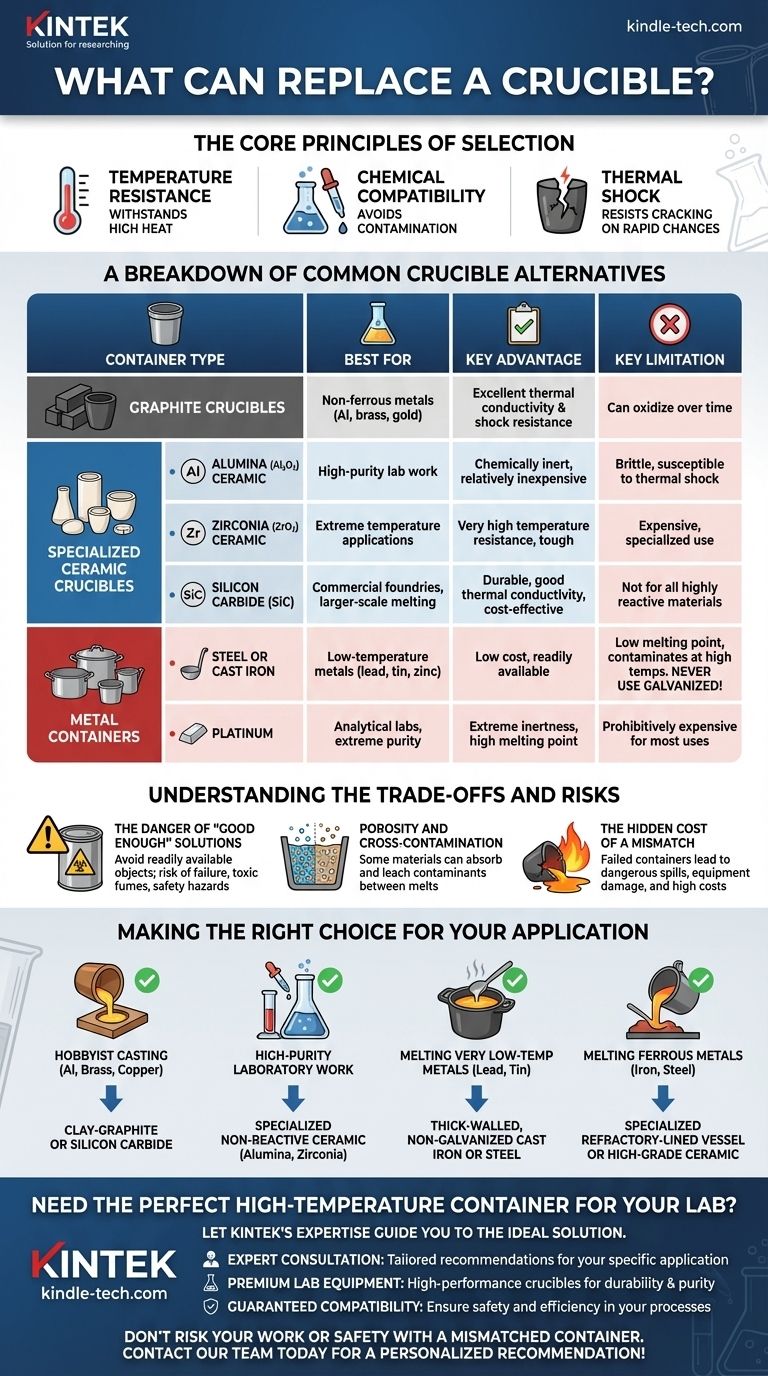
The most direct replacements for a traditional crucible fall into three main categories: graphite containers, specialized ceramic vessels, and in some cases, high-temperature metal containers. The ideal substitute depends entirely on what you are heating, how hot it needs to get, and the level of purity you need to maintain.
The challenge isn't finding a substitute for a crucible, but selecting the correct high-temperature vessel for your specific task. The right choice is a careful balance of three factors: the maximum temperature required, the chemical reactivity of your material, and the container's resistance to thermal shock.
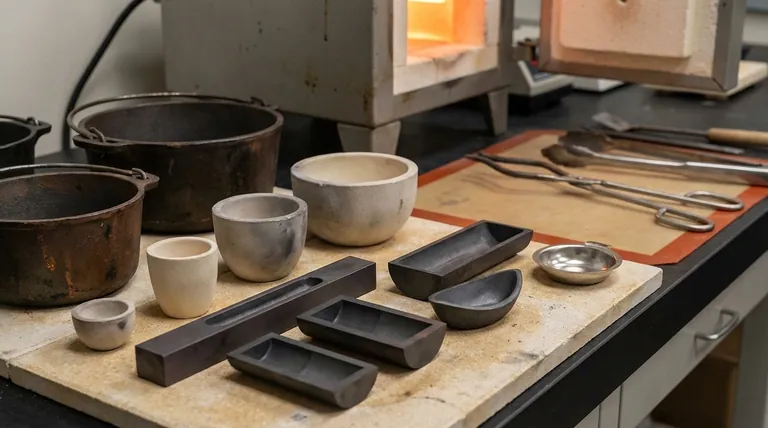

The Core Principles of Selection
Before examining specific materials, you must understand the fundamental principles that govern the choice of any high-temperature container. A mismatched vessel doesn't just fail; it can ruin your material, damage your equipment, and create significant safety hazards.
Temperature Resistance: The First Gatekeeper
This is the most critical factor. The container must be able to withstand temperatures significantly higher than the melting point of the material inside it without melting, deforming, or degrading.
Always check the maximum service temperature of any potential crucible or container.
Chemical Compatibility: Avoiding Contamination
A container that chemically reacts with its contents will contaminate your melt and weaken the container itself. This is a crucial consideration for achieving pure results, especially in laboratory settings or with reactive metals like aluminum.
For example, melting aluminum in a plain steel crucible can lead to iron contamination, making the resulting aluminum alloy brittle.
Thermal Shock: The Risk of Cracking
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when its temperature changes rapidly. A container with poor thermal shock resistance can crack or shatter when heated too quickly or when a cooler object is added to the hot melt.
Materials like graphite are excellent in this regard, while some ceramics can be quite fragile if not heated and cooled carefully.
A Breakdown of Common Crucible Alternatives
With the core principles in mind, we can evaluate the most common replacements for a standard crucible.
Graphite Crucibles
Graphite and clay-graphite crucibles are extremely popular, especially for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and gold.
They offer excellent thermal conductivity, which promotes even melting, and have superior resistance to thermal shock. However, they can oxidize and degrade over time, especially if not handled properly.
Specialized Ceramic Crucibles
For applications demanding high purity or extreme temperatures, ceramics are often the only choice.
- Alumina (Al2O3): A very common and relatively inexpensive lab ceramic. It is chemically inert for many applications but can be brittle and susceptible to thermal shock.
- Zirconia (ZrO2): Operates at much higher temperatures than alumina and is very tough. It is significantly more expensive and typically reserved for specialized applications.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): A very durable and robust material common in commercial foundries. It offers a great balance of thermal conductivity, strength, and cost-effectiveness for larger-scale melting.
Metal Containers
While less common for high-temperature melting, certain metal containers serve specific purposes.
- Steel or Cast Iron: Suitable only for low-temperature metals like lead, tin, or zinc. They are cheap and readily available but will melt and contaminate higher-temperature metals. Crucially, never use galvanized steel, as the zinc coating will vaporize and release highly toxic fumes.
- Platinum: Used almost exclusively in analytical labs for its extreme chemical inertness and high melting point. Its cost is prohibitive for nearly all other uses.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing an alternative is not without potential downsides. Being aware of them is key to a safe and successful outcome.
The Danger of "Good Enough" Solutions
The temptation to use a readily available object, like a steel food can or a pipe cap, is a serious safety risk. These items are not designed for thermal stress, may have coatings that release toxic fumes, and can fail without warning.
This approach should be avoided for anything other than low-temperature hobbyist work (e.g., melting lead), and even then, only with extreme caution and proper ventilation.
Porosity and Cross-Contamination
Some materials, particularly certain grades of clay-graphite or ceramics, can be slightly porous. They may absorb a small amount of material from a melt.
If you switch between different alloys or materials in the same crucible, you risk cross-contamination from a previous melt leaching out into the new one.
The Hidden Cost of a Mismatch
Using a cheaper but inappropriate container is often a false economy. A failed crucible can lead to a dangerous spill of molten material, potentially destroying your furnace and posing a severe fire or injury risk. The cost of a proper crucible is minimal compared to the potential damage of a failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal dictates the correct tool. Evaluate your primary need to select the most effective and safest container.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist casting of aluminum, brass, or copper: A clay-graphite or a silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of cost, durability, and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory work: Choose a specialized, non-reactive ceramic like alumina or zirconia to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is melting very low-temperature metals like lead or tin: A thick-walled, non-galvanized cast iron or steel pot is a viable, low-cost option.
- If your primary focus is melting ferrous metals like iron or steel: You require a specialized refractory-lined vessel or high-grade ceramic crucible capable of withstanding extreme temperatures.
Ultimately, selecting the right container is the foundational decision that ensures the safety, purity, and success of your high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Container Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite Crucibles | Non-ferrous metals (Al, brass, gold) | Excellent thermal conductivity & shock resistance | Can oxidize over time |
| Alumina (Al2O3) Ceramic | High-purity lab work | Chemically inert, relatively inexpensive | Brittle, susceptible to thermal shock |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) Ceramic | Extreme temperature applications | Very high temperature resistance, tough | Expensive, specialized use |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Commercial foundries, larger-scale melting | Durable, good thermal conductivity, cost-effective | Not for all highly reactive materials |
| Steel/Cast Iron | Low-temp metals (lead, tin, zinc) | Low cost, readily available | Low melting point, contaminates at high temps |
| Platinum | Analytical labs, extreme purity | Extreme inertness, high melting point | Prohibitively expensive for most uses |
Need the Perfect High-Temperature Container for Your Lab?
Choosing the wrong crucible alternative can lead to contamination, equipment damage, and safety hazards. Let KINTEK's expertise guide you to the ideal solution.
We provide:
- Expert Consultation: Our specialists will analyze your specific application—whether it's high-purity research, metal casting, or commercial melting—to recommend the perfect graphite, ceramic, or specialized container.
- Premium Lab Equipment: KINTEK supplies a wide range of high-performance crucibles and replacement vessels designed for durability, purity, and precise temperature control.
- Guaranteed Compatibility: Ensure your materials remain uncontaminated and your processes are safe and efficient.
Don't risk your work or safety with a mismatched container. Contact our team today for a personalized recommendation and get the right vessel for your high-temperature needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
People Also Ask
- How is sputtering done? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- Does a graphite crucible need to be seasoned? The Critical First-Use Safety Guide
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- What are five applications of soldering? From Electronics to Art, Master Material Joining
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition



















