In technical terms, an electrolysis cell is a specific type of electrochemical cell. While it falls under this broad category, it is critical to understand that "electrochemical cell" also describes another device—the galvanic cell—which performs the exact opposite function.
The crucial distinction is this: An electrolysis cell uses external electrical energy to force a chemical reaction that would not happen on its own. It consumes power. In contrast, a galvanic cell (like a battery) uses a spontaneous chemical reaction to produce electrical energy.
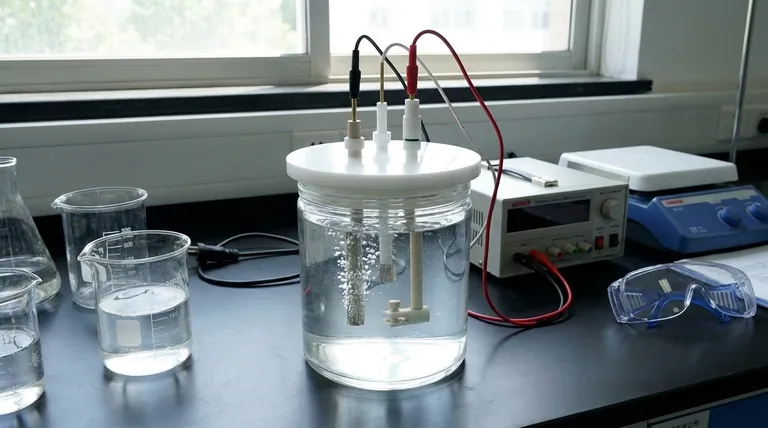

The Core Function: Forcing a Chemical Reaction
What is Electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the process of using a direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. In simple terms, it's using electricity to make a chemical change happen.
The device where this process occurs is the electrolysis cell or electrolytic cell.
The Role of External Power
The defining feature of an electrolytic cell is its need for an external power source, such as a battery or power supply. This external voltage overcomes the natural energy barrier of the reaction, forcing the chemicals to react.
Key Components
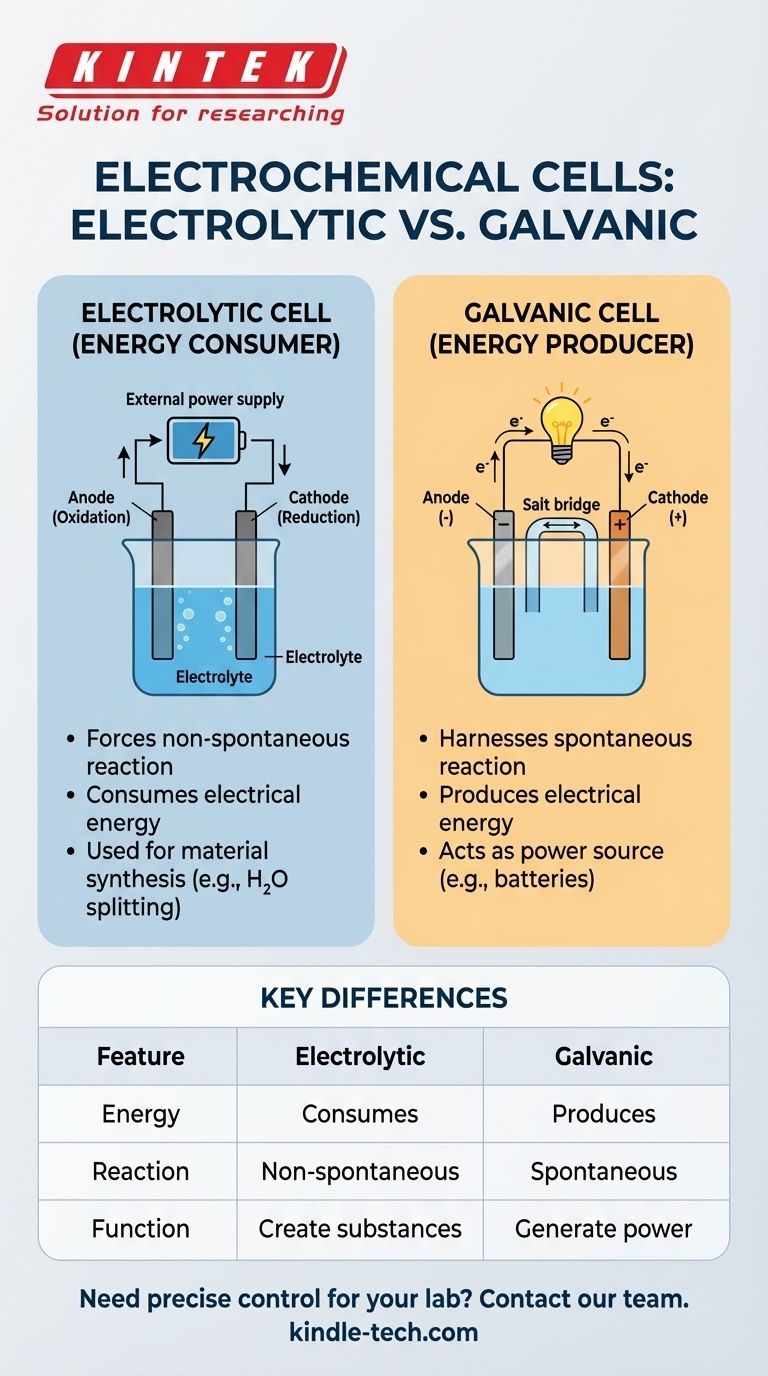
An electrolytic cell consists of two electrodes, an anode and a cathode, submerged in a liquid solution called an electrolyte. The external power source pulls electrons from the anode (oxidation) and pushes them to thecathode (reduction), driving the desired chemical change.
Electrolytic vs. Galvanic: The "Electrochemical Cell" Umbrella
The term electrochemical cell is a parent category for any device that converts between chemical and electrical energy. Understanding the two main types is essential for clarity.
Electrolytic Cells: Energy Consumers
These cells consume electrical energy to produce a chemical change. Their primary purpose is to create substances or alter materials through a forced reaction.
A common example is using an electrolytic cell to split water (H₂O) into hydrogen and oxygen gas, a process that requires a significant energy input.
Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells: Energy Producers
These cells do the opposite. They harness a spontaneous chemical reaction to generate an electric current. This is the fundamental principle behind all common batteries.
When you use a battery, you are using a galvanic cell to convert stored chemical energy into usable electrical power.
Why the Distinction Matters
Calling an electrolytic cell an "electrochemical cell" is technically correct but imprecise. It's like calling a square a "rectangle." While true, it omits the specific properties that define it. The key difference is always the direction of energy conversion.
Common Applications and Trade-offs
Where Electrolysis is Used
The ability to force chemical reactions has immense industrial value. Electrolytic cells are essential for producing pure hydrogen for fuel, refining metals like aluminum and copper from ore, and electroplating objects with a thin layer of metal like chromium or gold.
The Primary Trade-off: Energy Cost
The main limitation of electrolysis is its high energy consumption. Because you are forcing a non-spontaneous reaction, the process always requires more energy than the chemical energy you store or the value of the product you create. This energy cost is the central economic and environmental consideration for any industrial electrolysis process.
How to Identify the Right Cell for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is storing energy or creating materials (like hydrogen fuel or pure aluminum): You are dealing with an electrolytic cell, which consumes electricity to drive a chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is generating power from a chemical source (like a battery): You are dealing with a galvanic (or voltaic) cell, which produces electricity from a spontaneous reaction.
- If your primary focus is the general scientific field covering both processes: You should use the umbrella term electrochemical cell.
Ultimately, understanding the direction of energy flow—whether it is being consumed or produced—is the key to distinguishing between these fundamental devices.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electrolytic Cell | Galvanic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Consumes electrical energy | Produces electrical energy |
| Reaction Type | Non-spontaneous (forced) | Spontaneous |
| Primary Function | Create substances (e.g., H₂, refined metals) | Generate power (e.g., batteries) |
| Power Source | Requires external source (e.g., battery, power supply) | Is the power source itself |
Need precise control over chemical reactions in your lab?
Whether your research involves material synthesis, electroplating, or energy storage, having the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrochemical cells and power supplies, designed for reliability and accuracy.
Let our experts help you select the perfect setup for your specific application. Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be operated during an experiment? Master Precise Control for Reliable Results
- What is the proper way to handle a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate and Safe Electrochemical Experiments
- What are the standard components of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the Precision Instrument for Electrochemical Analysis
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy



















