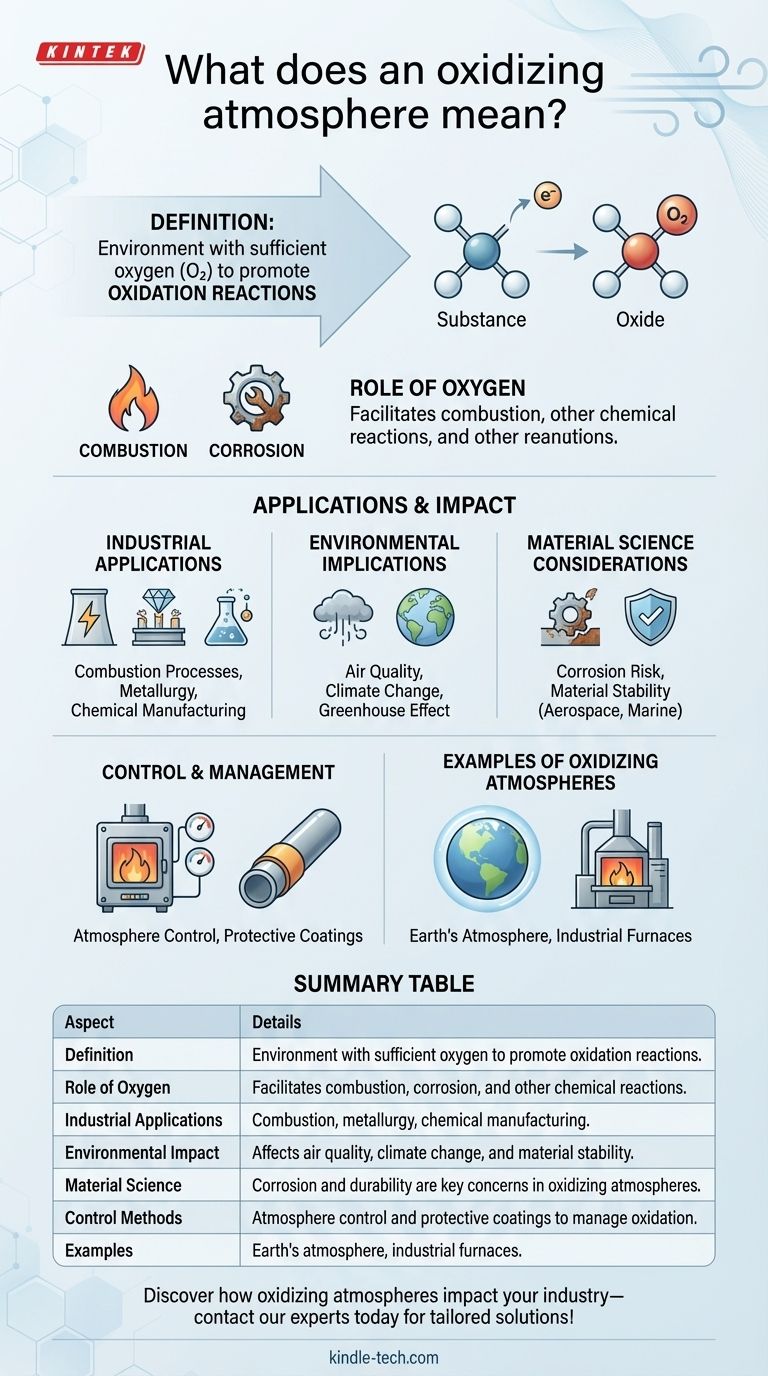
An oxidizing atmosphere refers to an environment where oxygen is present in sufficient quantities to promote oxidation reactions. Oxidation involves the loss of electrons by a substance, often resulting in the formation of oxides. In practical terms, an oxidizing atmosphere is one where oxygen or other oxidizing agents are abundant, enabling processes such as combustion, rusting, or other chemical reactions that involve the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen. This concept is critical in various industrial processes, material science, and environmental studies, as it influences the behavior of materials and the efficiency of chemical reactions.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of an Oxidizing Atmosphere:
- An oxidizing atmosphere is characterized by the presence of oxygen or other oxidizing agents that facilitate oxidation reactions.
- Oxidation is a chemical process where a substance loses electrons, often leading to the formation of oxides.
-
Role of Oxygen in Oxidation:
- Oxygen is the most common oxidizing agent in an oxidizing atmosphere.
- It reacts with other elements or compounds, leading to processes such as combustion (e.g., burning of fuels) or corrosion (e.g., rusting of metals).
-
Industrial Applications:
- Combustion Processes: In industries like power generation, an oxidizing atmosphere is essential for the efficient burning of fuels to produce energy.
- Metallurgy: In metal processing, controlled oxidizing atmospheres are used to refine metals by removing impurities through oxidation.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Many chemical reactions require an oxidizing atmosphere to produce desired products, such as the synthesis of certain polymers or chemicals.
-
Environmental Implications:
- Air Quality: High levels of oxidizing agents in the atmosphere can lead to the formation of pollutants like ozone and nitrogen oxides, which can harm human health and the environment.
- Climate Change: Oxidizing atmospheres can influence the greenhouse effect by affecting the concentration of gases like carbon dioxide and methane.
-
Material Science Considerations:
- Corrosion: Metals exposed to an oxidizing atmosphere are prone to corrosion, which can degrade materials over time.
- Material Stability: The stability of materials in an oxidizing atmosphere is a critical factor in designing durable products, especially in harsh environments like aerospace or marine applications.
-
Control and Management:
- Atmosphere Control: In industrial settings, the composition of the atmosphere can be controlled to either promote or inhibit oxidation, depending on the desired outcome.
- Protective Coatings: Materials can be coated with protective layers to prevent oxidation in oxidizing atmospheres, extending their lifespan.
-
Examples of Oxidizing Atmospheres:
- Earth's Atmosphere: While primarily composed of nitrogen, the presence of oxygen makes it an oxidizing atmosphere, supporting life and various chemical processes.
- Industrial Furnaces: Furnaces often operate with an oxidizing atmosphere to facilitate high-temperature reactions like smelting or glass production.
By understanding the concept of an oxidizing atmosphere, industries can better control chemical processes, improve material durability, and mitigate environmental impacts. This knowledge is essential for engineers, scientists, and environmentalists working in fields where oxidation plays a critical role.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Environment with sufficient oxygen to promote oxidation reactions. |
| Role of Oxygen | Facilitates combustion, corrosion, and other chemical reactions. |
| Industrial Applications | Combustion, metallurgy, chemical manufacturing. |
| Environmental Impact | Affects air quality, climate change, and material stability. |
| Material Science | Corrosion and durability are key concerns in oxidizing atmospheres. |
| Control Methods | Atmosphere control and protective coatings to manage oxidation. |
| Examples | Earth's atmosphere, industrial furnaces. |
Discover how oxidizing atmospheres impact your industry—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process



















