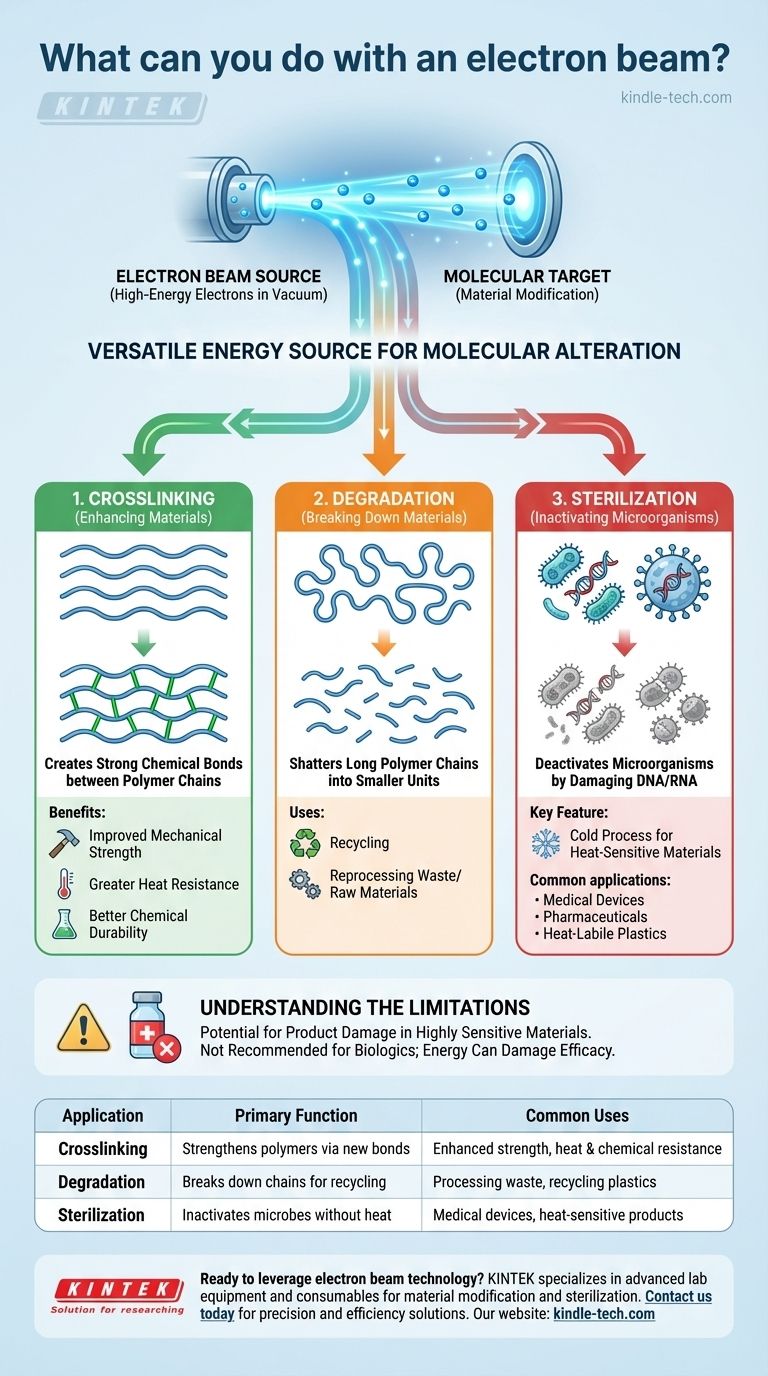
At its core, an electron beam is a highly controlled tool for altering materials at a molecular level. It is primarily used in industry for three distinct modifications: strengthening polymers through a process called crosslinking, breaking down materials for purposes like recycling, and sterilizing medical and pharmaceutical products.
An electron beam is not just a single tool but a versatile energy source. Its ability to precisely deliver energy allows it to either forge strong chemical bonds to enhance materials or break existing ones to degrade or sterilize them, all without significant heat.

The Principle: Energy Transfer on a Molecular Scale
An electron beam is a stream of high-energy electrons generated in a vacuum. When directed at a material, these electrons transfer their energy to the target's molecules.
This energy transfer is the key to all of its applications. It initiates chemical reactions that can either build new molecular structures or dismantle existing ones, providing a powerful method for material modification.
Key Industrial Applications
The ability to precisely trigger chemical reactions leads to three main industrial uses, each leveraging the same fundamental principle for a different outcome.
Enhancing Materials via Crosslinking
Crosslinking is a process where the electron beam's energy creates new, strong chemical bonds between long polymer chains. This effectively turns a collection of individual strands into a robust, interconnected net.
This modification significantly improves the material's properties. The result is a product with enhanced mechanical strength, greater resistance to high temperatures, and better durability when exposed to chemicals.
Breaking Down Materials via Degradation
The same energy that forges bonds can also be used to break them. In a process called scissioning or degradation, the electron beam shatters long polymer chains into smaller, shorter ones.
This process is often used in recycling. By breaking down complex or used materials into a more basic form, they can be more easily reprocessed into new products.
Sterilizing Products via Inactivation
In sterilization, the goal is to deactivate microorganisms like bacteria. The electron beam's energy damages the DNA or RNA of these microbes, destroying their ability to reproduce and rendering the product sterile.
This is a "cold" process, making it ideal for heat-labile (heat-sensitive) materials. It is widely used to sterilize items that would be damaged by traditional heat-based methods, such as plastics, powders, certain types of glass, and even biological materials like bone and heart valves.
Understanding the Limitations
While powerful, electron beam processing is not a universal solution. The primary limitation lies in the very energy that makes it useful.
Potential for Product Damage
The same radiation that kills microbes can also harm the product itself if it is sufficiently sensitive.
Electron beam sterilization is not recommended for biologics, such as complex vaccines or protein-based therapies. The energy can damage delicate nucleoproteins, destroying the product's efficacy. This highlights the critical need to match the process to the material's tolerance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct application depends entirely on your desired outcome at the molecular level.
- If your primary focus is improving product durability: Electron beam crosslinking is an effective method for enhancing the thermal, chemical, and mechanical strength of polymers.
- If your primary focus is processing waste or raw materials: The degradation capabilities of an electron beam can be used to break down long-chain polymers, a valuable step in recycling.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive devices: E-beam sterilization is a superior choice for single-use medical plastics, tissues, and powders that cannot withstand high temperatures.
Ultimately, harnessing an electron beam is about precisely controlling energy to achieve a specific molecular change.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Crosslinking | Strengthens polymers by creating new bonds | Enhancing mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical durability |
| Degradation | Breaks down polymer chains for recycling | Processing waste materials, recycling plastics |
| Sterilization | Inactivates microorganisms without heat | Sterilizing medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and heat-sensitive products |
Ready to leverage electron beam technology for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your material modification and sterilization needs. Whether you're enhancing polymer durability, recycling materials, or ensuring sterile products, our expertise ensures precision and efficiency. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is an autoclave laboratory equipment? The Ultimate Guide to Steam Sterilization
- What should be autoclaved in a lab? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What autoclave is used for sterilization? The Definitive Guide to Steam Sterilization
- Which autoclave is used in microbiology lab? Gravity Displacement vs. Pre-Vacuum Explained
- What is autoclave in laboratory? Achieve Total Sterility for Your Lab


















