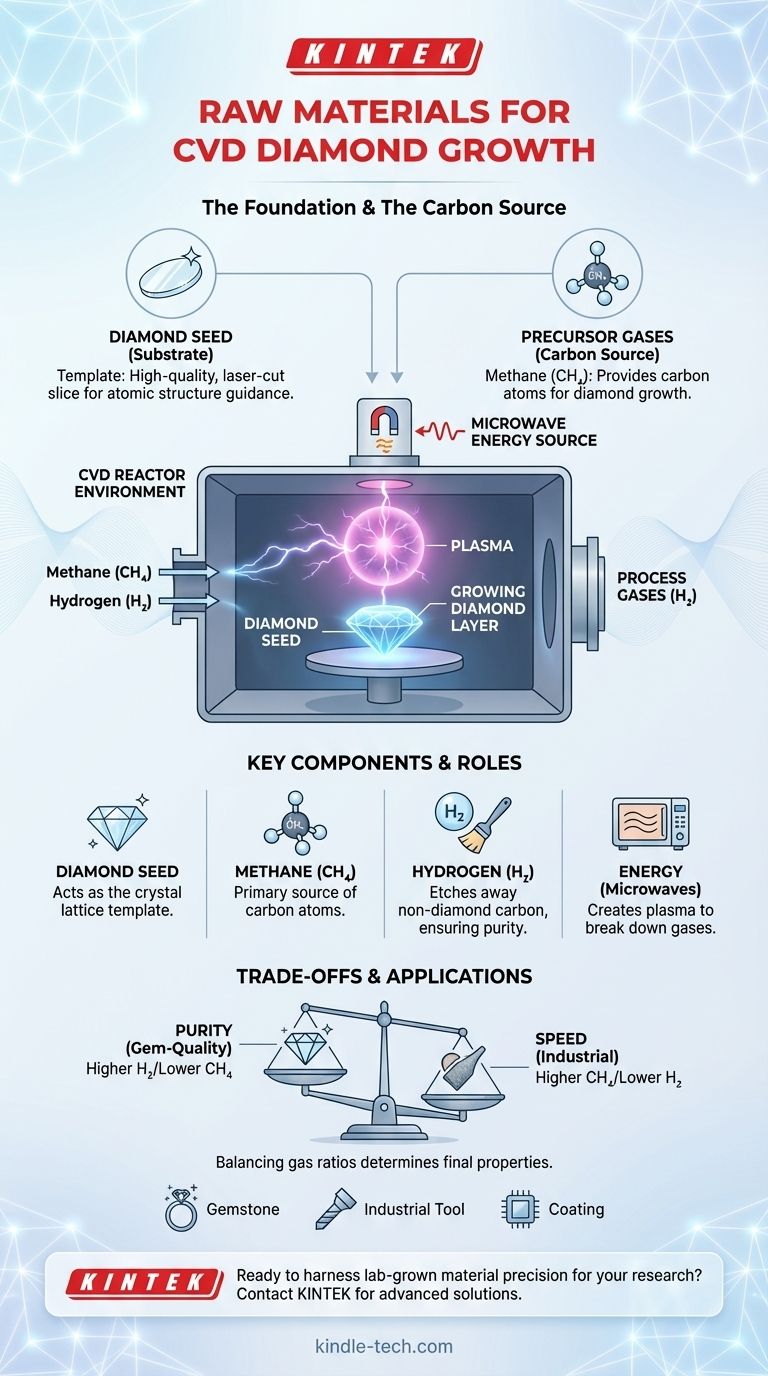
At its core, the creation of a lab-grown diamond via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) relies on two fundamental raw materials. These are a substrate to act as a foundation, which is typically a thin slice of a pre-existing diamond, and a precise mixture of gases, primarily a carbon-rich gas like methane. The process uses energy to break down these gases and deposit pure carbon atoms onto the diamond seed, growing a new diamond layer by layer.
The question of raw materials for CVD diamonds reveals a deeper truth: modern diamond synthesis is not about sourcing a rare element, but about meticulously controlling an environment. The "raw materials" are less about the substances themselves and more about the process of transforming simple, abundant gases into a perfectly structured crystal.
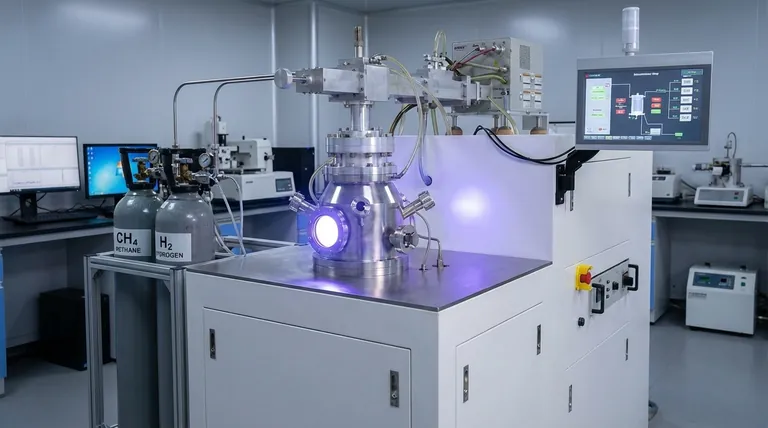

The Core Components of CVD Diamond Growth
The CVD process is a sophisticated form of atomic-level construction. Each component is chosen for a specific role in building the diamond's crystal lattice.
The Foundation: The Diamond Seed
The entire process begins with a substrate, most commonly referred to as a diamond seed. This is a very thin, laser-cut slice of a high-quality diamond, often from a previously grown lab diamond.
This seed acts as a perfect template. As carbon atoms from the gas phase deposit onto its surface, they follow the seed's existing crystal structure, ensuring the new material grows as a diamond and not another form of carbon, like graphite.
The Carbon Source: Precursor Gases
The actual carbon that forms the diamond comes from a precursor gas. The most common choice is methane (CH4).
Methane is an ideal source because it is a simple, readily available hydrocarbon gas. It provides the necessary carbon atoms in a form that can be easily broken down within the CVD reactor.
The Catalyst and Purifier: Process Gases
In addition to the carbon source, other gases are introduced, with hydrogen (H2) being the most critical. While hydrogen doesn't become part of the final diamond, it plays two essential roles.
First, it helps create and stabilize the plasma environment required for the reaction. Second, and more importantly, hydrogen selectively etches away any non-diamond carbon (like graphite) that might form, ensuring the final product is a pure, high-quality diamond. In some processes, small amounts of oxygen or other gases may also be used to fine-tune the growth.
The Environment: Turning Gas into Diamond
The raw materials are useless without the precise environmental conditions that facilitate the chemical reaction. The CVD chamber is a highly controlled vacuum environment.
Creating the Plasma State
The chamber is flooded with the methane and hydrogen gas mixture at very low pressure. Energy, typically in the form of microwaves, is then introduced.
This intense energy strips electrons from the gas molecules, ionizing them into a glowing ball of superheated gas known as plasma. Within this plasma, the methane molecules break apart, freeing the carbon atoms to participate in the growth process.
Temperature and Pressure Control
The process occurs at a high temperature, typically around 800°C to 950°C. This temperature provides the necessary thermal energy for the carbon atoms to bond correctly to the diamond seed's lattice.
This combination of low pressure and high temperature mimics the conditions found in interstellar gas clouds, allowing for the slow, methodical, layer-by-layer deposition of carbon. The entire growth process can take anywhere from two to four weeks, depending on the desired size and quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The selection and management of these raw materials involve critical trade-offs that directly impact the final diamond.
Purity vs. Growth Speed
The ratio of methane to hydrogen in the gas mixture is a delicate balance. A higher concentration of methane can significantly speed up the growth rate, but it also increases the risk of defects and the formation of non-diamond carbon, which can impact the stone's clarity and color.
The Quality of the Seed
The final diamond is only as good as the seed it grew from. Any imperfections, strains, or dislocations in the initial diamond seed's crystal lattice will be propagated into the new diamond as it grows. This is why sourcing high-purity, defect-free seeds is critical for producing top-tier gem-quality diamonds.
Versatility of the CVD Process
It is important to recognize that this principle of decomposing a gas to form a solid is not unique to diamonds. The CVD method is a platform technology used to create other high-purity materials. For example, the semiconductor industry uses CVD to deposit polysilicon from silane gas (SiH4) to manufacture microchips and solar cells.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "right" raw materials and process parameters depend entirely on the intended application of the final diamond.
- If your primary focus is gem-quality clarity and color: The process will require a top-tier, flawless diamond seed and a hydrogen-rich gas mixture, prioritizing purity over growth speed.
- If your primary focus is rapid production for industrial use: The process may use a higher concentration of methane for faster growth, as microscopic internal defects are less critical than hardness and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is creating a durable coating: The "seed" might be a non-diamond substrate like a metal tool bit, and the process is optimized for strong adhesion and creating a hard, polycrystalline diamond film.
Ultimately, the CVD process is a remarkable demonstration of how simple, abundant materials can be transformed into one of the most valuable and durable substances known to science.
Summary Table:
| Raw Material | Role in CVD Diamond Growth |
|---|---|
| Diamond Seed | Acts as a template for the new diamond's crystal structure to grow upon. |
| Methane (CH₄) | The primary carbon source that provides the atoms to build the diamond. |
| Hydrogen (H₂) | A critical process gas that purifies the growth environment by etching away non-diamond carbon. |
| Energy (Microwaves) | Creates a plasma state to break down gas molecules and initiate the deposition process. |
Ready to harness the precision of lab-grown materials for your research or production? The controlled synthesis of high-purity materials like CVD diamond is at the heart of modern innovation. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve these results. Whether you are developing new semiconductor materials, creating durable industrial coatings, or growing high-quality crystals, our expertise can support your project from concept to completion. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of CVD coating? Achieve Superior Hardness and Uniform Coverage
- What are the fundamentals of CVD? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Deposition
- What is ion beam sputtering deposition technique? Achieve Superior Thin Film Quality and Precision
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is deposition of a thin solid film on a substrate from vapor precursors? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD
- How is CVD coating done? A Step-by-Step Guide to Superior Surface Engineering
- What is the vacuum deposition of film? A Guide to Ultra-Thin, High-Purity Coatings
- What is the deposition rate of sputtering? A Guide to Controlling Your Thin Film Process



















