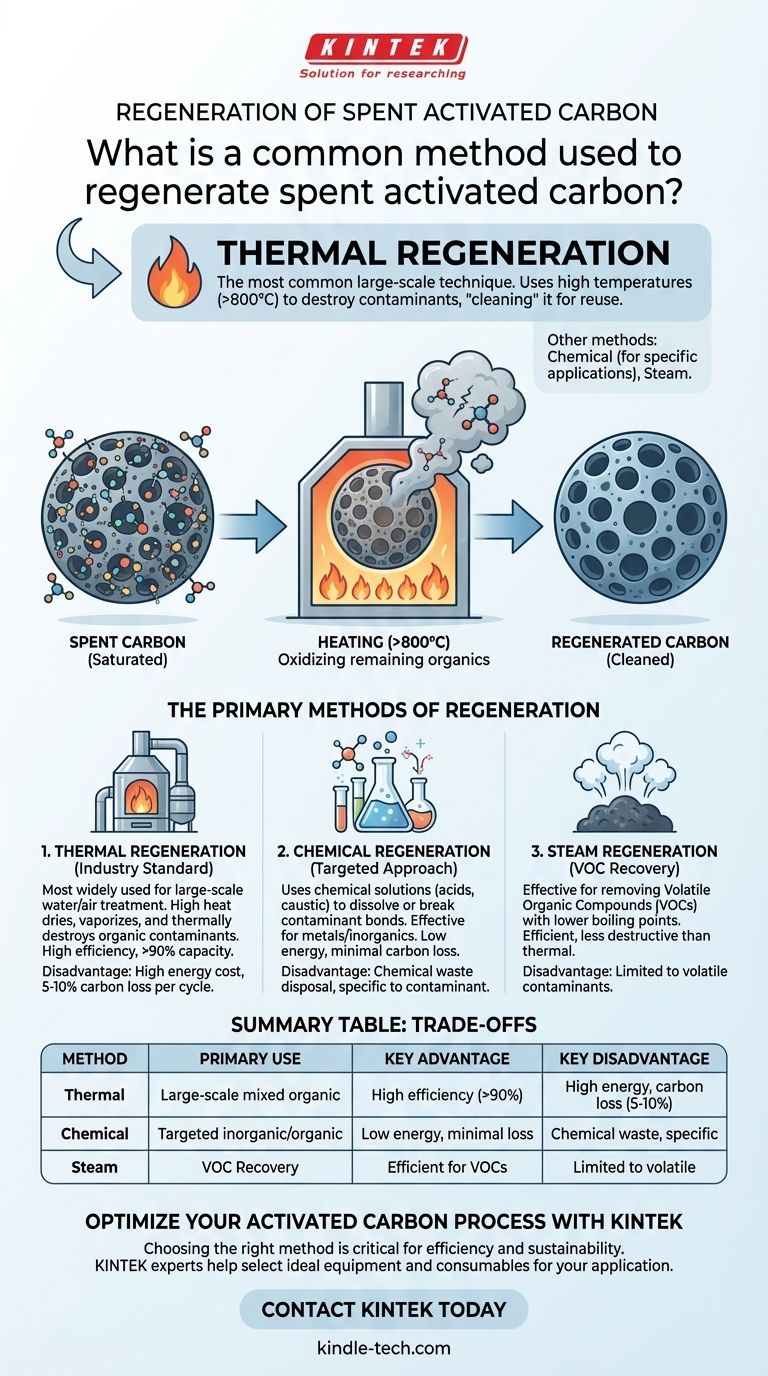
While several methods exist, the most common large-scale technique for regenerating spent activated carbon is thermal regeneration. This process uses high temperatures to destroy or desorb the contaminants that have accumulated on the carbon's surface, effectively "cleaning" it for reuse. Methods like chemical regeneration, which uses substances such as hydrochloric acid and hot water, are also employed for more specific applications.
The core principle of regeneration is to reverse the adsorption process by providing enough energy—whether through heat, chemical reaction, or pressure change—to break the bonds holding the contaminants to the carbon's surface. The best method depends on the contaminant being removed and the scale of the operation.

Why Activated Carbon Becomes "Spent"
To understand regeneration, we must first understand how activated carbon works. Its effectiveness comes from an incredibly vast network of microscopic pores that create immense surface area.
The Principle of Adsorption
Activated carbon doesn't filter particles in the traditional sense. Instead, it works through adsorption, a process where contaminant molecules (the adsorbate) physically stick to the internal surfaces of the carbon (the adsorbent).
Reaching Saturation
Over time, these internal surfaces become completely covered with contaminant molecules. When there are no more available sites for adsorption to occur, the carbon is considered "spent" or "saturated" and can no longer effectively remove impurities.
The Primary Methods of Regeneration
Regenerating spent carbon is an essential step in making its use economically and environmentally sustainable. The chosen method is determined by the nature of the adsorbed material.
Thermal Regeneration (The Industry Standard)
This is the most widely used method, especially for large industrial applications like water and air treatment. The process involves heating the spent carbon in a controlled, low-oxygen environment to temperatures typically exceeding 800°C (1500°F).
This intense heat accomplishes two things: it dries and vaporizes the adsorbed contaminants, and then it thermally destroys (oxidizes) any remaining organic molecules, leaving the carbon pores clean.
Chemical Regeneration
As noted in certain studies, chemical regeneration is a more targeted approach. It uses a chemical solution (a regenerant) to either dissolve the contaminant or break the bond holding it to the carbon.
For example, using an acid like hydrochloric acid (HCl) is effective for removing adsorbed metals or inorganic compounds. Using a caustic solution can remove certain organic acids. This method is less about brute force and more about precise chemical reactions.
Steam Regeneration
This method is particularly effective for removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that have a lower boiling point. Passing hot steam through the carbon bed provides enough thermal energy to vaporize these specific contaminants, which are then carried away by the steam flow.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single regeneration method is universally superior. Each comes with a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed for any given application.
Efficiency vs. Carbon Loss
Thermal regeneration is highly effective at removing a broad range of organic contaminants, often restoring the carbon to over 90% of its original capacity. However, the high heat inevitably damages a small portion of the carbon structure, resulting in a 5-10% loss of material with each cycle.
Chemical and steam methods are gentler on the carbon itself, leading to minimal material loss. Their trade-off is often lower regeneration efficiency, as they are only effective against the specific contaminants they are designed to target.
Cost and Energy Consumption
The high temperatures required for thermal regeneration make it an energy-intensive and costly process, typically only feasible for large-scale operations where the economy of scale justifies the capital investment in a furnace.
Chemical regeneration avoids high energy costs but introduces the expense of the chemical reagents and the need to treat or dispose of the resulting chemical-laden liquid waste, which adds complexity and cost.
Contaminant Specificity
Thermal regeneration is a "brute force" approach that works on a wide spectrum of organic compounds. In contrast, chemical regeneration is highly specific. A solvent chosen to remove one compound will likely be useless against another, requiring precise knowledge of the captured contaminant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate regeneration technique is critical for balancing cost, efficiency, and environmental impact.
- If your primary focus is large-scale removal of mixed organic contaminants: Thermal regeneration is the established industrial standard due to its high efficiency and broad applicability.
- If your primary focus is removing a specific, known inorganic or reactive compound: Chemical regeneration offers a targeted, low-energy alternative that can be highly effective.
- If your primary focus is recovering adsorbed volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Steam regeneration is a proven and efficient method that is less destructive to the carbon than high-temperature thermal processes.
Ultimately, successful regeneration hinges on matching the method to the specific contaminant you have captured and your operational scale.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Regeneration | Large-scale removal of mixed organic contaminants | High efficiency, restores >90% capacity | High energy cost, 5-10% carbon loss per cycle |
| Chemical Regeneration | Targeted removal of specific inorganic/organic compounds | Low energy, minimal carbon loss | Chemical waste disposal, specific to contaminant |
| Steam Regeneration | Recovery of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | Efficient for VOCs, less destructive than thermal | Limited to volatile contaminants |
Need to Optimize Your Activated Carbon Regeneration Process?
Choosing the right regeneration method is critical for your lab's efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. The experts at KINTEK can help you select the ideal equipment and consumables for your specific application, whether you're working with water treatment, air purification, or chemical recovery.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet your precise laboratory needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your activated carbon processes and deliver superior results for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker

















