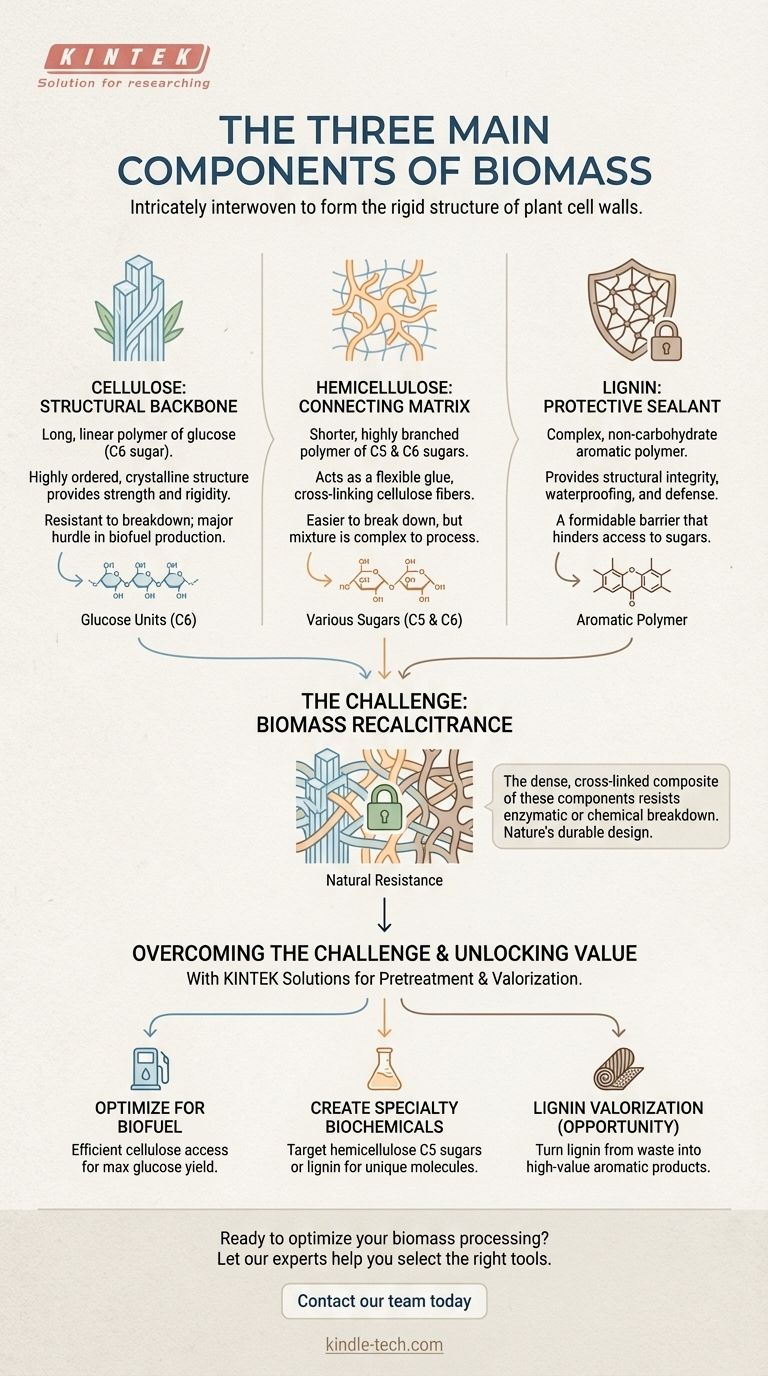
The three primary components of virtually all plant biomass are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. These organic polymers are not simply mixed together; they are intricately interwoven to form the rigid structure of plant cell walls. Understanding the distinct role of each component is the key to unlocking the energy and materials stored within biomass.
The core challenge in using biomass isn't just knowing its components, but in overcoming their complex and highly resistant structure. This natural "recalcitrance," created by the interaction of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, dictates the entire strategy for converting biomass into fuel or other valuable products.

Deconstructing the Building Blocks of Biomass
To effectively utilize biomass, we must first understand its constituent parts as if we were disassembling a machine. Each component has a unique structure, function, and potential.
Cellulose: The Structural Backbone
Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, forming the primary structural element of plant cell walls.
It is a long, linear polymer made of repeating glucose (a six-carbon, or C6, sugar) units. These long chains are bundled together into highly ordered, crystalline fibers that give plants their strength and rigidity.
This crystalline structure makes cellulose very strong and resistant to chemical breakdown, which is a major hurdle in biofuel production. The ultimate goal is often to break cellulose down into its glucose components for fermentation.
Hemicellulose: The Connecting Matrix
Hemicellulose is a shorter, highly branched polymer that acts as a flexible matrix, cross-linking cellulose fibers together and providing structural support.
Unlike cellulose, it is composed of various five-carbon (C5) and six-carbon (C6) sugars, such as xylose, mannose, and galactose.
Its amorphous, branched structure makes it much easier to break down (hydrolyze) than cellulose. However, processing its mixture of different sugars can be more complex.
Lignin: The Protective Sealant
Lignin is a complex, non-carbohydrate aromatic polymer that provides structural integrity, waterproofing, and defense against microbial attack.
It acts as a rigid "glue," encrusting and binding the cellulose and hemicellulose fibers together. This creates a formidable physical barrier.
Lignin does not contain sugars and actively hinders the enzymes and chemicals used to access the cellulose and hemicellulose. This makes its removal a critical step in many biorefinery processes.
Why This Composition Creates a Challenge
The specific arrangement of these three components is what makes biomass such a robust material. This robustness, while excellent for the plant, is the central problem for its industrial use.
The Concept of Recalcitrance
Biomass recalcitrance is the natural resistance of plant cell walls to being deconstructed by enzymes or chemical treatments.
This resistance is a direct result of the dense, cross-linked composite of crystalline cellulose, amorphous hemicellulose, and rigid lignin. Nature designed this structure to be durable, and we must expend significant energy to take it apart.
The Goal of Pretreatment
Nearly all biomass conversion processes begin with a pretreatment step. The primary goal of pretreatment is to overcome recalcitrance.
Effective pretreatment disrupts the lignin and hemicellulose sheath, increasing the surface area of the cellulose and making it accessible to the enzymes that can break it down into fermentable sugars.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Biomass Utilization
Processing biomass is a constant balancing act. The ideal approach depends on the end goal, as aggressive methods can have unintended consequences.
The Purity vs. Yield Dilemma
Harsh pretreatment methods can effectively remove lignin but may also degrade some of the valuable sugars in the cellulose and hemicellulose. This reduces the overall yield of the final product.
The challenge is to find a process that is strong enough to break apart the structure without destroying the target components.
The Lignin Problem (and Opportunity)
Historically, lignin has been treated as a major waste product, often burned for low-grade heat. Its presence inhibits access to valuable sugars, making it a "problem" that must be removed.
However, modern biorefineries view lignin as an opportunity. As a vast source of renewable aromatic chemicals, lignin valorization—turning it into high-value products like carbon fiber, bioplastics, or specialty chemicals—is key to making biomass conversion economically sustainable.
Feedstock Variability
The exact ratio of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin varies significantly between different types of biomass. For example, hardwoods have more cellulose and less lignin than softwoods, while agricultural residues like corn stover have a different composition altogether.
This means there is no universal, one-size-fits-all process. Each type of feedstock requires a tailored approach to maximize efficiency and product yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to processing biomass is defined entirely by which component holds the most value for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is biofuel production (e.g., ethanol): Your goal is to efficiently access the cellulose to maximize glucose yield, which requires effective delignification and hemicellulose removal.
- If your primary focus is creating specialty biochemicals: You might target the hemicellulose for its unique C5 sugars or develop processes to convert lignin into high-value aromatic platform molecules.
- If your primary focus is direct combustion for heat and power: The individual chemical components matter less than the overall energy content, moisture, and ash content of the raw biomass.
Understanding that biomass is not a single substance but a complex composite is the foundational step toward unlocking its immense potential.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Structural backbone | Linear polymer of glucose; highly crystalline and strong. |
| Hemicellulose | Connecting matrix | Branched polymer of various sugars; amorphous and easier to hydrolyze. |
| Lignin | Protective sealant | Complex aromatic polymer; provides rigidity and resistance. |
Ready to optimize your biomass processing? Understanding the intricate balance of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin is crucial for efficient conversion into biofuels, biochemicals, or materials. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for effective biomass pretreatment, analysis, and valorization. Let our experts help you select the right tools to overcome recalcitrance and maximize your yield. Contact our team today to discuss your specific biomass challenges and goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
People Also Ask
- What are the two methods that can be used to prevent corrosion of a metal? Barrier vs. Sacrificial Protection Explained
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- What are the barriers to plastic recycling? The Economic, Material, and Technical Hurdles Explained
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection















