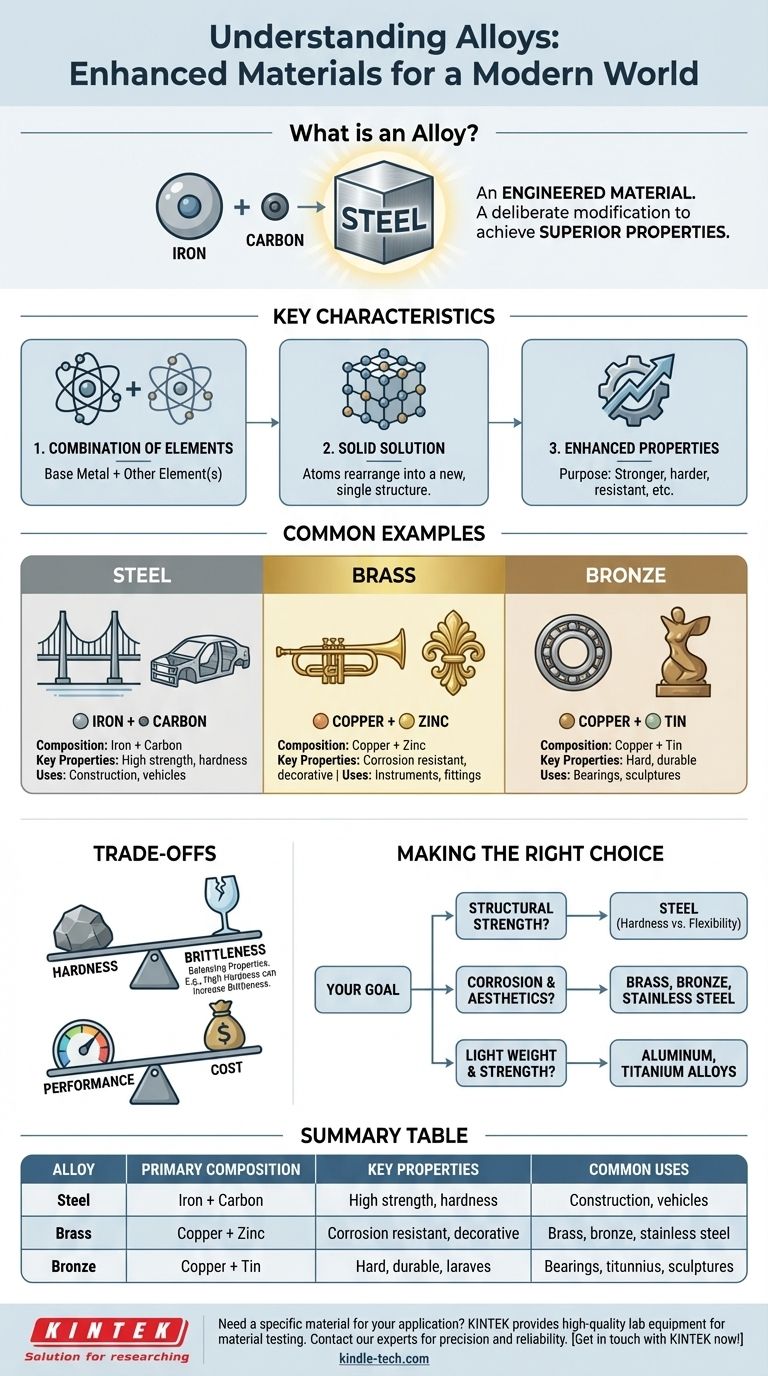
A classic example of an alloy is steel. At its most basic level, steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. This combination creates a material that is significantly stronger and more versatile than pure iron, demonstrating the fundamental purpose of creating alloys: to enhance the properties of a base metal.
The core concept to understand is that an alloy is not just a simple mixture, but an engineered material. It is a substance formed by combining a metal with at least one other element to achieve specific, superior properties like increased strength or corrosion resistance.

What Fundamentally Defines an Alloy?
To truly grasp the concept, it's important to move beyond simple examples and understand what is happening at a material level. An alloy is a deliberate modification of a metal's structure.
A Combination of Elements
The defining characteristic of an alloy is its composition. It starts with a primary metal, known as the base or parent metal, and intentionally introduces other elements.
These added elements can be other metals (like zinc added to copper to make brass) or non-metals (like carbon added to iron to make steel).
A Solid Solution
In many cases, an alloy is a solid solution. This means the atoms of the different elements arrange themselves into a new, single crystal structure.
Think of it like dissolving salt in water to create saltwater. In an alloy, you are essentially "dissolving" one element into another while they are in a solid state, creating a new, unified material.
The Goal is Enhanced Properties
The entire purpose of making an alloy is to create a material with more desirable characteristics than its components have on their own.
Engineers create alloys to achieve specific goals, such as making a metal harder, lighter, more resistant to rust, or able to withstand higher temperatures.
Common Examples and Their Composition
Looking at a few well-known examples makes the concept much clearer. Each was developed to solve a specific problem that the base metal could not handle alone.
Steel: Iron and Carbon
By adding a small amount of carbon to iron, the resulting steel becomes immensely stronger and harder. This is arguably the most important alloy in the modern world, used in everything from construction to vehicles.
Brass: Copper and Zinc
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. It is harder and has better corrosion resistance than pure copper, and its gold-like appearance makes it popular for decorative items and musical instruments.
Bronze: Copper and Tin
Historically significant enough to name an entire era (the Bronze Age), bronze is an alloy of copper, typically with tin as the main additive. It is much harder and more durable than pure copper.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Creating an alloy is a process of balancing properties. Improving one characteristic often comes at the expense of another, a critical concept in material science.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
Increasing an alloy's hardness can often make it more brittle. For example, very high-carbon steel is extremely hard but can fracture more easily under sharp impact compared to lower-carbon, more ductile steel.
Performance vs. Cost
Alloying elements and the processes required to create the alloy can significantly increase the cost of the final material. Pure iron is far cheaper than specialized stainless steel, which contains additional elements like chromium and nickel.
Not a Universal Improvement
An alloy is not inherently "better" in all situations. For instance, while alloys of copper are strong, pure copper is a superior electrical conductor. For applications like electrical wiring, the pure metal remains the ideal choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific alloy used for any application is a deliberate engineering choice based on the primary requirements of the task.
- If your primary focus is structural strength and hardness: Steel is often the answer, with the specific type determined by the exact balance of strength and flexibility needed.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and aesthetics: Alloys like brass, bronze, or stainless steel are designed specifically for these purposes.
- If your primary focus is low weight and high strength: Aluminum and titanium alloys are engineered for aerospace and high-performance applications.
Ultimately, alloys represent humanity's ability to intentionally design and create materials that meet the precise needs of our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Alloy | Primary Composition | Key Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Iron + Carbon | High strength, hardness | Construction, vehicles |
| Brass | Copper + Zinc | Corrosion resistant, decorative | Instruments, fittings |
| Bronze | Copper + Tin | Hard, durable | Bearings, sculptures |
Need a specific material for your application? The right alloy is critical for performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material testing and analysis. Whether you are developing new alloys or verifying material properties, our solutions support precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can meet your laboratory's specific material science needs. Get in touch with KINTEK now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Gaskets and More
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of electron beam? A Guide to Precision Energy Delivery
- Can you see mold with an infrared camera? How Thermal Imaging Reveals Hidden Moisture Problems
- What are the methods of sample preparation in FTIR? Choose the Right Technique for Your Sample
- Can brazing be used to join two different base metals? Unlock Strong, Reliable Dissimilar Metal Joints
- What is batch pyrolysis? A Start-Stop Process for Flexible Waste Conversion
- What are the end products of pyrolysis? Turn Waste into Biochar, Oil, and Syngas
- What is high temperature sintering? Boost Strength and Durability for Demanding Parts
- Why must a laboratory oven be used for the dehydration of sodium molybdate precursors? Ensure Synthesis Success
















