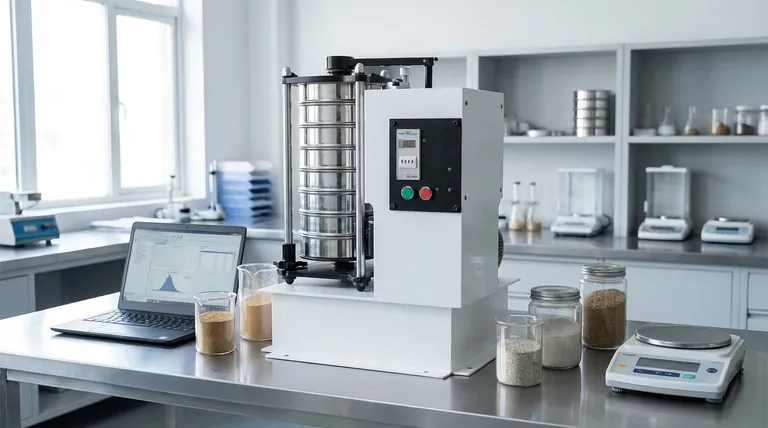
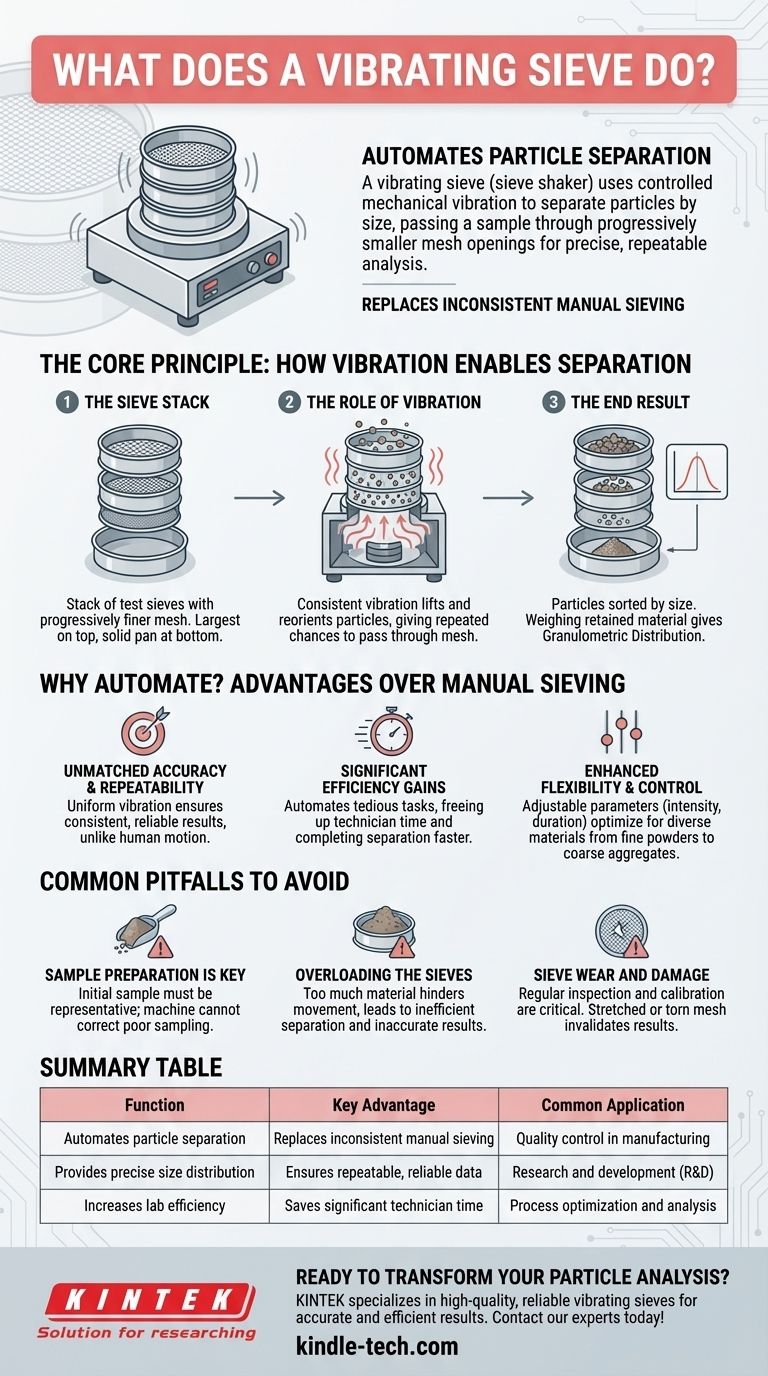
At its core, a vibrating sieve is a machine that automates the process of separating particles by size. Often called a sieve shaker, it uses controlled mechanical vibration to agitate a sample, causing it to pass through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. This allows for precise and repeatable particle size analysis.
The fundamental purpose of a vibrating sieve is to replace inconsistent manual hand sieving with a highly efficient and accurate method. This ensures that particle size analysis is reliable, which is critical for quality control and research in countless industries.

The Core Principle: How Vibration Enables Separation
A vibrating sieve operates on a simple yet effective principle. It standardizes the process of sorting materials, turning it from an approximation into a scientific measurement.
The Sieve Stack
The process begins with a stack of test sieves. The sieve with the largest mesh openings is placed at the top, and each subsequent sieve below it has a progressively finer mesh, ending with a solid collection pan at the bottom.
The Role of Vibration
The entire stack of sieves is secured onto the machine. When activated, the shaker imparts a consistent, controlled vibration. This agitation lifts and reorients the particles, giving each one repeated opportunities to pass through the mesh openings.
The End Result: A Granulometric Distribution
Larger particles are retained on the upper sieves, while smaller particles continue to travel downward until they are caught by a sieve with openings too small for them to pass. By weighing the material retained on each sieve, you can accurately determine the particle size distribution of the original sample.
Why Automate? The Advantages Over Manual Sieving
While hand sieving can provide a rough estimate, a mechanical sieve shaker offers significant advantages that are non-negotiable for professional applications.
Unmatched Accuracy and Repeatability
Human motion is inherently inconsistent. A machine provides a uniform vibration amplitude and frequency, ensuring that results are highly repeatable. This is essential for comparing different batches of material or for validating a product against a specification.
Significant Efficiency Gains
Manually sieving a sample can be a tedious and time-consuming task. A vibrating sieve automates this process, freeing up valuable technician time for other critical duties and completing the separation far more quickly.
Enhanced Flexibility and Control
Modern sieve shakers allow operators to adjust parameters like vibration intensity and duration. This flexibility means the process can be fine-tuned and optimized for a wide variety of materials, from fine powders to coarse aggregates.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While powerful, a vibrating sieve is a precision instrument. Its effectiveness depends on proper usage and awareness of potential issues.
Sample Preparation is Key
The machine cannot correct for a poorly collected sample. To get a meaningful result, the initial sample must be representative of the entire batch of material being tested.
Overloading the Sieves
Placing too much material onto the sieve stack is a common mistake. Overloading prevents particles from moving freely, leading to inefficient separation and inaccurate results as the mesh can become blinded or clogged.
Sieve Wear and Damage
Over time, sieve mesh can stretch, warp, or tear. Regular inspection and calibration of sieves are critical to ensure the openings are accurate and the results remain valid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting a vibrating sieve is about moving from estimation to precise characterization.
- If your primary focus is quality control: A vibrating sieve is essential for providing the repeatable data needed to ensure product consistency and meet industry standards.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The machine offers a precise and efficient method for characterizing new materials and understanding their physical properties.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Use it to analyze materials at different stages of production to identify inefficiencies or opportunities for improvement.
Ultimately, a vibrating sieve transforms particle separation from a manual chore into a reliable scientific measurement.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Advantage | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Automates particle separation | Replaces inconsistent manual sieving | Quality control in manufacturing |
| Provides precise size distribution | Ensures repeatable, reliable data | Research and development (R&D) |
| Increases lab efficiency | Saves significant technician time | Process optimization and analysis |
Ready to transform your particle analysis from a manual chore into a precise scientific measurement?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable vibrating sieves designed for accuracy and efficiency. Whether you're in quality control, R&D, or process optimization, our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect vibrating sieve for your laboratory needs and elevate your particle size analysis!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a sieve shaker in sieve analysis? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Data
- What is the critical function of high-precision sieving for aluminum powders? Ensure Uniform Composite Integrity
- What is the purpose of using high-precision vibrating sieving systems? Master Filler Quality in Wood-Plastic Composites
- Which types of diameter or size can be determined using sieve shaker method for the given granular sample? A Guide to the 38 µm to 4 mm Range
- What is the merit of a sieve shaker? Achieve Reliable, Cost-Effective Particle Size Analysis
- What role does a constant temperature shaker play in evaluating boron removal? Ensure Data Accuracy in Brine Adsorption
- Which equipment is operated for sieves when perform sieving tests? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- Why is precise speed control necessary for a mechanical shaker or stirrer during microalgae anaerobic digestion?



















