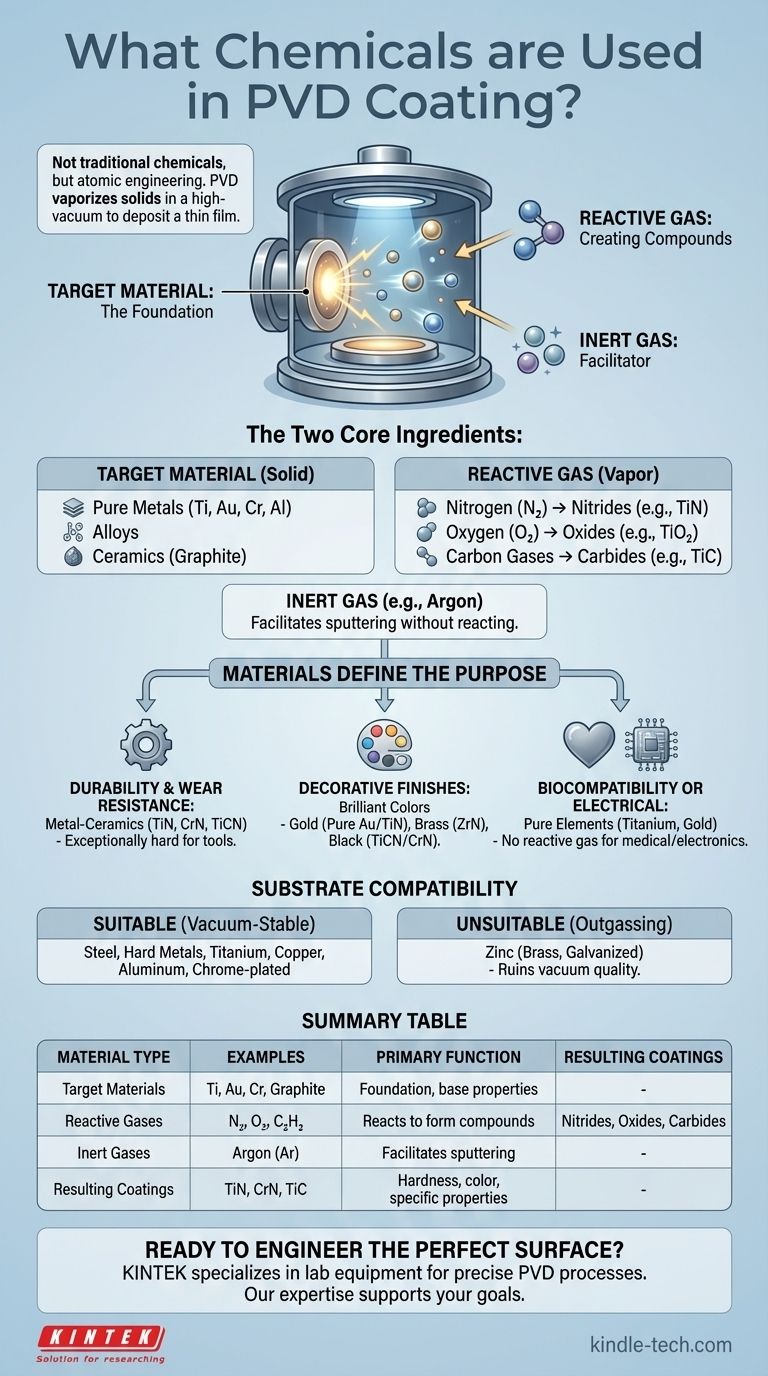
In practice, PVD does not use "chemicals" in the traditional liquid sense. Instead, the process vaporizes solid materials in a high-vacuum environment to deposit a thin film onto a surface. The primary materials used are pure metals like titanium and gold, metal alloys, and ceramics like graphite, which are combined with specific reactive gases like nitrogen to form the final coating.
The core principle of PVD is not chemical mixing, but atomic engineering. The process combines a vaporized solid target material (like a metal) with a carefully chosen reactive gas inside a vacuum to create a new, high-performance material directly on the surface of your part.

The Two Core "Ingredients" of a PVD Coating
To understand what PVD coatings are made of, you must think in terms of two separate components that come together during the process: the solid source material and the reactive gas.
The Target Material: The Foundation of the Coating
The process begins with a solid block or puck of the desired base material, known as the target. This target is what gets vaporized by a high-energy source (like an electron beam or ion bombardment).
The choice of target material dictates the fundamental properties of the final coating. Common examples include:
- Pure Metals: Titanium (Ti), Zirconium (Zr), Chromium (Cr), Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), and Gold (Au).
- Alloys: Various metal alloys can be used as targets to achieve specific properties.
- Non-Metals/Ceramics: Materials like Graphite (Carbon) can also be used.
The Reactive Gas: Creating Advanced Compounds
This is the key to creating the most functional PVD coatings. While the target is being vaporized, a precise amount of a reactive gas is often introduced into the vacuum chamber.
The vaporized metal atoms react with this gas to form entirely new compounds on the substrate's surface. This is how strong, durable ceramic coatings are made. Common reactive gases include:
- Nitrogen (N₂): Reacts with metals to form Nitrides (e.g., Titanium Nitride, TiN).
- Oxygen (O₂): Reacts with metals to form Oxides (e.g., Titanium Oxide, TiO₂).
- Carbon-based gases (e.g., Acetylene): Reacts with metals to form Carbides (e.g., Titanium Carbide, TiC).
For example, bombarding a pure Titanium target while introducing Nitrogen gas creates the extremely hard, gold-colored Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating—a material not present at the start of the process.
The Inert Gas: The Unseen Facilitator
In many PVD methods, an inert gas like Argon (Ar) is also used. It does not become part of the final coating. Instead, its ions are accelerated to bombard the target, physically knocking atoms loose in a process known as sputtering.
How Materials Define the Coating's Purpose
The specific combination of target material and reactive gas is chosen to achieve a desired outcome.
For Durability and Wear Resistance
The hardest and most durable PVD coatings are typically metal-ceramics. These are formed by reacting a metal vapor with a gas. Coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), and Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) are exceptionally hard and are used on cutting tools and industrial components.
For Decorative and Aesthetic Finishes
PVD is widely used to create brilliant, durable colors. The color is determined by the final compound deposited on the surface.
- Gold: A pure Gold target produces a true gold finish.
- Gold Color: Titanium Nitride (TiN) produces a finish nearly identical to gold.
- Brass/Zirconium Gold: Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) produces a light, brass-colored finish.
- Black/Gray: Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) or Chromium Nitride (CrN) can create various gray, anthracite, and black finishes.
For Biocompatibility or Electrical Function
For applications like medical implants or sensitive electronics, a pure, un-reacted metal is often desired. In these cases, a Titanium or Gold target is vaporized without introducing a reactive gas, depositing a thin film of the pure element.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Substrate Compatibility
The PVD process itself places limitations on what materials can be successfully coated. The high-vacuum environment is the primary factor.
What Materials Can Be Coated
PVD works exceptionally well on materials that are stable under vacuum and can withstand the moderate heat of the process. This includes nearly all types of steel, hard metals, and non-ferrous metals like titanium, copper, and aluminum. Items that are already chrome or nickel-plated are also excellent candidates.
What Materials Are Unsuitable
Some materials are considered "vacuum-unfriendly" because they release gases (outgas) when the pressure is lowered. This contamination ruins the vacuum and prevents a high-quality coating from forming.
The most common examples are materials containing zinc, such as brass (unless first sealed with another coating) and any galvanized parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "chemical" choice in PVD is a strategic decision based on the desired performance of the final surface.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: Your best choice is a nitride or carbonitride coating, such as TiN, CrN, or TiCN.
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color: Choose based on the final compound, such as TiN for a gold color, ZrN for a brass color, or pure gold for a true gold finish.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility or chemical inertness: A pure elemental coating, like vaporized titanium or gold, is the correct path.
Ultimately, the materials in PVD are a toolkit of elements and gases, engineered to build a high-performance surface atom by atom.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Target Materials | Titanium (Ti), Gold (Au), Chromium (Cr), Graphite | Foundation of the coating; determines base properties |
| Reactive Gases | Nitrogen (N₂), Oxygen (O₂), Acetylene (C₂H₂) | Reacts with vaporized metal to form nitrides, oxides, or carbides |
| Inert Gases | Argon (Ar) | Facilitates the sputtering process without reacting |
| Resulting Coatings | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Titanium Carbide (TiC) | Provides hardness, wear resistance, color, and specific functional properties |
Ready to Engineer the Perfect Surface for Your Application?
Choosing the right PVD coating materials is critical for achieving the performance, durability, and aesthetics your product demands. Whether you need extreme wear resistance for cutting tools, a brilliant decorative finish for consumer goods, or a biocompatible layer for medical devices, the strategic combination of target materials and gases makes it possible.
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables that enable precise PVD processes. Our expertise supports laboratories and manufacturers in developing and applying these advanced coatings. Let us help you select the right materials and equipment to meet your specific surface engineering goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your PVD coating capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- How many types of sputtering are there? A Guide to DC, RF, and Advanced Techniques
- How many types of vapor phase deposition techniques are present? PVD vs. CVD Explained
- What is the RF frequency for sputtering? Unlocking the Standard for Insulating Materials



















