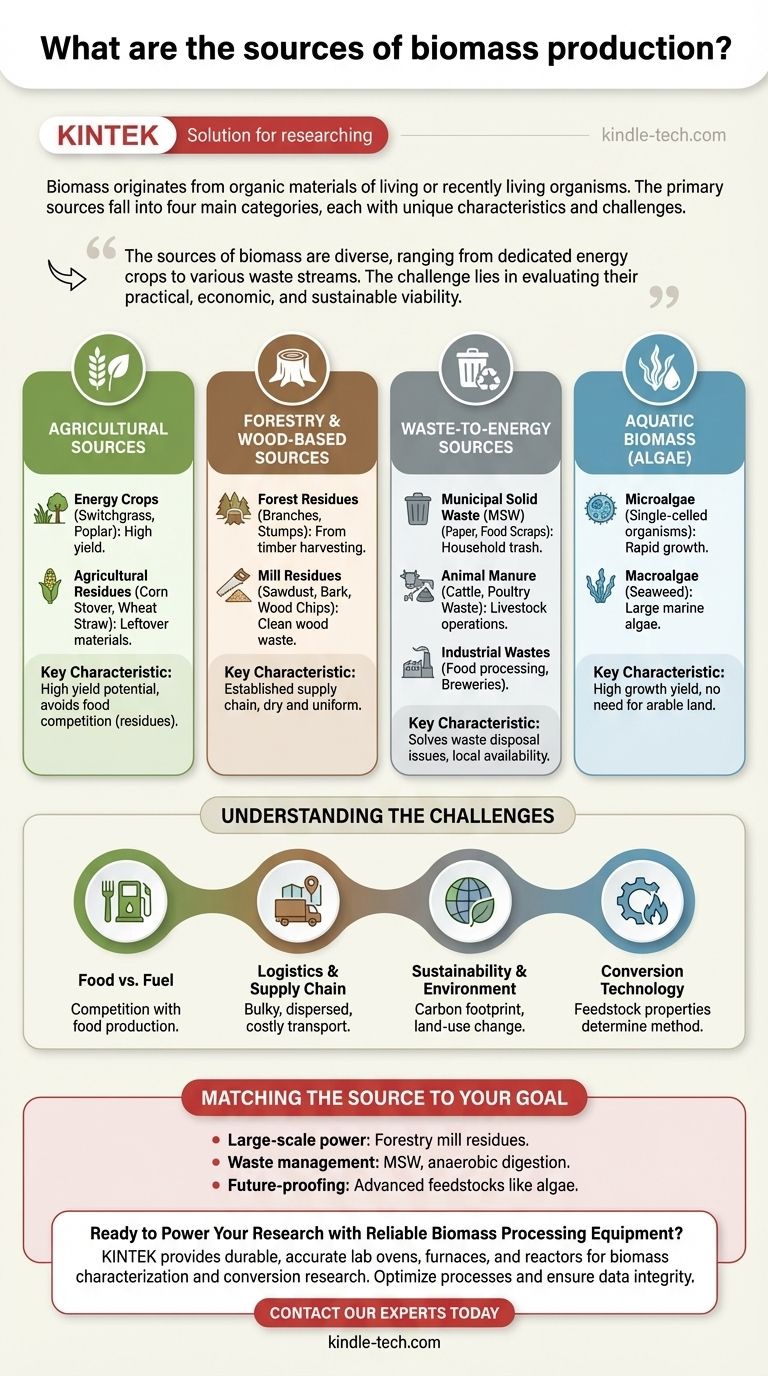
Biomass originates from a wide range of organic materials derived from living or recently living organisms. The primary sources can be broadly categorized into four main groups: agricultural materials, forestry and wood waste, municipal and industrial waste streams, and aquatic plants like algae. These materials, known as feedstocks, are the foundational components of the entire bioenergy supply chain.
The sources of biomass are diverse, ranging from dedicated energy crops to various waste streams. The central challenge lies not in simply identifying these sources, but in evaluating their practical, economic, and sustainable viability for energy production based on logistics, land use, and conversion technology.

The Primary Categories of Biomass Feedstock
To understand the potential of bioenergy, you must first understand the characteristics of its raw materials. Each category of feedstock comes with a unique profile of availability, cost, and technical requirements.
Agricultural Sources
This is one of the largest and most varied categories, encompassing materials grown specifically for energy as well as byproducts from food production.
- Energy Crops: These are plants grown explicitly for their energy content. They include fast-growing grasses like switchgrass and miscanthus, as well as short-rotation woody crops like poplar and willow. Their key advantage is high yield per acre.
- Agricultural Residues: These are the leftover materials from traditional farming. Common examples include corn stover (stalks and leaves), wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse. Using residues avoids direct land competition with food crops.
Forestry and Wood-Based Sources
Wood has been humanity's oldest fuel source and remains a cornerstone of modern bioenergy, primarily sourced from managed forests and industrial byproducts.
- Forest Residues: This includes branches, treetops, and stumps left in the forest after timber harvesting. Utilizing this material can reduce wildfire risk while providing an energy source.
- Mill Residues: This is "clean" wood waste generated by sawmills, furniture factories, and pulp mills. Materials like sawdust, bark, and wood chips are highly desirable because they are often dry, uniform, and already collected at a central facility.
Waste-to-Energy Sources
This category turns a societal problem—waste disposal—into an energy solution. These sources are often readily available in populated areas.
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): This refers to the organic portion of household and commercial trash. It includes paper, cardboard, food scraps, and yard trimmings. Converting MSW to energy diverts waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions.
- Animal Manure: Waste from livestock operations like cattle ranches and poultry farms is a potent source of biomass. It is most commonly processed through anaerobic digestion to produce biogas, a renewable natural gas.
- Industrial Wastes: Organic waste streams from food processing plants, breweries, and wastewater treatment facilities can also be captured and converted into energy.
Algae and Aquatic Biomass
Often considered a "third generation" feedstock, algae represents a high-potential future source of biomass that avoids many of the limitations of land-based crops.
- Microalgae: These are single-celled, microscopic organisms that can be cultivated in ponds or bioreactors. They grow extremely quickly and can produce oils suitable for conversion into biodiesel and jet fuel.
- Macroalgae (Seaweed): Large marine algae can be farmed offshore, eliminating the need for fresh water and arable land. It is a promising source for producing biofuels and biogas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
No feedstock is a perfect solution. A clear-eyed assessment of the limitations is critical for developing a viable bioenergy project.
The "Food vs. Fuel" Dilemma
Using agricultural land to grow energy crops can create competition with food production, potentially impacting food prices and security. This is a primary ethical and economic concern, driving interest in non-food feedstocks like residues and algae.
Logistics and Supply Chain Complexity
Biomass is bulky, has a low energy density, and is often geographically dispersed. Collecting, transporting, and storing feedstocks like corn stover or forest residues can be costly and energy-intensive, significantly impacting the overall economic viability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
While often termed "carbon neutral," the true carbon footprint of biomass depends on its entire lifecycle. Factors like emissions from transportation, fertilizer use for energy crops, and the impacts of land-use change must be carefully accounted for. Sustainable harvesting practices are essential to prevent deforestation and biodiversity loss.
Conversion Technology Compatibility
The physical and chemical properties of a feedstock—such as moisture content, ash content, and chemical composition—determine its suitability for different energy conversion technologies. Wet waste like manure is ideal for anaerobic digestion, while dry, woody biomass is better suited for combustion or gasification.
Matching the Source to Your Goal
The optimal biomass source is entirely dependent on your specific objective, scale, and location.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent power generation: You will likely rely on established feedstocks like forestry mill residues and, where sustainable, dedicated energy crops where robust supply chains can be developed.
- If your primary focus is waste management and local energy production: Municipal solid waste (MSW) and animal manure processed through anaerobic digestion are ideal solutions that address environmental problems while creating value.
- If your primary focus is future-proofing and sustainable fuel innovation: Advanced feedstocks like algae offer a long-term path to high-yield energy production with minimal conflict over land and water resources.
Understanding these sources and their inherent trade-offs is the first step toward building a truly effective and sustainable bioenergy strategy.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Sources | Energy crops (switchgrass), agricultural residues (corn stover) | High yield potential, avoids food competition (residues) |
| Forestry & Wood Waste | Forest residues, mill residues (sawdust) | Established supply chain, dry and uniform |
| Waste-to-Energy | Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), animal manure | Solves waste disposal issues, local availability |
| Aquatic Biomass | Microalgae, macroalgae (seaweed) | High growth yield, no need for arable land |
Ready to Power Your Research with Reliable Biomass Processing Equipment?
Navigating the complexities of biomass feedstocks requires robust and precise laboratory equipment. Whether you are analyzing the energy content of agricultural residues, testing the conversion efficiency of algae, or developing new waste-to-energy processes, KINTEK provides the durable and accurate lab equipment you need.
We specialize in supplying ovens, furnaces, reactors, and consumables essential for biomass characterization, pyrolysis, gasification, and other thermal conversion research. Our products help researchers and engineers like you optimize processes, ensure data integrity, and accelerate the development of sustainable bioenergy solutions.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your biomass research and development workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does the use of a vacuum freeze dryer benefit cys-CDs powder preparation? Preserve Nanoparticle Integrity
- What are the advantages of using freeze drying for phase change materials with biopolymer shells? Optimize Stability
- What is the application of freeze dryers in the preparation of enzyme catalysts? Preserve Bioactivity and Porosity
- How does liquid nitrogen provide physical protection for heat-sensitive drugs? Ensure Superior Biological Integrity
- What are the applications of vacuum freeze-drying technology? Unlock Superior Preservation Across Industries



















