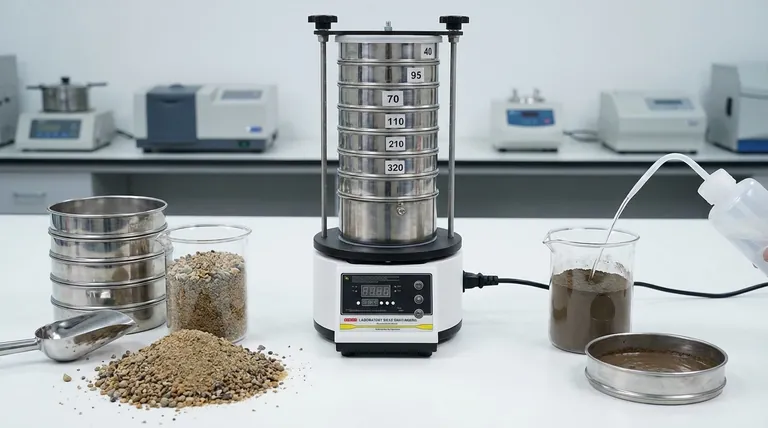
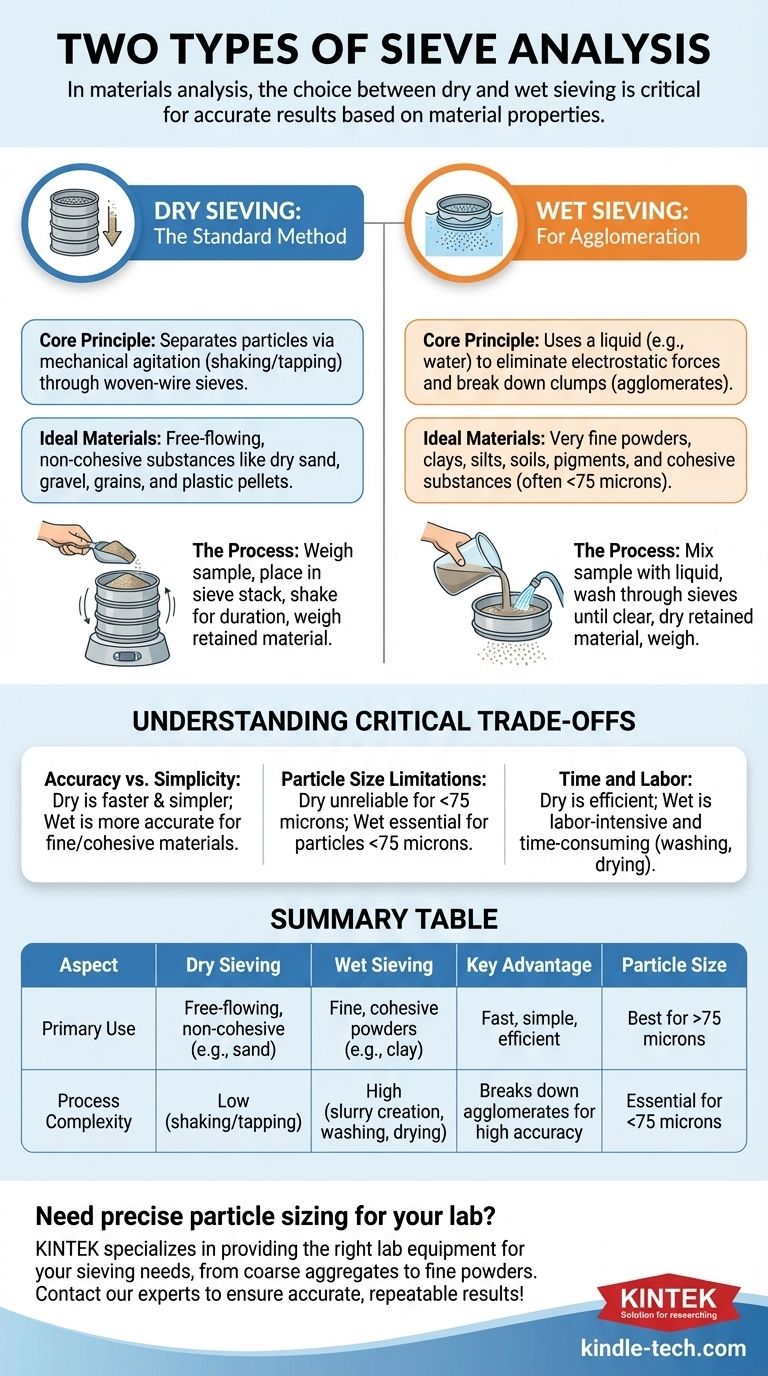
In materials analysis, the two primary types of sieve analysis are dry sieving and wet sieving. Dry sieving is the most common method, used for particles that flow freely and do not clump together. Wet sieving is a more specialized technique required for fine powders or materials that tend to agglomerate, using a liquid to separate the particles accurately.
The choice between wet and dry sieving is not a matter of preference; it is a critical decision dictated by the physical properties of your material. The core challenge is overcoming inter-particle attraction in fine or cohesive powders, a problem that only wet sieving can reliably solve.

The Standard Method: Dry Sieve Analysis
Core Principle
Dry sieve analysis separates particles based on size by passing a sample through a stack of woven-wire sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. The separation is achieved through mechanical agitation, such as shaking or tapping, which allows particles to find their way to an opening they can pass through.
Ideal Materials
This method is the standard for materials that are free-flowing and non-cohesive. The particles must not stick to each other or to the sieves due to moisture or electrostatic forces.
Typical examples include dry sand, gravel, grains, plastic pellets, and other coarse, granular substances.
The Process in Brief
The process begins with weighing a representative sample of the dry material. The sample is placed on the top sieve of a pre-stacked nest of sieves, which is then secured in a mechanical shaker. After shaking for a standardized duration, the stack is disassembled, and the material retained on each sieve is weighed to determine the particle size distribution.
When Agglomeration is an Issue: Wet Sieve Analysis
Core Principle
Wet sieve analysis is designed to overcome the limitations of the dry method. It uses a liquid—typically water, often with a wetting agent—to eliminate electrostatic forces and break down mechanical clumps (agglomerates). The liquid acts as a medium to wash fine particles through the sieve openings.
Ideal Materials
This method is essential for materials containing very fine particles (often below 75 microns) or for substances that are naturally cohesive. This includes clays, silts, soils, pigments, and fine pharmaceutical or chemical powders that would provide inaccurate results with dry sieving.
The Process in Brief
A pre-weighed sample is first mixed with the liquid to form a slurry. This slurry is poured onto the top sieve while being rinsed. The washing process continues until the liquid passing through the sieves runs clear. After washing, the material retained on each sieve must be carefully dried in an oven before it can be weighed to calculate the final distribution.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Accuracy vs. Simplicity
Dry sieving is significantly faster, simpler, and requires less equipment. It is the go-to method for its efficiency.
However, for fine or cohesive materials, wet sieving provides far more accurate and repeatable results. It physically separates agglomerated particles that would otherwise be registered as a single, larger particle in a dry analysis.
Particle Size Limitations
Dry sieving becomes unreliable for very fine powders. Electrostatic attraction between tiny particles can cause them to clump or "blind" the sieve mesh, preventing proper separation.
Wet sieving neutralizes these forces, making it the only reliable method for accurately determining the distribution of particles smaller than about 75 microns (200 mesh).
Time and Labor
The primary drawback of wet sieving is that it is a much more labor-intensive and time-consuming process. The additional steps of creating a slurry, washing the sample, and, most importantly, oven-drying the retained fractions add significant time and complexity to the analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your material's inherent properties will dictate the correct method. There is no ambiguity; choosing the wrong technique will lead to flawed data.
- If your primary focus is speed and the material is coarse and free-flowing (e.g., sand, gravel): Dry sieving is the correct and most efficient method.
- If your material contains fine particles, clay, or tends to clump (e.g., soil, pigments): Wet sieving is mandatory to achieve an accurate particle size distribution.
- If you are adhering to an industry standard (e.g., ASTM, ISO): The standard will explicitly define the required method, and in some cases, may call for a combination of both wet and dry techniques for a single sample.
Ultimately, understanding your material is the key to selecting the right analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Dry Sieving | Wet Sieving |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Free-flowing, non-cohesive materials (e.g., sand, gravel) | Fine, cohesive powders (e.g., clay, pigments) |
| Key Advantage | Fast, simple, efficient | Breaks down agglomerates for high accuracy |
| Particle Size | Best for particles >75 microns | Essential for particles <75 microns |
| Process Complexity | Low (shaking/tapping) | High (slurry creation, washing, drying) |
Need precise particle sizing for your lab?
Choosing the wrong sieve analysis method can lead to inaccurate results and wasted time. KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific sieving needs—whether you're working with coarse aggregates or fine, cohesive powders.
Our experts can help you select the ideal sieving setup to ensure accurate, repeatable particle size distribution data for your materials.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when doing a sieve analysis? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Data
- What are the sieve used in laboratory? A Guide to Choosing the Right Sieve for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is sieving used for in science? A Guide to Particle Size Analysis & Control
- What size sieves are used in sieve analysis? A Guide to Mesh, Frame, and Standard Selection
- What are standard sieves in pharmaceutical? Precision Instruments for Particle Size Control
- Why is sieve test important? Ensure Product Quality and Performance with Precise Particle Analysis
- What is the wet method of sieve analysis? A Guide to Accurate Particle Sizing for Clumpy Materials
- What is the purpose of sieving in chemistry? Master Particle Size Control for Better Reactions & Quality



















