ultimately, viewing slow pyrolysis not as a fixed recipe but as a tunable platform is the key to creating valuable, targeted products from biomass.

Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich, charcoal-like solid; primary product. | Used for soil amendment, carbon sequestration. Yield up to 30% of feedstock weight. |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Complex liquid mixture; secondary by-product. | Also called pyroligneous acid or wood vinegar. |
| Syngas (Gas) | Non-condensable gas mixture; secondary by-product. | Contains H₂, CO, CO₂, CH₄. Often used to fuel the pyrolysis process. |
Ready to harness the power of slow pyrolysis in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for biomass conversion and analysis. Whether you're researching biochar production, bio-oil characterization, or process optimization, our reliable tools help you achieve precise and reproducible results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's pyrolysis needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















