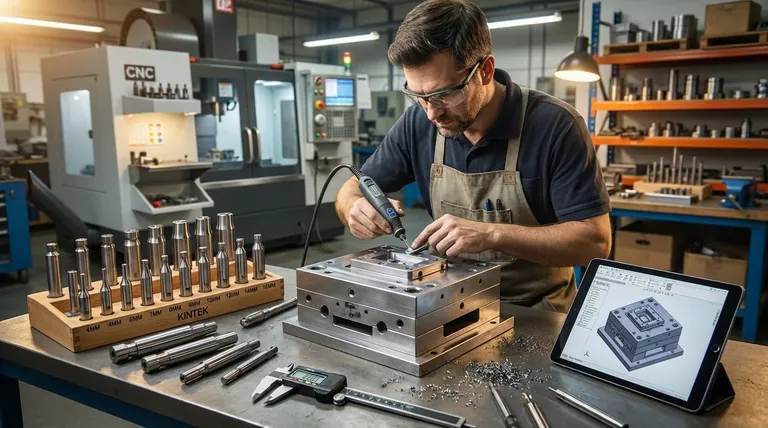
At its core, a mould maker is a high-precision artisan of the modern industrial age. They design, fabricate, and maintain the critical tools—the moulds—that enable the mass production of virtually every plastic or metal part you encounter. From car bumpers and medical devices to bottle caps and electronic enclosures, a mould maker’s work is the essential link between a digital design and a physical, replicable product.
The role of a mould maker extends far beyond simply cutting metal. They are responsible for translating a theoretical design into a flawless physical tool that can withstand the immense pressures of mass production and operate with micron-level accuracy.

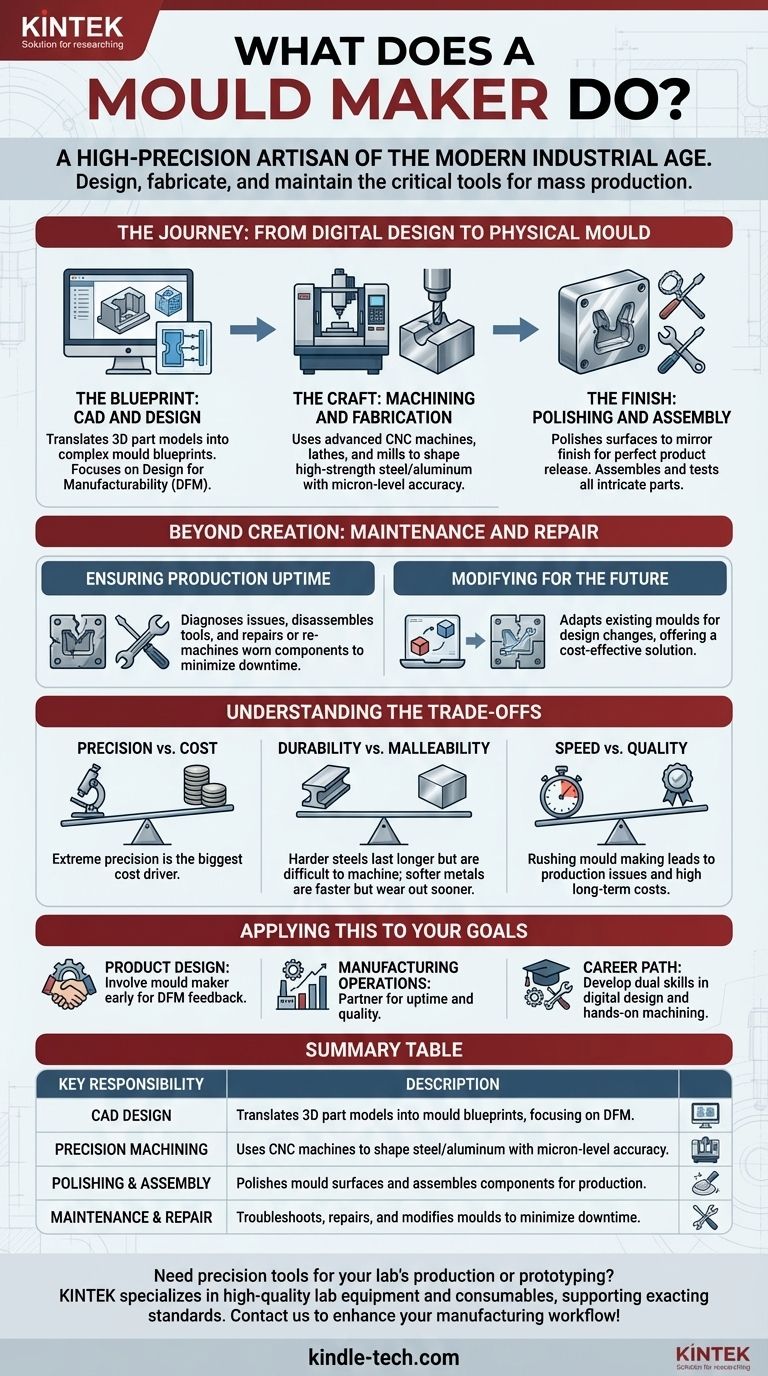
The Journey: From Digital Design to Physical Mould
The creation of a mould is a multi-stage process that demands a blend of digital expertise and hands-on mechanical skill. The mould maker is the master of this entire workflow, ensuring the final tool is perfect.
The Blueprint: CAD and Design
A mould maker's work begins in the digital realm. They typically receive a 3D model of the final part from a product designer or engineer.
Their first task is to design the mould that will create that part. This involves using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to engineer a complex tool with multiple components, including cavities, cores, cooling channels, and ejector systems.
This design phase is critical for anticipating how molten material will flow, cool, and solidify, a principle known as Design for Manufacturability (DFM).
The Craft: Machining and Fabrication
With a digital blueprint complete, the mould maker moves to the workshop to fabricate the tool. This is a process of extreme precision.
They use advanced Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, lathes, mills, and grinders to cut and shape blocks of high-strength steel or aluminum.
The tolerances are incredibly tight, often measured in microns (thousandths of a millimeter). A slight error at this stage can result in thousands of defective products down the line.
The Finish: Polishing and Assembly
Once the primary components are machined, the work is far from over. The internal surfaces of the mould that shape the product must be polished to a mirror finish.
This painstaking process ensures the final product has the desired surface texture and can be easily released from the mould. Finally, the mould maker assembles all the intricate parts, tests the mechanisms, and prepares the tool for the production line.
Beyond Creation: Maintenance and Repair
A mould maker's responsibility doesn't end when the mould is delivered. These tools are subjected to extreme heat and pressure, leading to inevitable wear and tear.
Ensuring Production Uptime
Mould makers are essential for troubleshooting and repair. When a mould begins producing flawed parts or breaks down, they are called upon to diagnose the issue.
They carefully disassemble the tool, identify the worn or damaged component, and then repair or re-machine it to restore its original precision. This work is critical for minimizing production downtime.
Modifying for the Future
Product designs often evolve. A mould maker is frequently tasked with modifying an existing mould to accommodate a small design change.
This is a highly cost-effective solution, as altering a complex mould is far cheaper and faster than building an entirely new one from scratch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The work of a mould maker is a constant balance of competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to appreciating the complexity of the role.
Precision vs. Cost
The extreme precision required in mould making is its biggest cost driver. The combination of expensive machinery, high-grade materials, and highly skilled labor makes industrial moulds significant investments, often costing tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Durability vs. Malleability
The choice of metal for a mould is a critical decision. Harder steels will result in a mould that lasts for millions of cycles but is more difficult and time-consuming to machine and repair. Softer metals like aluminum are cheaper and faster to machine but have a much shorter operational lifespan.
Speed vs. Quality
Rushing the mould-making process is a false economy. A poorly designed or finished mould can lead to a host of production issues, including flawed parts, high scrap rates, and frequent downtime, ultimately costing a company far more than the initial time saved.
Applying This to Your Goals
Understanding the mould maker's role is crucial for anyone involved in bringing a physical product to market.
- If your primary focus is product design: Involve a mould maker early in the process to get feedback on Design for Manufacturability (DFM), which can save enormous costs later.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing operations: Treat your mould maker as a critical partner in maintaining uptime and quality, not just as a fabricator.
- If you are considering this as a career: Focus on developing a dual skill set in both digital design (CAD/CAM) and hands-on precision machining to become an invaluable asset.
Ultimately, the mould maker is the silent architect behind the physical world, ensuring that great designs become tangible, reliable products.
Summary Table:
| Key Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| CAD Design | Translates 3D part models into mould blueprints using CAD software, focusing on Design for Manufacturability (DFM). |
| Precision Machining | Uses CNC machines and mills to shape high-strength steel/aluminum with micron-level accuracy. |
| Polishing & Assembly | Polishes mould surfaces for perfect product finish and assembles complex components for production. |
| Maintenance & Repair | Troubleshoots, repairs, and modifies moulds to minimize downtime and adapt to design changes. |
Need precision tools for your lab’s production or prototyping? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, supporting the exacting standards mould makers rely on. From durable materials to precision instruments, we provide the reliable tools your team needs to excel. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your manufacturing workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of tablet press machine? Achieve High-Speed, Consistent Production
- What components of a tablet press define the size and shape of the tablets? Mastering Die and Punch Tooling
- How do a pelletizing die and a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to magnesium pellet formation? Optimize Your Lab.
- Which type of tablet press is more suitable for large scale production? Rotary Presses for High-Volume Efficiency
- What are pill presses used for? Transforming Powders into Precise Tablets for Medicine, Supplements, and More



















