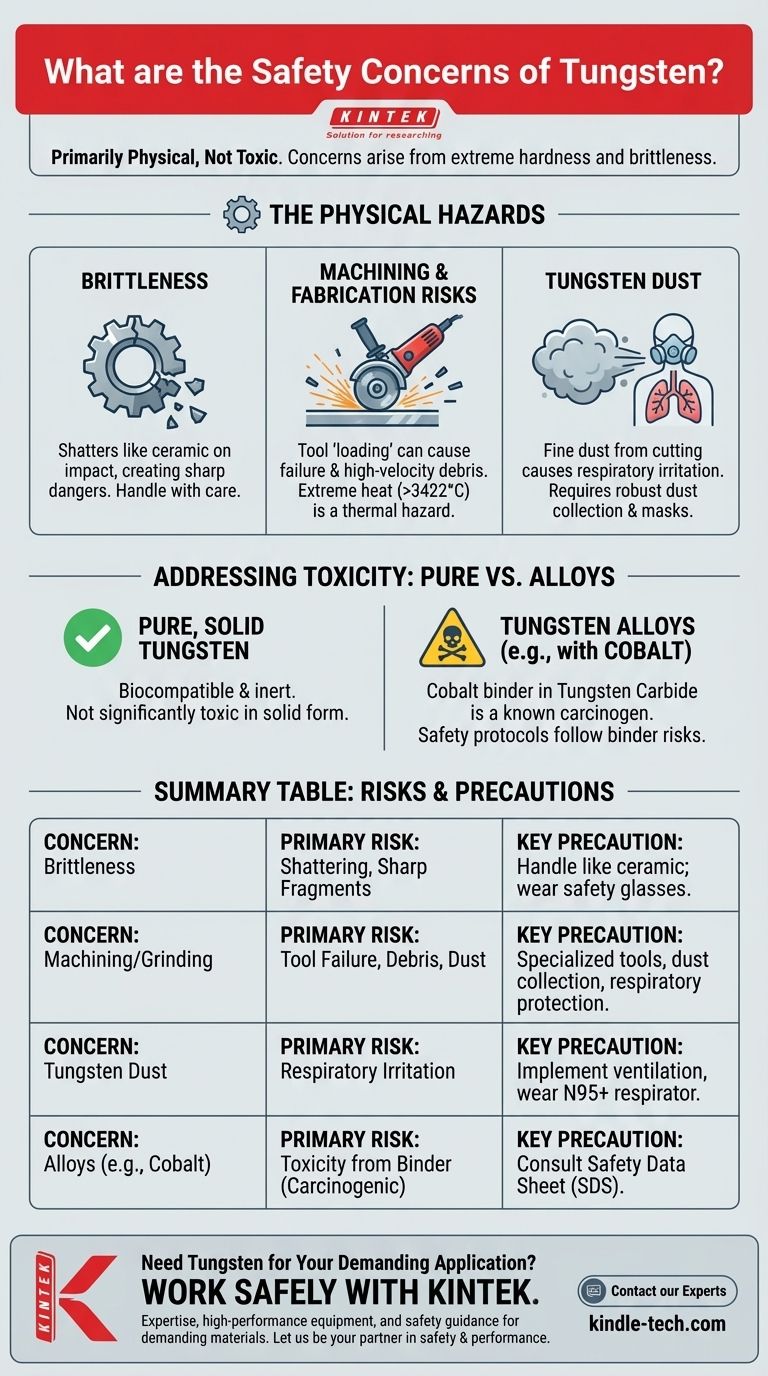
Contrary to what its industrial strength might suggest, the primary safety concerns with pure tungsten are not related to toxicity but to its physical properties. Solid tungsten is generally considered non-toxic and biologically inert. The real hazards arise from its extreme hardness and its tendency to be brittle at room temperature, which creates significant risks during machining and handling.
The core safety issue with tungsten is managing its physical state. Its brittleness can lead to shattering, and the dust generated during machining can pose an inhalation risk, even if the solid material itself is relatively benign.

The Physical Hazards of Working with Tungsten
While tungsten's strength is its greatest asset, that same strength is the source of its primary safety challenges. Understanding its unique physical behavior is critical.
The Brittleness Problem
Tungsten has a ductile-to-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) that is often above room temperature.
This means that at normal temperatures, it can behave more like a ceramic than a metal. If dropped or struck, it can shatter, creating sharp, dangerous fragments.
Risks During Machining and Fabrication
Attempting to machine pure tungsten presents unique and hazardous challenges.
The material can compact into the spaces between the grit on cutting tools, a condition known as loading. This renders the tool ineffective and can lead to unpredictable tool failure, potentially launching debris at high velocity.
Furthermore, its exceptionally high melting point (3422 °C / 6192 °F) means that processes like sintering or hot working occur at extreme temperatures, introducing significant thermal and radiation hazards.
The Hazard of Tungsten Dust
Any machining, grinding, or cutting process will generate fine dust particles.
While solid tungsten has low toxicity, inhaling fine metallic dust of any kind can lead to respiratory irritation and long-term lung issues. This is a standard industrial hygiene concern that is particularly relevant given the difficulty of machining tungsten.
Addressing the Question of Toxicity
It's crucial to differentiate between pure tungsten and its various alloys and compounds, as their health profiles can differ significantly.
Pure, Solid Tungsten
In its solid, pure metallic form, tungsten is considered biocompatible and is not associated with significant toxicity. It does not readily react with the body.
Tungsten Alloys and Compounds
Safety considerations change when tungsten is alloyed with other metals. For instance, tungsten carbide tools often use cobalt as a binder.
Inhaled cobalt dust is a known respiratory sensitizer and is classified as a probable human carcinogen. Therefore, the safety protocols for working with tungsten carbide are often dictated by the hazards of cobalt, not the tungsten itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to work with tungsten means accepting a difficult trade-off between its unparalleled performance and its demanding handling requirements.
The Benefit: Unmatched Performance
Engineers select tungsten for its extreme hardness, density, and the highest melting point of any pure metal. These properties make it indispensable for high-performance applications like aerospace components, electrical filaments, and radiation shielding.
The Cost: A Demanding and Hazardous Material
The cost of this performance is difficulty and danger in fabrication. Its brittleness requires careful handling, and its resistance to machining necessitates specialized tools, coolants, and safety precautions to manage tool failure and hazardous dust.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your safety strategy should be dictated by the form of tungsten you are using and the process you are performing.
- If your primary focus is general handling: Treat solid tungsten parts as if they are brittle ceramics; avoid sharp impacts and always wear safety glasses to protect against potential shattering.
- If your primary focus is machining or grinding: Implement robust dust collection and ventilation systems, and always use appropriate respiratory protection (e.g., an N95 respirator or better).
- If your primary focus is working with tungsten alloys: Obtain the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the specific alloy and follow all precautions related to its constituent materials, such as cobalt or nickel.
Ultimately, ensuring safety when working with tungsten is about respecting its formidable physical properties.
Summary Table:
| Safety Concern | Primary Risk | Key Precaution |
|---|---|---|
| Brittleness | Shattering on impact, sharp fragments | Handle like ceramic; wear safety glasses |
| Machining/Grinding | Tool failure, high-velocity debris, dust generation | Use specialized tools, dust collection, respiratory protection |
| Tungsten Dust | Respiratory irritation, long-term lung issues | Implement ventilation, wear N95+ respirator |
| Alloys (e.g., with Cobalt) | Toxicity from binder materials (carcinogenic risk) | Consult Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for specific alloy |
Need Tungsten for Your Demanding Application? Work with KINTEK Safely.
Navigating the safety challenges of tungsten requires expertise and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing the robust solutions and safety guidance needed for working with demanding materials like tungsten. Our team understands the risks of brittleness, machining, and dust, and we can help you source the right tools and implement safe handling protocols.
Let KINTEK be your partner in safety and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your project's specific tungsten needs and ensure a safe, efficient workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- Why are high-intensity planetary ball mills preferred for reducing the crystallinity of lignocellulose?
- What is the specific role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Ag-doped sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- What is the function of a high-energy planetary ball mill in zirconium-doped CaO synthesis? Optimize Material Stability
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the preparation of NiCr-Al2O3-SrCO3 composite powders? Enhanced Homogeneity
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis



















